- The paper reveals that LLMs, while scoring high on individual creativity tasks, exhibit markedly more homogeneous outputs than human responses.
- Methodology employs standardized tests (AUT, FF, DAT) across 22 models, uncovering lower semantic variability in LLM outputs.
- Findings indicate that integrating LLMs in creative tasks may constrain diversity due to convergent output clustering even with optimized prompts.
Creative Homogeneity Across LLMs
The paper "We're Different, We're the Same: Creative Homogeneity Across LLMs" examines the creative output variability between human subjects and a range of LLMs. It seeks to understand whether the popular use of LLMs as creative partners intrinsically leads to more homogeneous creative outputs, as compared to human creativity.
Introduction and Motivation
LLMs have established themselves as prominent tools for augmenting writing, generating ideas, and other creative processes. Despite their advertised potential to enhance creativity, recent observations suggest that LLM-assisted creative endeavors often culminate in outputs that exhibit significant similarity. Previous studies only investigated this phenomenon with individual LLMs, raising anecdotal questions about whether this creative convergence is a result of individual model limitations or is inherent across all LLMs.
Methodology
The methodology involves eliciting creative outputs from both human participants and a diverse set of LLMs using standardized creativity tests: Guilford's Alternative Uses Task (AUT), Forward Flow (FF), and the Divergent Association Task (DAT). The study tests 22 models spanning different LLM architectures, with special analyses conducted on a subset to control for potential confounding variables such as model family.
Population-Level Variability: The analysis focuses on semantic similarity metrics to evaluate response diversity across populations.
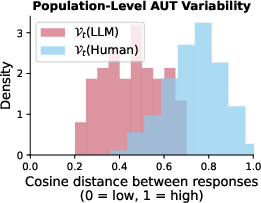
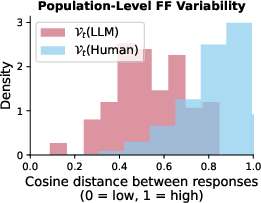
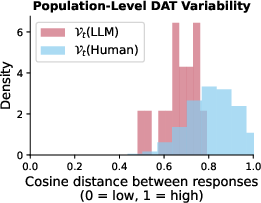
Figure 1: LLM responses exhibit far less variability than human responses
.
Key Findings
Population-Level Response Variability
The empirical results highlight a marked homogeneity in LLM outputs when compared to those of humans. Despite equivalently high scores for individual creativity, LLM responses are much more similar to each other than human responses are to each other, with LLM responses clustering closely in feature space.
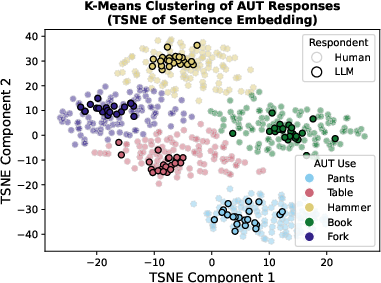
Figure 2: LLM responses cluster together in feature space more than do human responses.
Response Structure Influence
Despite the variations in prompt engineering to minimize structural differences in responses between LLMs and humans, the consistency of LLM output similarity persisted. Even with optimal prompt versions and one-word response comparisons, LLM outputs remained consistently more homogeneous.
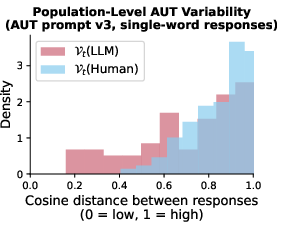
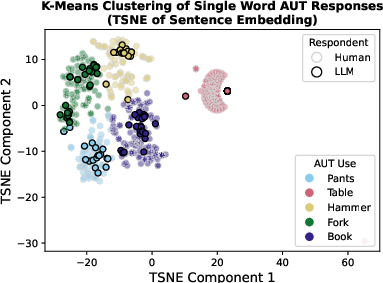
Figure 3: Even when considering only one-word responses to control for response structure, LLM AUT responses have lower population-level variability (left plot) and are closer in feature space (right plot) than human responses.
LLM Family Effects
The research further scrutinizes models from the same "family," specifically the Llama family, to deduce whether architectural or systemic similarities exacerbate output homogeneity. Models within the same lineage exhibited slightly higher homogeneity compared to varied-model evaluations.
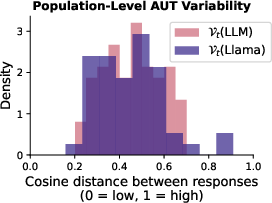
Figure 4: Models from the same family (Llama) exhibit slightly lower population-level variability than models from different families.
Analysis and Implications
The practical implications of using LLMs as creativity support tools are substantial. The study suggests that integrating LLMs into creative workflows might inadvertently promote a narrow band of creativity, potentially constraining the breadth of creative exploration and expression available to users.
Furthermore, the observed homogeneity across varying model architectures and prompt designs underlines a pivotal limitation in the current landscape of generative AI: while these models can simulate creativity to a commendable degree individually, their collective outputs lack the diversity and novelty akin to human creativity.
Conclusion
This research underscores the critical need for further exploration into enhancing LLM output diversity, potentially through revolutionary training paradigms or innovative prompt engineering strategies. While LLMs exhibit proficiency in individual instances of creative problem-solving, the broader challenge for future developments lies in fostering genuine diversity akin to human creativity. This pursuit will be central to ensuring LLM contributions can imbue rather than constrain creative processes across domains.






