- The paper introduces Beta, combining encoder-based fine-tuning with bagging and bootstrapped sampling to effectively reduce TabPFN's bias and variance.
- It demonstrates significant scalability and competitive accuracy across over 200 tabular classification tasks, especially in high-dimensional data settings.
- Experimental results validate Beta's state-of-the-art performance, notably outperforming on datasets with fewer than 10 classes and complex tasks.
TabPFN Unleashed: A Scalable and Effective Solution to Tabular Classification Problems
Introduction
The paper "TabPFN Unleashed: A Scalable and Effective Solution to Tabular Classification Problems" presents a novel approach to enhancing Tabular Prior-Fitted Networks (TabPFN) for tabular classification tasks. Despite its promise, TabPFN faces limitations such as handling high-dimensional features and scaling to larger datasets. The authors address these issues by introducing "Beta," a method that aims to simultaneously reduce bias and variance in TabPFN using a combination of bagging and lightweight encoder-based fine-tuning.
Theoretical Background and Methodology
TabPFN is a foundational model for tabular data, operating in two stages: pre-training on synthetic datasets and inference on new tasks using in-context learning. It has shown competitive performance for small datasets but struggles with more complex scenarios due to its fixed input dimensionality. This paper specifically tackles the generalization error of TabPFN by analyzing it through a bias-variance decomposition framework.
Bias and Variance in TabPFN:
- Increase in Context: Reducing variance but the bias plateaus as shown in Figure 1(b, c, e, f).
- Fine-tuning: Reduces bias but increases variance, particularly detrimental with small datasets.
- Bagging: Helps reduce variance without additional computational cost.
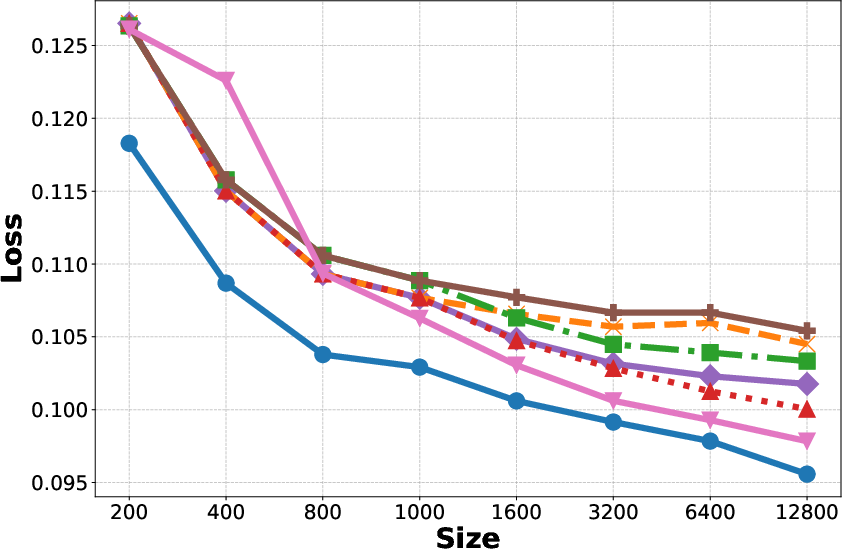
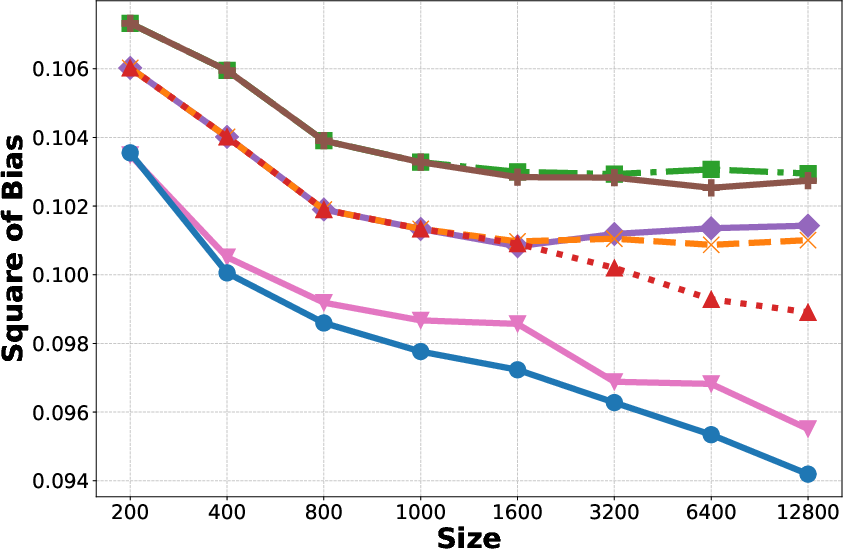
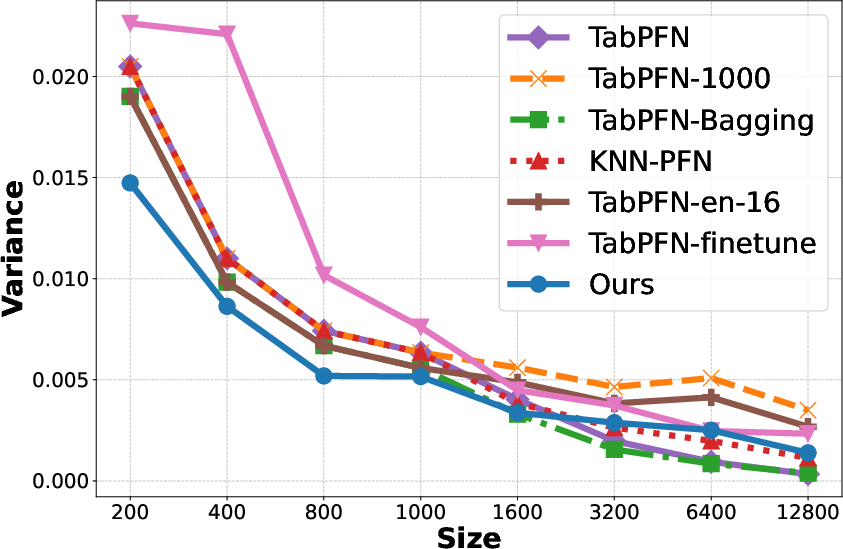
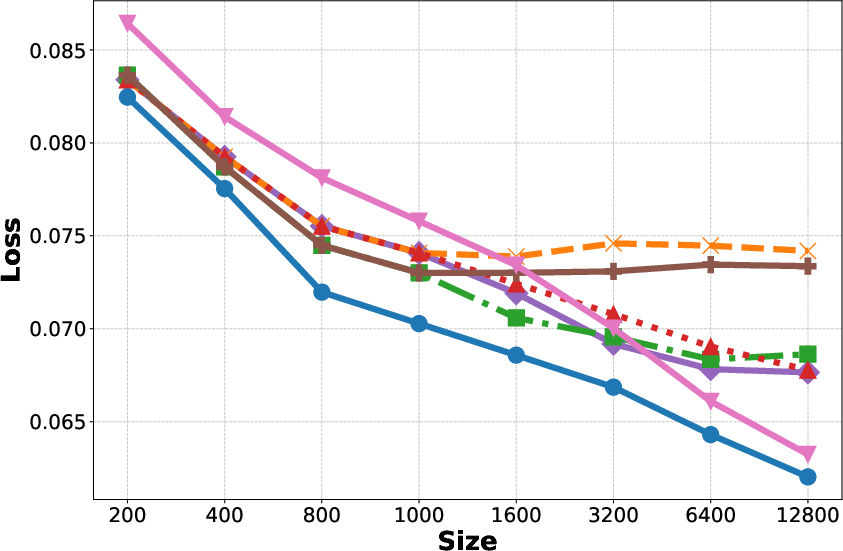
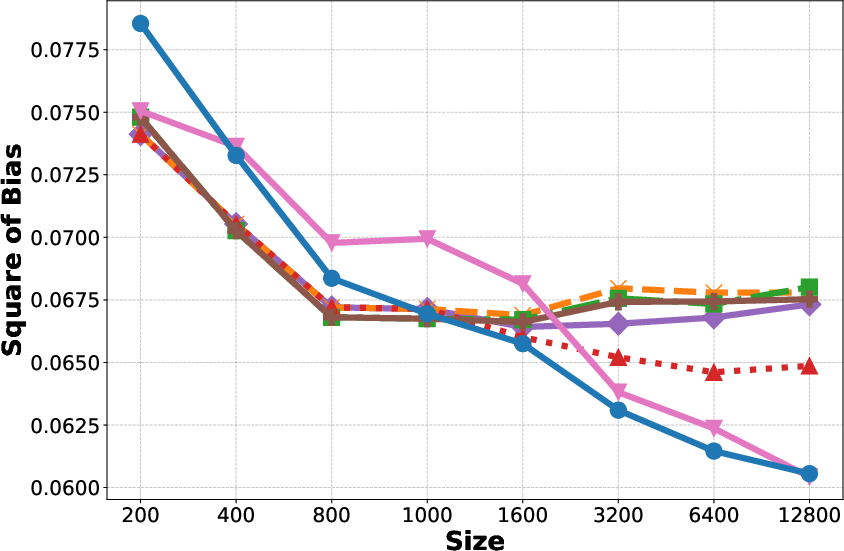

