- The paper presents an adaptive pseudo labeling method where the teacher model updates based on student feedback, enhancing label accuracy.
- The experimental results on ImageNet and JFT-300M demonstrate a state-of-the-art top-1 accuracy of 90.2%, highlighting significant performance gains.
- The approach reduces reliance on large labeled datasets, offering practical benefits in resource-constrained environments and paving the way for more adaptive learning systems.
The paper "Meta Pseudo Labels" proposes a novel approach to semi-supervised learning by introducing an adaptive method for generating pseudo labels, termed Meta Pseudo Labels (MPL). Here, we explore the methodology, experimental outcomes, and implications of this approach, providing insights into its novelty and efficacy within the landscape of machine learning, particularly in image classification tasks.
Methodology
Core Concept
Meta Pseudo Labels builds upon the concept of Pseudo Labels by introducing a dynamic interaction between a teacher and student network paradigm. Traditionally, in pseudo labeling, the teacher model provides pseudo labels to unlabeled data, which the student model then uses for training. However, the teacher model in prior approaches remains static after initial training, potentially propagating errors due to inaccurate pseudo labeling.
Innovation in MPL
The innovation in MPL lies in adapting the teacher model continually based on feedback from the student model's performance on a labeled dataset. This dynamic adjustment is facilitated by using the student's performance as a feedback signal or reward, which informs the teacher model's updates. This approach is aimed at mitigating confirmation bias, which is prevalent in static teacher models when their pseudo labels are inaccurate (2003.10580).
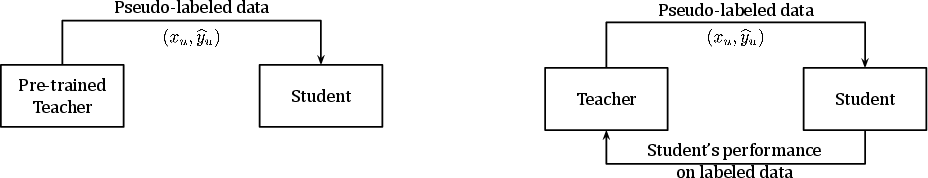
Figure 1: An overview of the Meta Pseudo Labels process, contrasting it with traditional Pseudo Labels.
Experimental Results
ImageNet and Beyond
MPL demonstrates significant performance improvements across multiple datasets, including ImageNet, where it achieves a state-of-the-art top-1 accuracy of 90.2%, a notable 1.6% increment over previous benchmarks (2003.10580). By employing datasets like ImageNet and JFT-300M, MPL leverages large-scale unlabeled data, showcasing its robustness and scalability.

Figure 2: Breakdown of performance gains showing significant improvement of Meta Pseudo Labels over Unsupervised Data Augmentation (UDA).
Ablation Studies
The paper conducts thorough ablation studies to dissect the contributions of various components within MPL. These studies highlight the substantial boosts provided by components like adaptive teacher modeling and illustrate how each contributes to the overarching efficacy of the approach (2003.10580).

Figure 3: Iterative training results showcasing that Meta Pseudo Labels outperform traditional Pseudo Labels in all iterations.
Implications and Future Directions
Theoretical Implications
The introduction of feedback in the pseudo labeling process is a pivotal shift, potentially influencing future research in semi-supervised learning paradigms. This technique not only enhances label accuracy but also integrates reinforcement learning concepts by utilizing feedback loops.
Practical Implications
From a practical standpoint, MPL can significantly reduce the dependency on large labeled datasets, thus diminishing resource requirements in training robust models. This facet is particularly beneficial in domains where acquiring labeled data is cost-prohibitive or logistically challenging.
Future Prospects
Moving forward, MPL could be explored in conjunction with other self-supervised or unsupervised learning techniques to further reduce the reliance on labeled datasets. Additionally, adapting this mechanism to different architectures beyond convolutional neural networks, such as transformers, could broaden its applicability and enhance its utility across various AI domains.
Conclusion
The Meta Pseudo Labels approach offers a novel and effective solution to challenges in semi-supervised learning, setting a new benchmark in image classification tasks. By employing a dynamic teacher-student feedback mechanism, MPL not only enhances accuracy but also paves the way for more adaptive learning models. As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, methodologies like MPL, which effectively harness both labeled and unlabeled data, will be pivotal in driving advancements across various domains.




