- The paper presents ContextFocus, which improves context-faithfulness by injecting a steering vector into transformer layers during inference.
- It utilizes a novel activation steering mechanism with joint contrastive signals, achieving over 35-point gains in context-adherence on QA benchmarks.
- The approach is deployable in real-time RAG pipelines without retraining, balancing efficiency with robust evidence alignment in diverse LLMs.
Activation Steering for Contextual Faithfulness in LLMs
Motivation and Problem Statement
The proliferation of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) architectures has shifted the functional dependence of LLMs from parametric memory to external evidence, particularly in applications where up-to-date facts and contextual precision are crucial. However, contemporary LLMs frequently default to memorized, pre-trained knowledge, ignoring retrieved context when contradictions arise, leading to context-unfaithful outputs. This undermines deployment reliability for tasks such as fact-grounded QA, summarization, and real-time decision-making. The paper "ContextFocus: Activation Steering for Contextual Faithfulness in LLMs" (2601.04131) addresses this deficiency by proposing a paradigm that leverages activation-level interventions, circumventing the limitations of model finetuning and decoding-intensive strategies.

Figure 1: ContextFocus steers generation toward context-consistent outputs when parametric memory conflicts with retrieved facts, illustrated by updating the CEO of Starbucks.
Methodology
Activation Steering Mechanism
ContextFocus utilizes activation steering, a technique whereby a steering vector—computing as the mean difference between last-token activations for context-grounded versus ungrounded prompts—is injected into the residual stream at a selected transformer layer during inference. The steering vector is constructed using the NQ-SWAP dataset, whose question-context pairs systematically induce knowledge conflicts. For robust estimation, steering directions are averaged across diverse system instructions and question phrasings.
Mathematically, let xi(l) be the residual activation at layer l and position i, and v(l) the steering vector. The model applies
xi(l):=xi(l)+m⋅v(l)
