- The paper introduces WisdomBot, a fine-tuned educational LLM that integrates Bloom’s Taxonomy-based concept extraction and instruction tuning to enhance learning tasks.
- The model employs a multi-stage training pipeline and retrieval augmentation to outperform baseline models in accuracy and cognitive abilities.
- Experimental evaluations demonstrate significant improvements in logical reasoning, personalized learning, and creativity, validated by both human and GPT-4 assessments.
Overview of "WisdomBot: Tuning LLMs with Artificial Intelligence Knowledge"
This paper introduces WisdomBot, an educational LLM fine-tuned from general LLMs to specifically address educational tasks. The model incorporates educational theories, such as Bloom’s Taxonomy, to enhance capabilities in educational contexts. By leveraging knowledge concept extraction and instruction tuning, WisdomBot provides improved comprehension and response generation in educational environments.
Limitations of General LLMs in Education
General LLMs exhibit specific deficiencies when applied to educational tasks, including limited comprehension ability, outdated knowledge, lack of personalized learning capacities, insufficient proficiency in languages other than English, and challenges in logical reasoning. These limitations hinder their effectiveness in education, demanding enhancements through specialized tuning approaches.
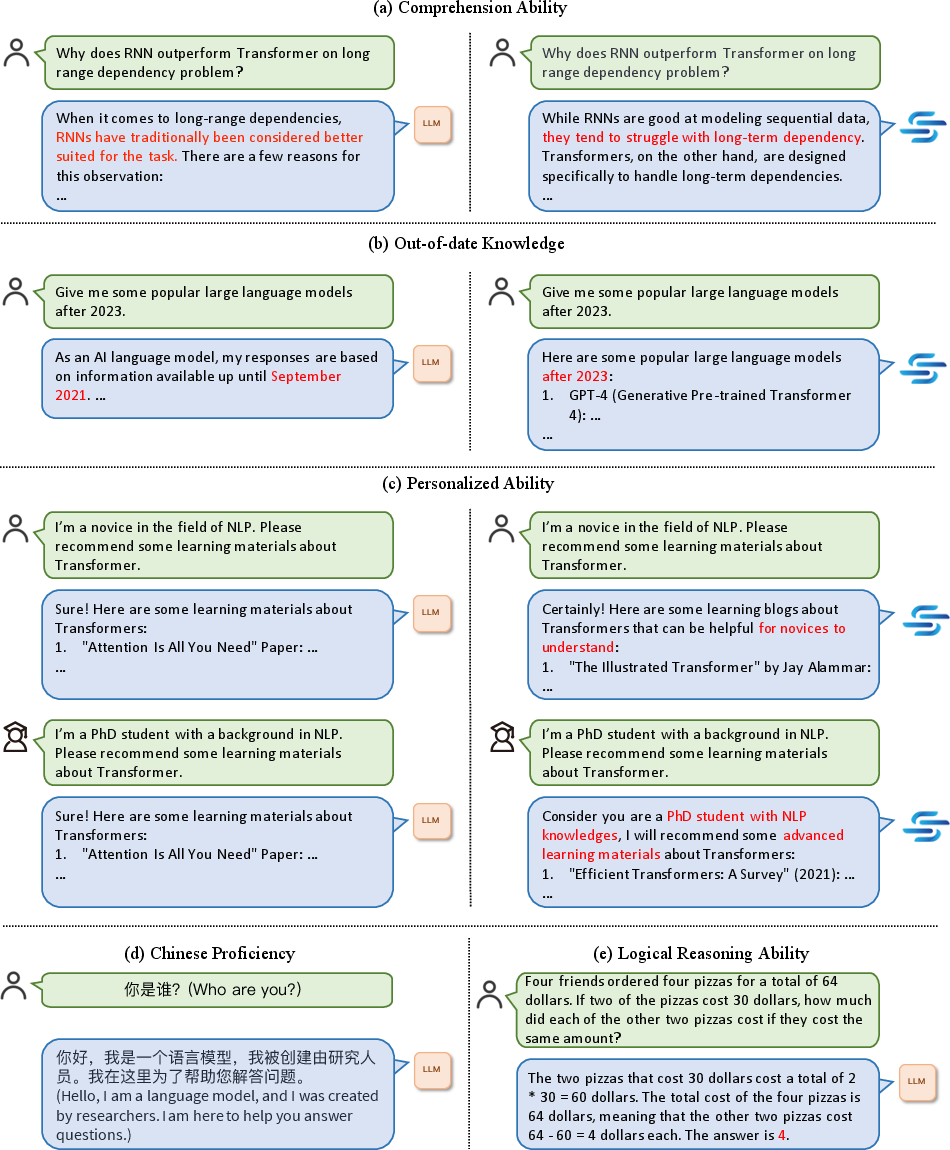
Figure 1: Limitations of general LLMs in education: (a) comprehension ability, (b) out-of-date knowledge, (c) personalized ability, (d) Chinese proficiency, (e) logical reasoning ability.
Methodology
Training Pipeline
The paper outlines a multi-stage training pipeline that starts with the collection of coarse and fine-grained knowledge concepts from textbooks and employs Bloom’s Taxonomy to structure these concepts. Instruction tuning is performed to align LLM outputs with educational tasks, supplemented by retrieval augmentation methods during inference, such as local knowledge base and search engine retrieval, to enrich responses with external knowledge.
