- The paper's main contribution is its comprehensive survey of reinforcement learning applications in finance, detailing both model-free and model-based strategies.
- The paper examines various RL methodologies including actor-only, critic-only, and actor-critic approaches, highlighting the use of policy gradient, PPO, and Q-learning to tackle financial decision-making.
- The paper underscores RL's potential in optimizing market making, portfolio management, and optimal execution while addressing challenges like market noise and risk sensitivity.
A Review of Reinforcement Learning in Financial Applications
Introduction
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is increasingly being utilized in the finance sector to address complex decision-making tasks. The paper "A Review of Reinforcement Learning in Financial Applications" provides an in-depth survey of these applications, exploring both the advantages and challenges of using RL in financial contexts. It covers a range of financial tasks such as market making, portfolio management, and optimal execution, each with its unique challenges and nuances. The survey also analyzes common patterns in RL research for finance and proposes future directions to advance the field.
Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Financial Applications
The paper categorizes RL algorithms into model-free and model-based methods. In the financial domain, model-free methods, including Q-learning and policy gradient methods, are prominently used. These methods are advantageous due to their flexibility and ability to learn policies directly from interaction with the environment without relying on explicit models of market dynamics.
Actor-only, Critic-only, and Actor-Critic Methods
Amongst model-free methods, actor-only algorithms optimize the policy directly using techniques like Policy Gradient and Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). Critic-only methods such as Q-learning evaluate the action values and select policies to optimize these values. Actor-critic methods combine both strategies, with examples such as the Advantage Actor-Critic (A2C) mechanism, allowing efficient learning through the calculation of advantage functions.



Figure 1: Distribution of different state variables. Prices include the asset price, returns, and a combination; represents the agent's portfolio information; Pred. means the prediction results of stock movement and company news sentiment; Market Idx represents the market indicators like SP500; Tech. Idx means the technical indicators like Relative Strength Index (RSI); LOB means the limit-order-book is used as state; Time Index means the time interval is used as a state.
Model-Based Methods
Model-based RL has gained less traction but offers significant potential by providing a detailed simulation of the financial environment. This approach employs simulators that can generate synthetic market conditions, aiding in optimal decision-making without the risks associated with live market trials.
Applications in Finance
Market Making
Market-making RL applications configure agents to establish optimal bid and ask prices by interacting dynamically with the market conditions. Single-agent frameworks focus on profit maximization while minimizing inventory risks through sophisticated reward function designs. Conversely, multi-agent frameworks foster competitive strategies where multiple market makers interact, improving both execution efficiency and model robustness through adversarial setups.
Portfolio Management
Integration of RL into portfolio management involves dynamic asset allocation to optimize returns. By adapting to market changes in real time, RL outpaces traditional static strategies. Various methods focus on neural network-based policy networks and ensemble strategies to reinforce learning robustness. The usage of market indicators and sentiment analysis augments the RL models, providing enhanced predictive accuracy and decision-making.
Optimal Execution
For task-oriented applications like optimal execution, RL algorithms are designed to minimize the cost of trading by splitting orders over time, considered through model-free approaches. Risk-sensitive RL algorithms, such as those with utility-based shortfall functions, highlight the adaptation of RL to manage and mitigate the inherent financial risks more effectively.

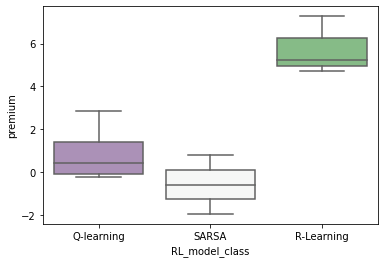
Figure 2: Impact of MDP Design on Model Performance.
The survey's meta-analysis section evaluates literature to extract insights on state design, algorithm choice, and reward engineering in RL applications for finance. It was found that while more complex state features or dimensions often result in enhanced performance, excessive information can introduce noise.






Figure 3: RL Premium Analysis.
Moreover, the analysis of RL Premium—defined as the relative performance gain of RL strategies over traditional methods—illustrates the contexts wherein RL excels, particularly in adapting to varying market sizes and action spaces. Techniques such as shaped rewards and inclusion of contextual information are noted to significantly boost performance, offering potential guidelines for future RL algorithm development in finance.
Conclusion
The paper comprehensively reviews RL in finance, emphasizing its transformative potential in financial applications. It identifies significant challenges due to the peculiarities of financial data, such as heavy-tailed distributions and non-stationarity, which necessitate further exploration and adaptation of RL algorithms. Addressing these challenges will be crucial in advancing RL's role in finance, leveraging approaches such as multi-agent frameworks, model-based strategies, and risk-sensitive algorithms to improve real-world applicability and performance.
The implications of RL's usage in finance are profound, promising enhanced efficiency and effectiveness in financial decision-making processes. Future research directions, as proposed by this paper, will be instrumental in blueprinting the trajectory of RL's integration into the finance industry, pushing towards more robust and practical implementations.