for all generation tokens i>N, with m controlling intervention strength. ContextFocus identifies the optimal layer l∗ via layerwise evaluation, maximizing context-faithful metric ps on held-out queries.
Prompting and Complementary Modes
The method is prompt-agnostic but compositional: it integrates seamlessly with engineered prompting strategies targeting context faithfulness (e.g., O{content}I). ContextFocus achieves single-pass generation without auxiliary decoding passes or parameter updates, yielding competitive inference-time efficiency.
Experimental Results
Knowledge-Conflict Benchmarks and Metrics
Evaluation leverages the ConFiQA benchmark, partitioned into QA (single-hop), MR (multi-hop), and MC (multi-hop multi-counterfactual) subsets. The key metrics are:
- ps: proportion of outputs aligned to the substituted answer (context-faithful)
- po: proportion aligned to the original (parametric knowledge)
- MR=po/(po+ps): knowledge-flight reluctance ratio
ContextFocus is tested on Llama-3.1-8B/70B-Instruct and Mistral-7B-Instruct, with steering typically at layer 13, 32, or 11, and m=2.
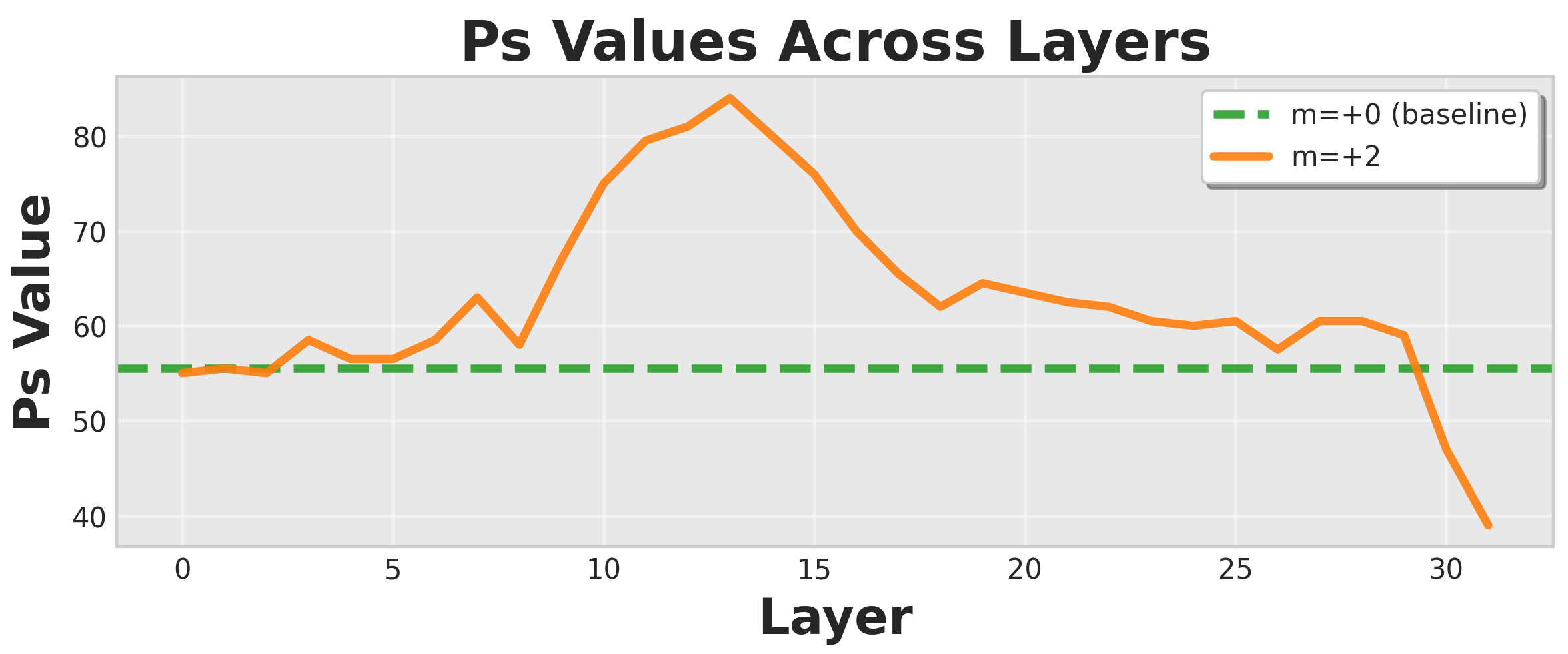
Figure 2: Layerwise steering vector evaluation for Llama-3.1-8B, identifying optimal context-adherence at layer 13.

Figure 3: Layer selection rule targeting maximal deviation in context-focus accuracy, illustrated via open-ended NQ-SWAP samples.
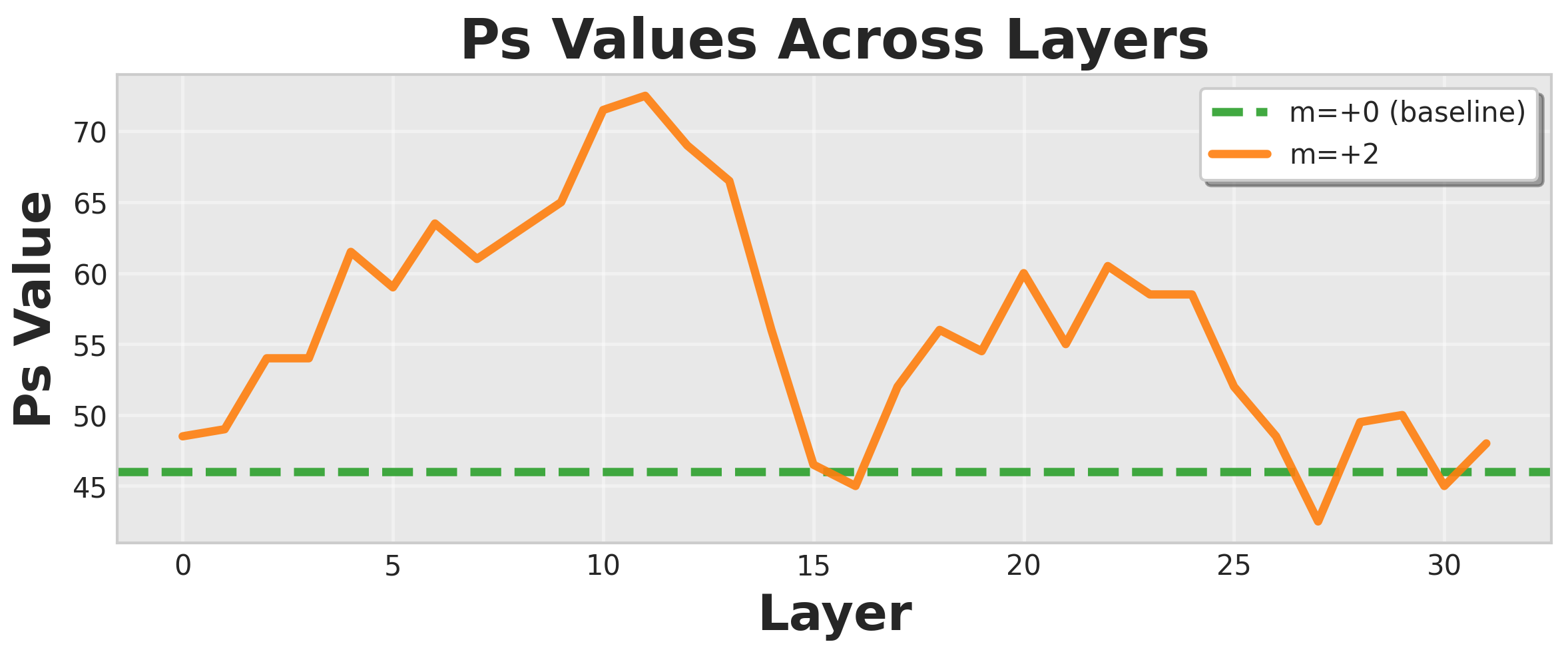
Figure 4: Layerwise steering analysis for Mistral-7B-Instructv0.3, showing strongest effect at layer 11.
Quantitative Outcomes
ContextFocus demonstrates strong gains in context adherence: for Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct on QA without specialized prompting, ps increases by >35 points over baseline (from 35.27% to 70.87%), po drops from 32.33% to 9.27%, and MR falls from 47.83% to 11.56%. ContextFocus performs comparably to or better than finetuned ContextDPO, decoding-intensive COIECD, and engineered prompting, consistently across model scales and benchmark settings. Fluency is retained at m=2; higher multipliers induce degradation, confirmed via the local loop rate metric.
ContextFocus is highly data-efficient: steering vectors saturate after 1.5k examples, achieving cosine similarity >0.9998 with larger sample estimates. Vector construction incurs sub-hour overhead on typical A100 hardware, substantially lower than multi-hour finetuning.
Ablation and Design Analysis
