- The paper introduces IAO Prompting which explicitly decomposes LLM reasoning into Input-Action-Output steps, enhancing transparency and verification.
- It demonstrates notable performance improvements, achieving 94.2% accuracy on GSM8K for arithmetic reasoning with GPT-4.
- The structured framework aids in error detection and robust knowledge application, establishing a new benchmark for LLM interpretability.
IAO Prompting: Making Knowledge Flow Explicit in LLMs through Structured Reasoning Templates
The paper "IAO Prompting: Making Knowledge Flow Explicit in LLMs through Structured Reasoning Templates" (2502.03080) presents a structured approach to reasoning with LLMs called Input-Action-Output (IAO) prompting. The goal of this methodology is to enhance the interpretability and verify the knowledge utilization process of LLMs during complex reasoning tasks. This paper lays out the framework of IAO prompting, evaluates its performance across various reasoning tasks, and explores its implications.
Introduction
LLMs, such as those developed by Vaswani et al. (Anil et al., 2023) [brown2020language] [chowdhery2023palm] [devlin_bert_2019], have demonstrated remarkable abilities in processing and generating human languages, prompting discussions around their internal mechanisms of knowledge acquisition and utilization [ju-etal-2024-large, meng2022locating, turpin2024language, zhang2024knowledge]. While methods like Chain-of-Thought prompting have improved transparency in LLM reasoning by revealing intermediate steps [wei2022chain, wang-etal-2022-iteratively], the implicit nature of knowledge flow remains a critical challenge.
The opacity of LLMs' reasoning poses significant reliability issues [chen2024survey, singh2024rethinking], especially in ensuring factual accuracy and identifying knowledge gaps. IAO prompting introduces a novel structured template approach, decomposing reasoning into explicit Input-Action-Output steps that clarify and verify the knowledge flow (Figure 1).
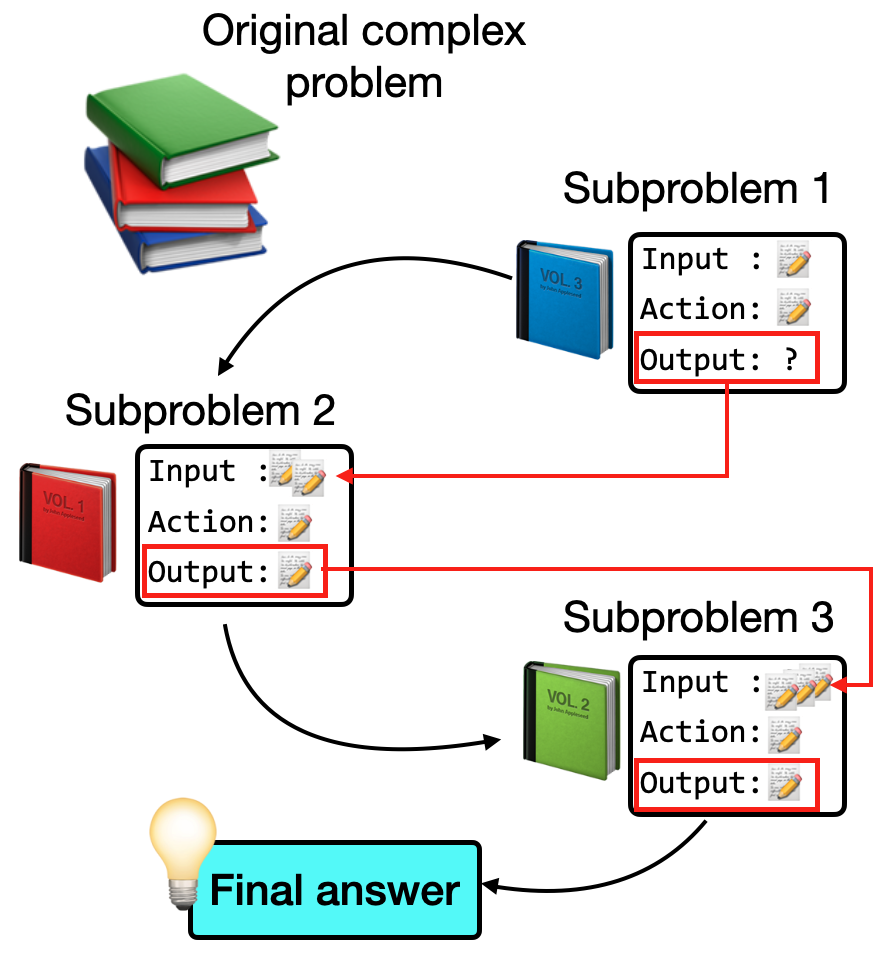
Figure 1: Illustration of IAO prompting demonstrating how knowledge is structured and applied through explicit Input-Action-Output steps. Each step's output becomes verified knowledge for subsequent reasoning.
