- The paper introduces a GPU-accelerated distributed algorithm for multi-phase OPF, using component-wise decomposition to isolate and efficiently solve subproblems.
- It leverages solver-free ADMM iterations and GPU parallelism to significantly reduce computational time and improve scalability in dynamic power systems.
- Empirical evaluations on IEEE test systems demonstrate notable improvements in convergence speed and communication efficiency compared to traditional CPU-based approaches.
A GPU-Accelerated Distributed Algorithm for Optimal Power Flow in Distribution Systems
Introduction
The paper presents a GPU-accelerated distributed optimization algorithm designed for multi-phase optimal power flow (OPF) in active distribution systems. This novel solution focuses on dynamically changing topologies within distribution networks and offers significant scalability improvements over CPU-based solutions through GPU parallelism. By implementing a component-wise decomposition strategy, the algorithm isolates equality constraints from inequality constraints, thereby reducing per-iteration time and enhancing the overall computational performance. Numerical experiments demonstrate its superior scalability across various IEEE test systems.
The paper introduces both centralized and distributed formulations for the multi-phase OPF problem, incorporating aspects such as power generation, voltage magnitude, power balance, and linearized power flow equations.
Centralized Multi-phase OPF Model
The model ensures operational bounds on power generation and voltage magnitude, alongside power balance equations ensuring equilibrium at each bus. A voltage-dependent load model accounts for wye and delta connections, while linearized power flow equations express the relationships within the network. The objective is to minimize operational costs subject to constraints, represented in standard LP form:
minf(x) s.t.Ax=b, x≤x≤x.
Distributed Multi-phase OPF Model
The implementation of a component-wise decomposition strategy enables the model to handle large-scale systems efficiently, decomposing the centralized model into smaller subsystems:
minc⊤x s.t.Asxs=bs, Bsx=xs, xs≤xs≤xs.
Implementation Overview
The proposed GPU-accelerated algorithm leverages solver-free ADMM iterations to optimize the distributed OPF model. By analyzing the convergence properties and computational requirements, the implementation isolates subproblems which admit closed-form solutions rather than relying on optimization solvers. This decision yields drastic improvements in computational efficiency, particularly through the reduction in communication time by applying precomputed matrix operations via GPU.


Figure 1: Primal (left) and dual (right) residuals at each iteration of Algorithm execution, showing stable convergence.
Empirical results based on IEEE test systems ranging from small (13-bus) to large-scale (8500-bus) configurations reveal substantial improvements in convergence times and computational efficiency:
- Local Update Optimization: By utilizing GPU threads, each local component achieves parallel computation, substantially reducing wall-clock time per iteration.
- Communication Efficiency: Implementing MPI across GPU nodes reduces the communication overhead compared with traditional CPU-based methods.
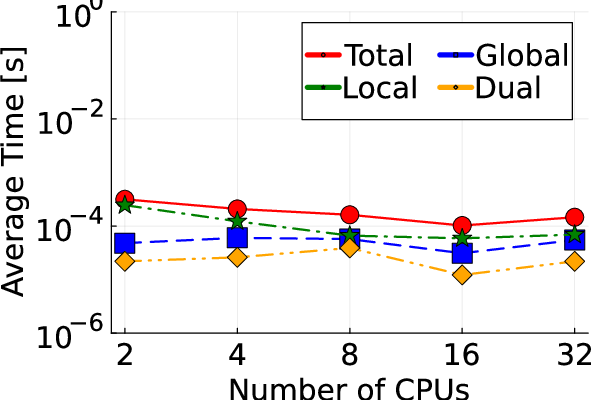
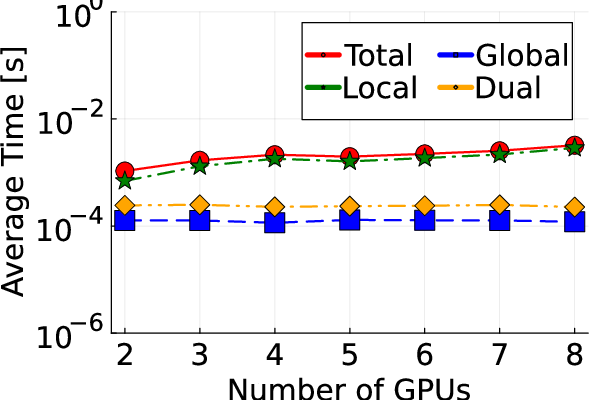

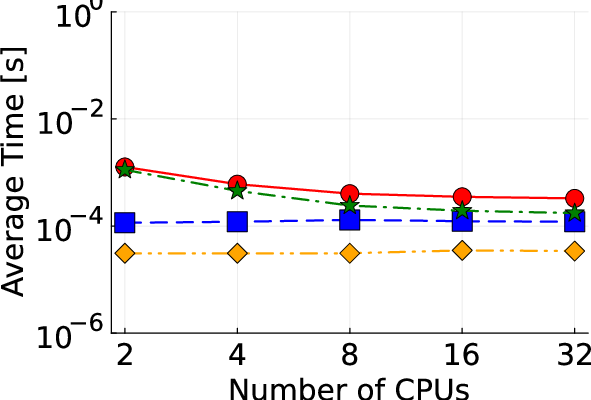

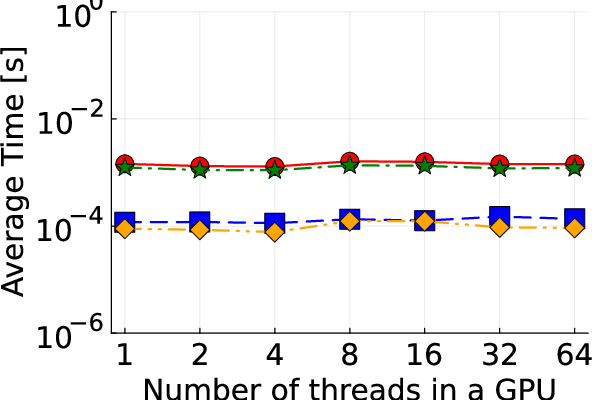



Figure 2: Detailed illustration of IEEE test systems used for benchmarking the proposed algorithm.
Conclusion
The introduction of a GPU-accelerated ADMM approach for distributed OPF marks a significant advancement in processing capabilities for power distribution networks. This approach simplifies the computational complexity associated with large-scale, dynamic systems, proving to outperform traditional CPU-implemented solutions. Future work will explore integrating advanced machine learning techniques into the distributed optimization framework, leveraging GPUs for scalable, efficient computation enhancements.

Figure 3: Comparison of total computation time between GPU and CPU, demonstrating marked time reduction on log-scale.













