- The paper presents AdaptiveNet, a novel framework that dynamically adapts deep learning models post-deployment to optimize performance in heterogeneous, resource-constrained edge environments.
- It utilizes on-cloud elastification to convert a pre-trained model into a versatile supernet and employs on-device, latency-guided search to select optimal subnets.
- Experimental results demonstrate significant accuracy improvements and efficient adaptation, achieving superior accuracy-latency trade-offs with minimal GPU hours and rapid on-device optimization.
AdaptiveNet: Post-deployment Neural Architecture Adaptation for Diverse Edge Environments
Introduction
The paper "AdaptiveNet: Post-deployment Neural Architecture Adaptation for Diverse Edge Environments" addresses the critical challenge of deploying deep learning models across heterogeneous edge devices. The diversity of edge environments, characterized by varying computational resources and data distributions, complicates the task of generating a single model that performs optimally across all scenarios. Traditional pre-deployment techniques, often reliant on centralized cloud processing for model generation, struggle to efficiently cope with this diversity.
AdaptiveNet proposes a novel solution by shifting the adaptation task to post-deployment, allowing the model to adapt dynamically to its specific edge environment. This approach not only enhances accuracy and resource utilization but also protects user privacy by eliminating the need for extensive edge data collection and processing in the cloud.
Methodology
AdaptiveNet combines on-cloud model elastification with on-device architecture search to handle the diversity and dynamic nature of edge environments effectively.
On-Cloud Elastification
The elastification process transforms a given pre-trained model into a "supernet," capable of adapting to varying environments through the selection of optimal subnet architectures. This involves:
- Granularity-aware Graph Expansion: The process starts by identifying basic blocks in the model's computational graph, determining replaceable paths, and expanding the model into a supernet with multiple paths. This expansion includes merging blocks for efficiency and creating varied structures that suit different computational budgets.
- Distillation-based Supernet Training: Incorporates a two-phase training strategy—branch-wise distillation followed by whole-model tuning. This method leverages knowledge from the original pre-trained model to ensure the quality of subnets generated from the supernet.
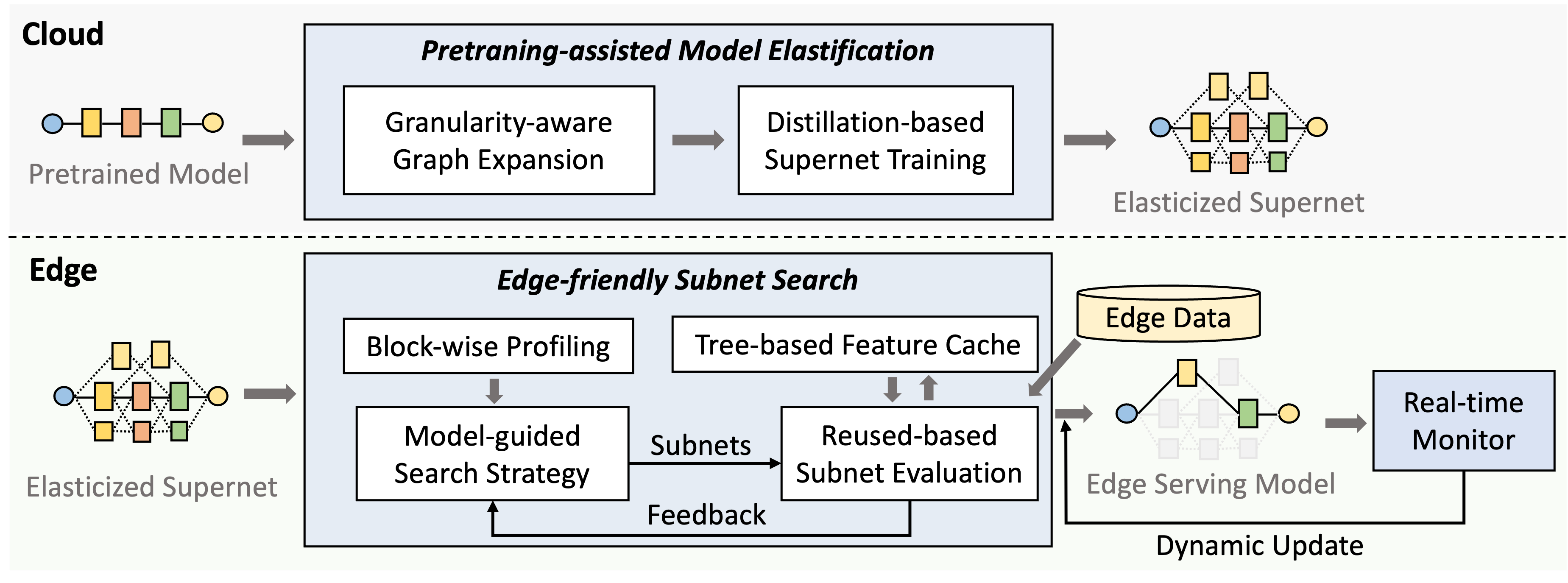
Figure 1: The architecture overview of AdaptiveNet.
On-Device Adaptation
Once deployed, the supernet undergoes edge-specific optimization to select the most appropriate subnet using efficient search strategies and model evaluation techniques:
Experimental Evaluation
Experimental results demonstrate that AdaptiveNet achieves superior accuracy-latency trade-offs across diverse tasks and devices:
Implications and Future Work
AdaptiveNet offers a paradigm shift in deploying neural networks to edge devices by facilitating real-time, privacy-preserving model adaptation. The approach holds significant promise for enhancing AI deployment in dynamic and resource-constrained environments. Future research may explore further reducing on-device adaptation latency and extending this framework to other modalities and applications beyond computer vision.
Conclusion
AdaptiveNet effectively addresses the limitations of pre-deployment model generation by leveraging post-deployment adaptation to improve accuracy and resource efficiency across heterogeneous and dynamic edge environments. The method’s integration of intelligent hardware-aware adaptation paves the way for broader adoption of AI applications in privacy-sensitive and resource-constrained edge scenarios.