Figure 1: Generalization Error, Bias, and Variance for different methods on the Adult and Bank datasets.
Proposed Approach: Beta
Beta is introduced to address both bias and variance in TabPFN through the following mechanisms:
- Encoder-Based Fine-Tuning: Introduces a lightweight encoder that better aligns downstream tasks with the pre-trained TabPFN, reducing bias.
- Multiple Encoders: By using multiple encoders to create diverse feature transformations, Beta jointly learns these encoders to mitigate variance.
- Batch Ensemble Integration: Used within the encoder to maintain diversity without the complexity of training multiple separate models.
- Bootstrapped Sampling: During inference, it uses bootstrapped sampling to further reduce variance while maintaining computational efficiency.

Figure 2: Overview of the proposed method,~Beta, which consists of the fine-tuning stage and the inference stage.
Experimental Results
The paper demonstrates Beta's effectiveness across various tasks:
- Accuracy and Performance: Beta outperforms or matches state-of-the-art methods on benchmark datasets, including over 200 classification tasks. Critical pairwise tests, such as the Wilcoxon-Holm test, highlight Beta’s performance superiority on datasets with fewer than 10 classes.

Figure 3: The critical difference diagrams based on the Wilcoxon-Holm test with a significance level of 0.05.
- Scalability: Beta shows significant performance improvements as dataset sizes increase, emphasizing its scalability and adaptability compared to existing models.

Figure 4: The relative improvement of Beta over TabPFN across datasets sorted by size.
- High-Dimensional Data: Visualizations and tests confirm Beta's superiority in handling high-dimensional datasets and multiclass tasks.

Figure 5: Average ranks of methods on 17 high-dimensional datasets comparing Beta with other state-of-the-art methods.
Conclusion and Implications
Beta provides a robust framework for extending the capabilities of TabPFN, effectively addressing its scalability and efficiency issues through bias and variance reduction strategies. By combining state-of-the-art techniques such as encoder-based fine-tuning and batch ensemble, Beta sets a new standard for handling complex tabular data tasks. This adaptable approach paves the way for future developments in tabular learning, particularly as it pertains to large-scale and high-dimensional datasets, positioning TabPFN and its variants as comprehensive solutions for real-world applications.











