- The paper introduces FactorTopy, a novel method that maps deep network features onto specific brain regions.
- It employs a brain encoding model with factorized selectors for space, layer, and scale to achieve smooth topological mappings.
- Results indicate that hierarchical alignment in models like CLIP enhances task performance and mitigates catastrophic forgetting.
Mapping Deep Network Features onto the Brain
This essay explores the methodology and findings from the research paper "Brain Decodes Deep Nets" (2312.01280), which presents a technique for visualizing and analyzing large pre-trained vision models by mapping them onto the brain. The paper's approach offers insights into how these models operate, their hierarchical structure, and their behavior during fine-tuning processes.
Introduction
Brain and Network Hierarchies
The paper investigates the hierarchical organization of the brain and its parallels with artificial neural networks (ANNs). The brain's feed-forward hierarchical organization is essential for efficient computation and adaptation, a trait that ANNs mimic with growing success. When scaling ANNs up in size and data, they sometimes lose hierarchical alignment to the brain. This research postulates that ideal computer vision models should align with the brain’s hierarchical structure.
FactorTopy Mapping
Central to this research is the innovative mapping method, FactorTopy, which creates explicit connections between brain regions and network features across dimensions such as layers and channels. This method enables researchers to visualize deep network features literally painted onto the brain's structure, providing an unprecedented view of how pre-trained models change when adapted to new, smaller datasets.
Methods
Brain Encoding Model
The study uses a brain encoding model to predict fMRI signals in response to image stimuli, exploiting the spatial, layer, and scale dimensions of network features. The encoding process leverages a sophisticated, factorized selector for deep-network layers that enables smooth topology-constrained mapping. This approach enhances the training stability, a crucial element given the unique and individualized mental processes inherent in each subject.
Factorized and Topological Selection
The FactorTopy method employs several key selectors:
- Space Selector: Maps 3D brain voxel coordinates into 2D spatial coordinates.
- Layer Selector: Determines the weight for each layer in the network.
- Scale Selector: Computes the weight for local versus global tokens.
This factorized selection, alongside a topology-constrained framework, stabilizes statistical mappings across images by ensuring smooth continuity in feature selection values.

Figure 1: Factorized-selectors trained with topological constraints improved confidence and mapping smoothness.
Results and Findings
Hierarchical Structure Preservation
Networks trained with hierarchical organization, such as CLIP, align closely with the brain's structure. This alignment improves with increasing model capacity, suggesting that hierarchical organization aids in adapting to dynamic tasks and reducing catastrophic forgetting during fine-tuning.
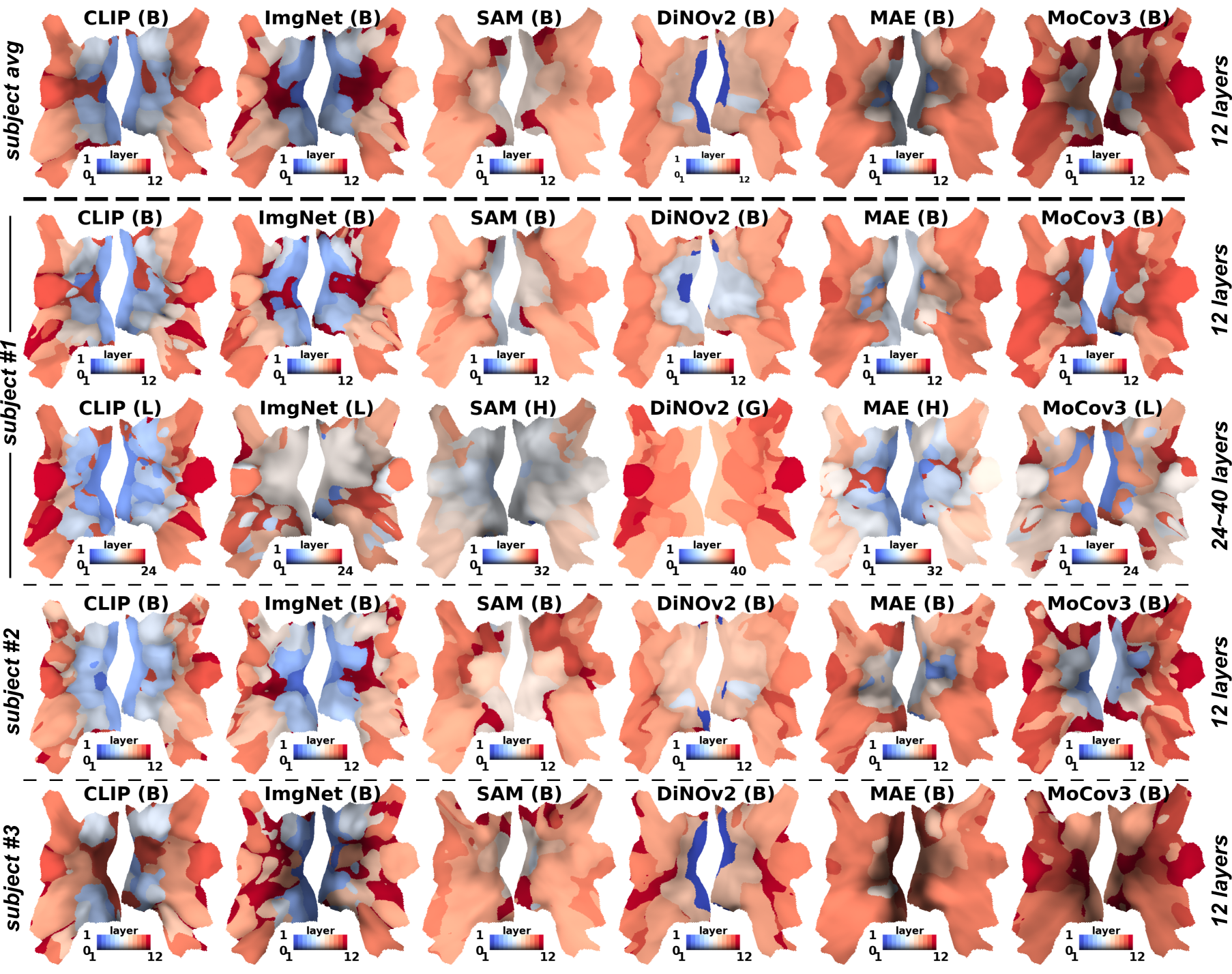
Figure 2: Layer Selectors indicating alignment of different model layers with various brain regions.
Brain Score Predictions
The research found that networks with high prediction scores for specific brain regions translate to improved performance in related tasks. CLIP, DiNOv2, and Stable Diffusion demonstrate high scores in predicting semantic regions, with varying competencies across different brain regions and visual processing tasks.

Figure 3: Brain Score analysis highlights the prediction accuracy of various models in different brain regions.
Discussion
Implications and Future Directions
The implications of this research are manifold, notably in how its tool facilitates the visualization of networks against known brain functionalities to predict downstream task performance. As the need for high-quality data persists, future work may explore extending factorized mapping to even more diverse network designs, paving the way for enhanced model development in AI.
(Motivations for aligning network features with brain functionality drive the pursuit of models capable of efficient computation and adaptability similar to biological systems.)
Conclusion
Overall, "Brain Decodes Deep Nets" offers a novel perspective on the internal mechanisms of neural networks by leveraging brain mapping techniques. FactorTopy transforms understanding of deep learning models and provides a robust framework for optimizing models to align with brain structure more accurately and effectively, marking a significant advancement in the intersection of neuroscience and AI research.




