- The paper presents CCC, an LLM-powered assistant that customizes workplace social media posts by distinguishing between professional and casual use cases.
- The system’s Co-Outline and Co-Edit functions leverage historical data and user input to generate structured, context-aware content effectively.
- Evaluation revealed that CCC improves user satisfaction and engagement without adding cognitive load, highlighting its potential for human-LLM collaboration.
Introduction to CCC
The paper "Corporate Communication Companion (CCC): An LLM-empowered Writing Assistant for Workplace Social Media" (2405.04656) presents a novel approach to enhancing corporate communication through social media. CCC is designed to assist users in composing workplace social media posts that are personalized and reflective of individual user preferences. Utilizing LLMs, CCC aims to overcome the limitations of generic content generation by offering customized assistance that aligns with the diverse needs of workplace social media environments.
Use Case Awareness and Personalized Assistance
The study began with an analysis of workplace social media, recognizing the blend of professional and casual use cases among users (Figure 1). CCC employs a use case matching strategy, leveraging LLMs to classify posts as "professional" or "casual" based on both user input and relevant historical posts. This classification allows the system to tailor its assistance appropriately, ensuring that content aligns with the user's intended persona in the workplace.

Figure 1: A visualization of users' post writing varying along Use Cases and Writing Style.
System Design and Implementation
CCC divides the writing process into two core functions: Co-Outline and Co-Edit. The Co-Outline feature assists users in generating structured outlines that form the backbone of their social media posts (Figure 2). Utilizing job status and historical post data, CCC generates contextually relevant suggestions and ideas that align with user profiles.
For text editing, CCC's Co-Edit function provides customization settings that allow users to specify the tone and style of the generated content. By adjusting attributes such as tailored vs. generic, conversational vs. structured, creative vs. conventional, and detailed vs. concise, users can control the personalization level and ensure alignment with their communication goals.

Figure 2: An illustration of the CCC system architecture highlighting user input handling and profile-based contextual assistance.
The research involved a comprehensive user study with 10 participants tasked with writing and evaluating social media posts using CCC and a standard writing assistant. Results demonstrated CCC's effectiveness in enhancing user experience and writing quality from both writer and audience perspectives. Participants engaged more with CCC due to its user-friendly interface and perceived collaboration in the writing process (Figure 3). No additional cognitive load was imposed despite increased customization.
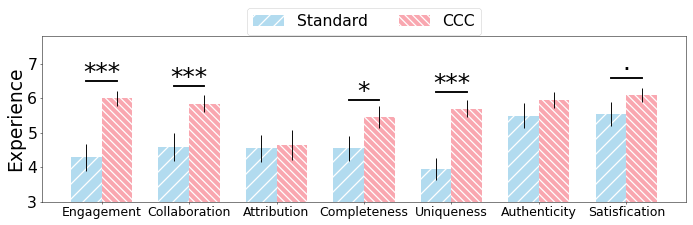
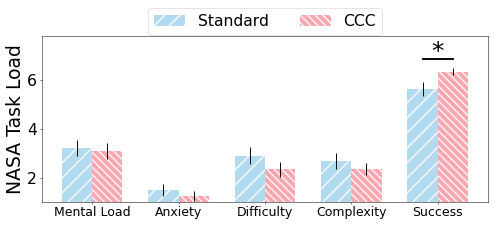
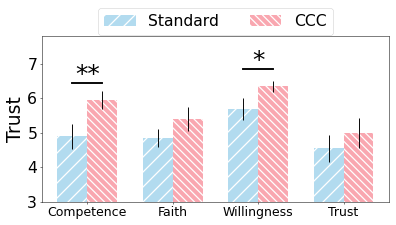
Figure 3: Depicts enhanced user experience and satisfaction with CCC in terms of interactivity and trust.
Audience evaluations further supported the superiority of CCC-enhanced posts in terms of informativeness, engagement, and overall quality. The study confirmed CCC's capability to produce diverse and contextually relevant content while maintaining a high degree of customization (Figure 4).
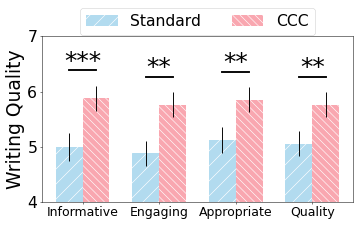
Figure 4: Illustrates improvements in writing quality with CCC, validated by audience feedback.
Implications for Human-LLM Collaboration
The findings underscore the necessity of integrating user-centric design and LLM adaptation into collaborative systems for workplace communication. The mixed-initiative interaction framework employed by CCC demonstrates how users can effectively collaborate with AI systems. By combining tailored content generation with strategic use case recognition, CCC navigates the complexities of workplace social media effectively.
Moreover, the contextual adaptation of CCC could inspire further exploration into personalized LLM applications across varied domains, emphasizing user control and intent recognition.
Conclusion
CCC exemplifies how LLMs can facilitate enhanced corporate communication by tailoring social media content to individual preferences and use cases. The comprehensive design framework and evaluation emphasize the system's potential to improve user experiences in a semi-formal environment. Future research can extend CCC’s methodologies to broaden the scope of personalized AI-assisted communication, addressing challenges inherent in various social and professional settings.





