- The paper introduces ARCO, a dynamic co-optimization compiler using multi-agent reinforcement learning to optimize both software and hardware configurations for DNNs.
- It employs a centralized training with decentralized execution approach and a confidence sampling method to improve throughput by up to 37.95% and reduce optimization time by up to 42.2%.
- Experimental evaluations on models like ResNet-18 and VGG demonstrate ARCO’s superior performance compared to traditional frameworks such as AutoTVM and CHAMELEON.
Introduction
The "Dynamic Co-Optimization Compiler" paper introduces ARCO, an innovative framework based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) for optimizing the deployment of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) on various hardware platforms. ARCO aims to enhance throughput and reduce optimization time by integrating multi-agent systems that focus on concurrent optimization of hardware and software configurations. It represents a significant step in the evolution of automated compilation frameworks.
Framework Overview
ARCO distinguishes itself by employing three MARL agents operating using an actor-critic model, with roles split between software and hardware optimization. This setup allows for fine-tuned adjustments across different aspects of the DNN deployment, translating directly to improved efficiency and reduced computational overhead. The framework exploits high-confidence configurations, effectively expanding the operational space (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Overall search flow of ARCO.
The agents in ARCO operate under a Centralized Training with Decentralized Execution (CTDE) paradigm. This paradigm ensures that, during training, all agents have access to a global state, while decisions during execution rely on local observations and policies refined through shared learning experiences.
Architecture and Implementation
Key components of ARCO include the MARL Exploration Module and the Confidence Sampling (CS) method:
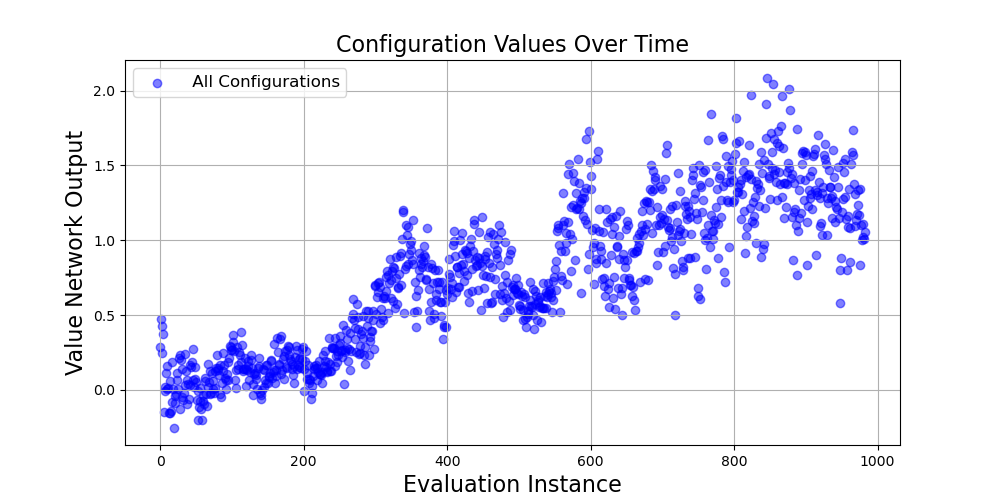
Figure 3: Configurations over time for ResNet-18 model before the CS method.
Experimental Evaluation
ARCO's effectiveness was validated through an extensive series of experiments against existing frameworks such as AutoTVM and CHAMELEON. The results demonstrated a marked enhancement in throughput and a reduction in optimization time, up to 37.95% and 42.2%, respectively. These improvements underscore the efficacy of the MARL and CS approach in real-world deployments, achieving superior throughput across models like ResNet-18 and VGG series.

Figure 4: Comparing the achieved throughput of different frameworks over AutoTVM on VTA++.
Conclusion
The paper showcases ARCO as a significant advance in DNN compiler frameworks, addressing key challenges in hardware-software co-optimization. By leveraging MARL, ARCO not only optimizes the deployment of DNNs across different hardware platforms but also sets a benchmark for future developments in adaptive, intelligent mapping systems. Further research could enhance these techniques, possibly integrating hybrid models or exploring more complex feedback mechanisms to continue refining optimization strategies.