Methodology: IAO Prompting Framework
IAO prompting explicitly organizes the LLM's internal knowledge access and application, drawing inspiration from procedural reasoning frameworks. This enables the decomposition of a problem into manageable sub-tasks, applying relevant knowledge components to attain intermediate results before achieving the final solution.
In contrast to zero-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting, which often leaves knowledge utilization implicit, the structured format required by IAO mandates that LLMs explicitly articulate how each piece of knowledge is utilized throughout the reasoning process (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Comparison of knowledge application between IAO prompting and zero-shot CoT using PALM-2 on GSM8K. IAO's structured format reveals how knowledge is accessed and applied at each step, while CoT misses crucial information.
IAO prompting is built on the following core components:
- Subquestion: Breaks down the main question into smaller, manageable components.
- Input: Identification of relevant knowledge required for each step.
- Action: Specification of operations or procedures derived from input knowledge.
- Output: Generation of new knowledge at each step, applied sequentially in the reasoning process.
This explicit breakdown affords improved verification of knowledge paths, allowing for a deeper understanding and identification of misapplications or gaps.
Experimental Results
Arithmetic Reasoning
Significant improvement in arithmetic reasoning tasks was observed with IAO prompting using both PALM-2 and GPT-4. For the GSM8K dataset, IAO achieved a remarkable 94.2% accuracy with GPT-4, surpassing zero-shot CoT by 4.1 percentage points and highlighting benefits in structured resource utilization.
Logical Reasoning
IAO prompting demonstrated its value in logical reasoning tasks such as Date Understanding and Object Tracking, where it significantly surpassed zero-shot CoT approaches with both models, underscoring increased accuracy from explicit knowledge decomposition and application tracking.

Figure 2: Comparison of knowledge application between IAO prompting and zero-shot CoT using PALM-2 on GSM8k. IAO's structured format reveals how knowledge is accessed and applied at each step, while CoT misses crucial information.
Commonsense and Symbolic Reasoning
IAO prompting showed enhancements across the commonsense and symbolic reasoning tasks, with consistent improvements noted in data such as StrategyQA and CommonsenseQA. In symbolic reasoning tasks, IAO significantly outperformed zero-shot CoT and other decomposition methods like L2M and PS, particularly evident on datasets like Last Letter, suggesting the efficacy of IAO in dealing with abstract pattern-based tasks.
Detailed case studies, including arithmetic, date understanding, commonsense reasoning, and symbolic reasoning, are displayed in the figures. These illustrations depict the substantial difference in approach and the value of structured knowledge decomposition.
Conclusion
IAO Prompting offers a structured framework to explicitly model and verify the knowledge flow within LLMs, providing transparency and enhancing reasoning performance across diverse tasks. The technique's effectiveness is statistically substantiated in arithmetic, logical, commonsense, and symbolic reasoning tasks, showcasing its practical utility and domain-independence. The framework's capacity for error detection, as evidenced by human evaluations, underscores its contribution to increasing reliability and interpretability in LLM-based reasoning tasks. Continued exploration in domain applications and optimization for concise output is recommended for wider adoption and practical deployment.

