- The paper introduces a multi-agent system that integrates LLMs and KGs to improve reasoning and reduce hallucinations.
- It employs Few-Shot Learning, Chain-of-Thought, and ReAct frameworks for efficient query processing and task decomposition.
- Evaluation shows 95.12% task classification accuracy and 90.45% task execution success, validating its robust application in complex domains.
AGENTiGraph is proposed to address inherent challenges in the integration of LLMs with Knowledge Graphs (KGs) for domain-specific applications, notably in question answering (QA). This platform aims to mitigate issues such as hallucination and limited reasoning abilities of LLMs by employing KGs for factual consistency and enhancing reasoning capabilities. It introduces an intelligent multi-agent architecture designed for adaptive interaction and management of KGs, optimizing user interaction and ensuring dynamic knowledge integration.
Architecture Design of AGENTiGraph
AGENTiGraph leverages a novel multi-agent system for intelligent interaction with KGs. Each agent specializes in specific tasks such as user intent interpretation, key concept extraction, task planning, KG interaction, reasoning, dynamic knowledge integration, and response generation.
Multi-Agent System Components
- User Intent Interpretation: Utilizes Few-Shot Learning and CoT reasoning to accurately interpret diverse query types and determine user intents.
- Key Concept Extraction: Employs Named Entity Recognition and Relation Extraction to identify entities and map them to KGs using semantic similarity with BERT-derived vector representations.
- Task Planning: Decomposes user intent into executable tasks employing CoT reasoning to model task dependencies.
- Knowledge Graph Interaction: Converts high-level tasks into executable graph queries using Few-Shot Learning and ReAct framework.
- Reasoning: Enhances raw query results with logical inference to bridge structured knowledge and natural language understanding.
- Dynamic Knowledge Integration: Supports continuous knowledge extraction, ensuring KGs remain up-to-date through interactions with the Neo4j database.
- Response Generation: Synthesizes processed information into structured and contextually relevant responses using CoT, ReAct, and Few-Shot Learning.
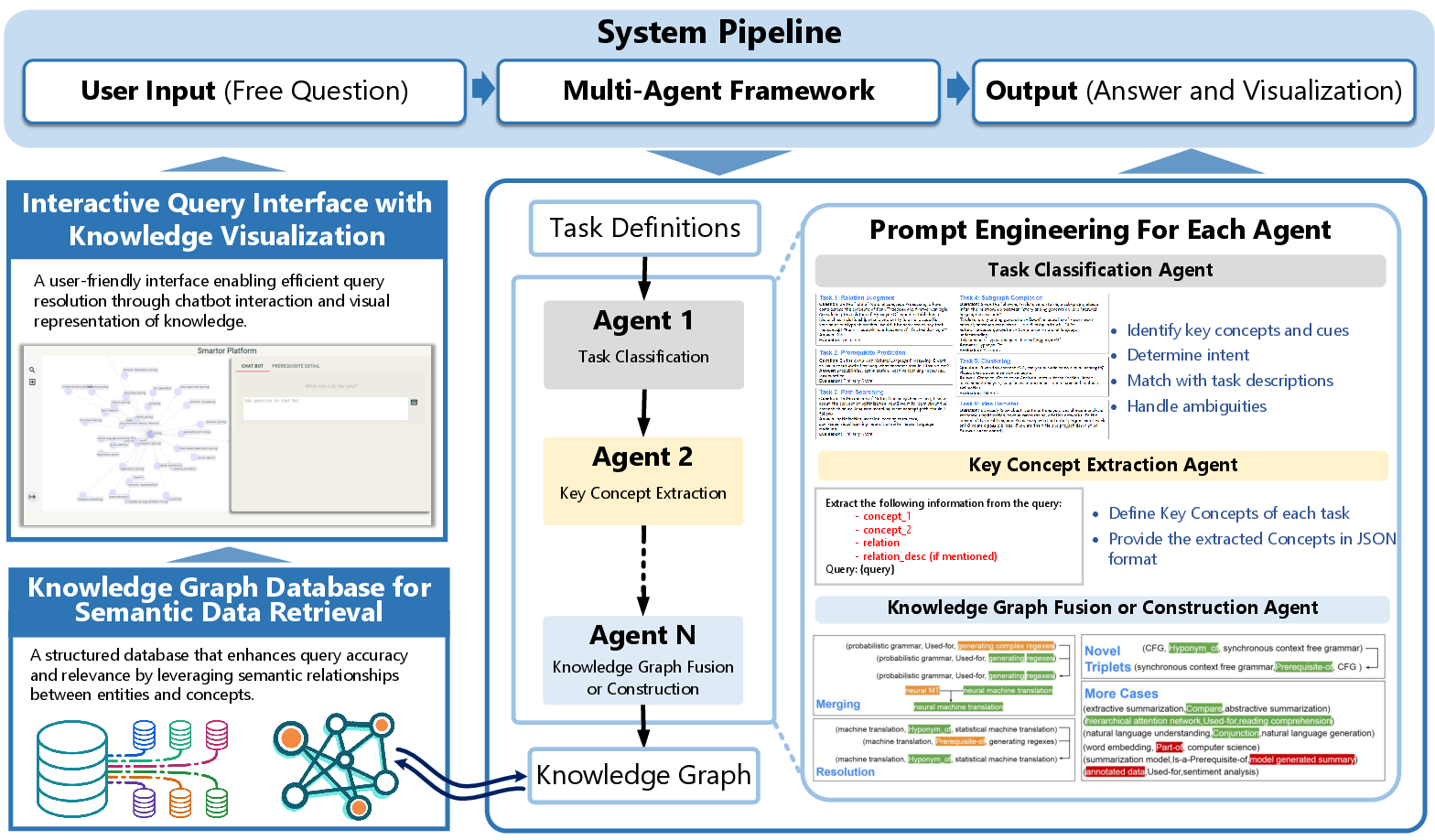
Figure 1: AGENTiGraph Framework: A multi-agent system for intelligent KG interaction and management.
