- The paper introduces Structured Chain-of-Thought Prompting to decompose multi-turn QA into distinct states, enhancing document grounding for LLMs.
- It employs a state machine architecture with specialized algorithms, such as Falcon and Flan-UL, to improve answer accuracy and reduce hallucinations by up to 16.8%.
- The experiments demonstrate that SC prompting outperforms unstructured methods and can augment human-labeled data for training in document-specific QA tasks.
Structured Chain-of-Thought Prompting for Few-Shot Generation of Content-Grounded QA Conversations
This paper presents a new approach called Structured Chain-of-Thought (SC) Prompting, designed to enhance the generation of content-grounded multi-turn Q&A conversations using pre-trained LLMs. The paper specifically addresses the challenge of closed-domain hallucinations, where models, even when explicitly instructed, fail to generate text grounded in a provided document.

- Figure 1: A multi-turn QA conversation grounded in a document. If the document does not have an answer to a user query, the agent acknowledges so in its response.*
Structured Chain-of-Thought (SC) Prompting Approach
SC prompting involves breaking down the complex task of generating document-grounded multi-turn QA conversations into a series of states in a state machine. Each state corresponds to specific subtasks like content reading and utterance generation, executed with dedicated resources such as prompts and optional tools.
State Machine Architecture
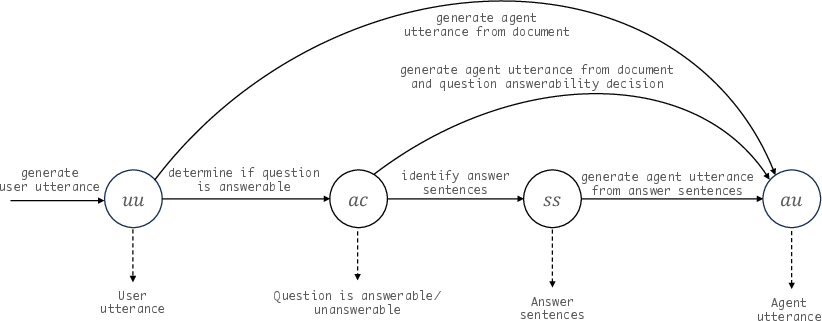
Figure 2: State machine for generating a single user-agent utterance pair within a multi-turn conversation \S{\ref{section:preliminaries}}.
The state machine comprises four states:
- User Utterance Generation (UU): Generates the next user query within an ongoing conversation grounded in the document.
- Question Answerability Classification (AC): It ascertains whether the given document contains an answer to the user query, thus mitigating hallucinated answers.
- Answer Sentence Selection (SS): Identifies relevant sentences in the document that likely contain information pertinent to a user's query.
- Agent Utterance Generation (AU): Generates a response to the user's query, factoring in its grounding to selected document sentences if applicable.
Two algorithms, Falcon and Flan-UL, are utilized for various tasks in the state machine. While Falcon handles user and agent utterance generation, Flan-UL assists in question answerability classification and answer sentence selection where needed.

Figure 3: Prompts for states au and ss. Left: Agent utterance generation (au) with a pre-trained LLM. Right: Answer sentence selection (ss) with an instruction-following LLM. This diagram only shows 1-shot prompts for brevity; we use more demonstrations in practice.
Methodology for Multi-Turn QA Generation
The paper investigates five algorithms, delineated by their state transition sequences and the resources used in the respective states. Notably, two state transition sequences were implemented: one with a two-state sequence } and another full sequence }.
A focal point is the distinction between reading tasks (ac, ss) and generation tasks (uu, au), probing where pre-trained LLMs require additional support. For instance, question answerability classification (AC) was performed either with the same pre-trained LLM used for generation or with an instruction-tuned model.
Performance Evaluation
In the experiments conducted, the structured chain-of-thought (SC) prompted methods that deployed an instruction-tuned assistant in the AC and SS states considerably reduced hallucinations -- up to 16.8% -- compared to an unstructured } approach (Table~\ref{table:sft-results}). Furthermore, in few-shot prompting evaluation with an LLM as the agent, data generated with the SC prompted model with Flan-ul demonstrated a superior balance of performance on both answerable/Unanswerable classes.
Conclusion
This paper extends structured chain-of-thought prompting to the synthesis of multi-turn, content-grounded QA conversations using few-shot LLM prompting. Experimental analysis demonstrates the efficacy of structured CoT prompting in both intrinsic and extrinsic evaluations over baseline methods, even facilitating improvements over conventional human-labeled data when used in data augmentation for training. This signifies strong potential for the approach to bolster LLM performance in document-specific QA tasks, ultimately enhancing faithfulness and accuracy. Future work could explore its extension to more complex multi-document and multi-lingual scenarios.