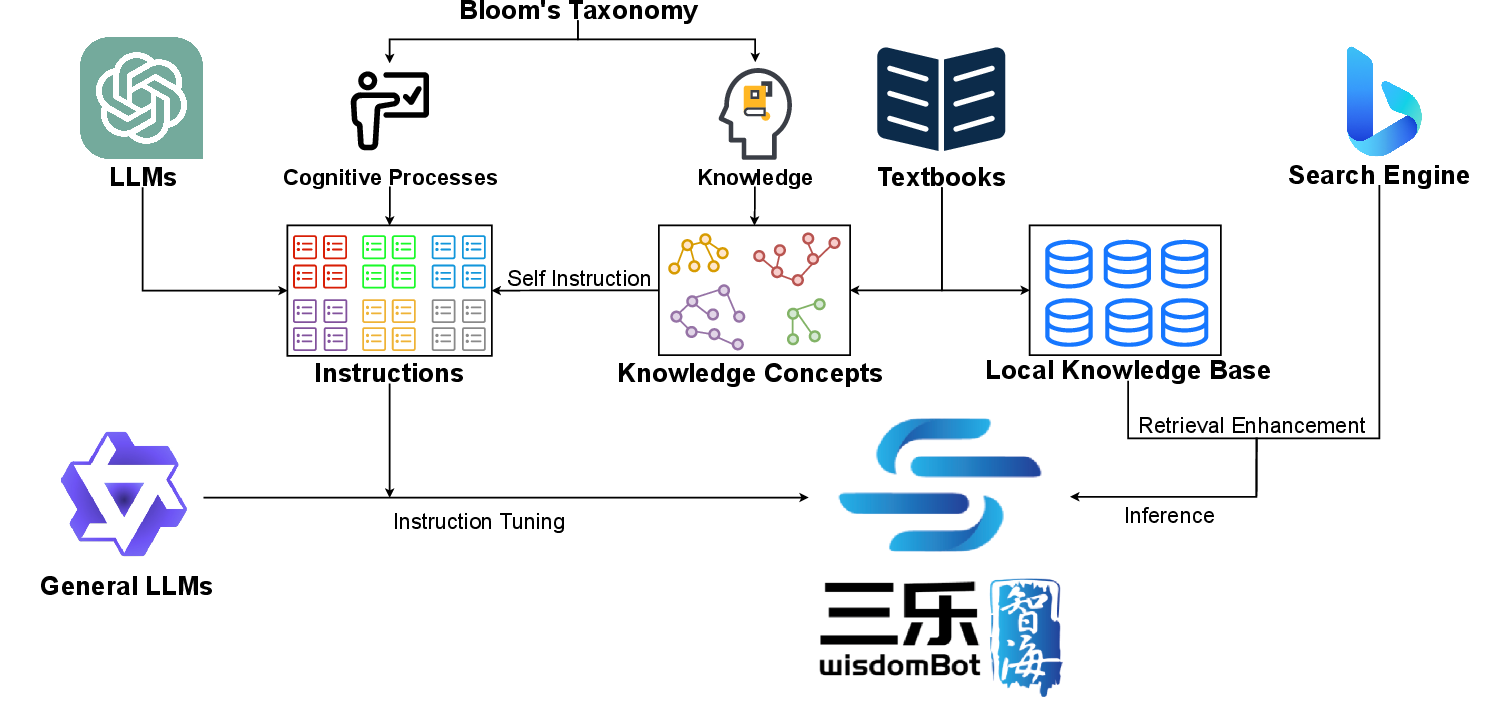
Figure 2: Training pipeline. We collect knowledge concepts and instructions under the guidance of textbooks, Bloom’s Taxonomy, and strong LLMs, serving as instruction-tuning data to transform general LLMs to educational LLMs.
Knowledge Concept Extraction and Instruction Tuning
Coarse-grained concepts are manually extracted from educational materials, then expanded into fine-grained concepts with the assistance of self-instruct methods and LLMs. Simultaneously, instructional templates are crafted around educational tasks, filling these with knowledge concepts to create a rich dataset for model tuning.
Experimental Validation
WisdomBot’s performance is validated through a series of experiments against baseline models such as Chinese-LLaMA-Alpaca and Qwen, utilizing both self-constructed and public datasets.
Performance evaluations reveal WisdomBot attaining higher accuracy and reliability over baselines in professional question answering and cognitive tasks, substantiated by both human and GPT-4 assessments.
(Figures 5-8)
Figures 5-8: Evaluation of WisdomBot vs. baseline models, illustrating its superior performance across various educational tasks.
Results on C-Eval
WisdomBot's effectiveness is further corroborated by its performance on the C-Eval benchmark, where it excels in subjects closely aligned with AI and computer science.
Enhancement of Cognitive Abilities
WisdomBot exhibits marked improvements in advanced cognitive abilities, including creativity, personalized learning, and logical reasoning. These enhancements are supported by GPT-4 evaluations for personalized and creative tasks, while logical reasoning accuracy increases are directly measured.
Retrieval Enhancement Evaluations
This paper demonstrates that retrieval enhancement methods substantially augment WisdomBot's ability to provide professional and factually accurate responses, showcasing the benefits of integrating local knowledge bases and search engine data during inference.
Case Study
The case studies illustrate WisdomBot’s capabilities, demonstrating improved performance over baseline models in areas like creativity and personalized learning due to retrieval enhancements.

Figure 3: Case examples generated by WisdomBot and baselines: (a) creativity, (b) personalized ability, (c) logical reasoning. WisdomBot with two retrieval enhancement methods: (d) local knowledge library retrieval, (e) search engine retrieval.
Conclusion
WisdomBot effectively addresses the constraints of general LLMs in educational settings by leveraging domain-specific instruction tuning and retrieval techniques to enhance accuracy and cognitive capabilities. The proposed methods offer significant improvements, positioning WisdomBot as a potent tool for educational applications in AI.
The findings and methodologies presented in this paper hold promise for future work in combining educational theories with AI to refine LLMs for specialized applications.