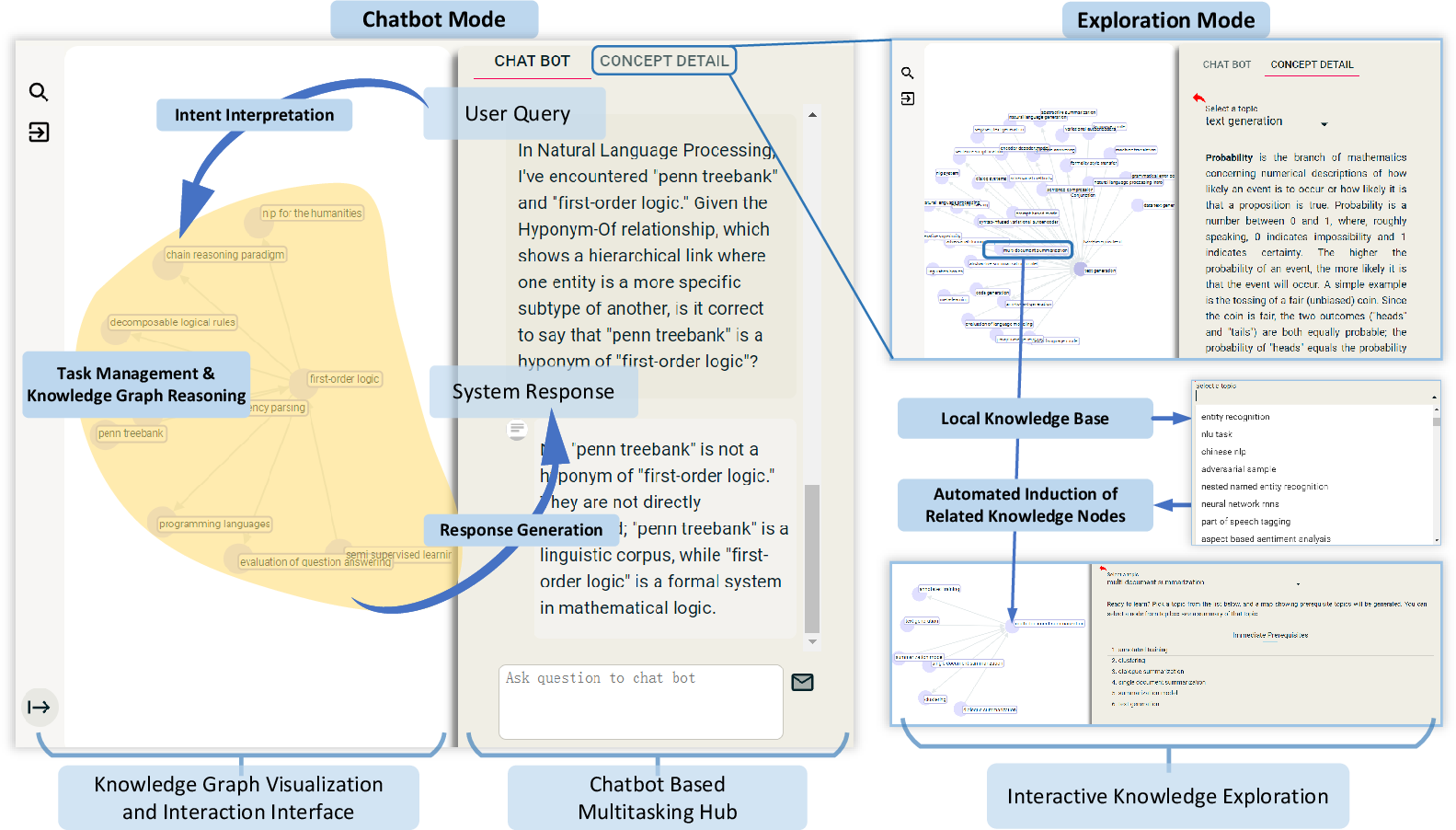
System Demonstration and Interaction Paradigm
AGENTiGraph offers a dual-mode interface combining conversational AI with interactive knowledge exploration. Users interact through natural language in a user-friendly environment that supports seamless KG management and exploration.
Key Features
AGENTiGraph was evaluated against state-of-the-art zero-shot baselines using various LLMs. The integrated framework demonstrated impressive improvements, achieving 95.12% accuracy in task classification and a 90.45% success rate in task execution. Its capability extends to diverse domains, where it efficiently constructs specialized KGs in areas such as legislation and healthcare, enabling complex queries in these contexts.
Future Developments
AGENTiGraph sets a foundation for further enhancements in multi-hop reasoning, optimizing response conciseness and completeness. Future developments will focus on continuous learning from user interactions and expanding its applicability to additional domains requiring customized KG solutions.
Conclusion
AGENTiGraph significantly advances knowledge graph interaction capabilities, bridging LLMs and structured knowledge for robust domain-specific applications. Its design ensures adaptable, efficient, and user-friendly interactions, demonstrating potential across various complex tasks and real-world scenarios. Future research and development will drive enhancements in reasoning capabilities and expand its applicability to more domains, further refining its role in intelligent knowledge management and exploration systems.