Disentangling vector sources reveals that joint contrastive vectors (system instruction + context) substantially outperform context-only or instruction-only alternatives, indicating synergistic signal:
| Vector Type |
ps↑ |
po↓ |
MR↓ |
| Unsteered |
55.5 |
22.8 |
29.12 |
| Context-only |
67.0 |
11.4 |
14.53 |
| Instruction-only |
64.0 |
18.1 |
21.98 |
| Joint (ContextFocus) |
75.4 |
8.0 |
9.59 |
ContextFocus outperforms options-based contrastive activation addition (CAA) using multiple-choice grounding.
Practical Implications and Theoretical Significance
ContextFocus is immediately deployable in RAG pipelines and applications demanding real-time fidelity to external evidence—no model retraining or complex multi-pass decoding required. The approach is scalable: demonstrated on Llama-3.1-70B with similar gains. Its compatibility with existing prompting and zero-shot inference protocols renders it highly practical for production models and rapid response to knowledge drift.
Theoretically, the success of activation steering corroborates the linear representation hypothesis for behavior controllability in LLM hidden state spaces. The finding that joint context-instruction signals are crucial for robust direction induction has implications for steering methods targeting other desiderata (safety, bias mitigation, instruction adherence).
Limitations and Future Directions
The framework is tailored to controlled QA and knowledge-conflict diagnostics; its efficacy for abstractive long-form generation and subtle faithfulness errors remains to be validated. Fixed global steering strength may be suboptimal for heterogeneous inputs; adaptive or input-tuned interventions are an open direction. Extending activation-level control to broader contextual or stylistic fidelity, and theoretical modeling of steerability thresholds relative to model depth and embedding geometry, are promising avenues.
Conclusion
ContextFocus represents a rigorous, efficient solution to the context-faithfulness failure mode endemic in modern LLMs, leveraging activation steering over vectorized contrastive signals. It yields competitive or superior adherence to external evidence compared to prior finetuning, decoding, or prompting strategies, with minimal computational overhead, data requirement, and inference latency. The method’s compositionality and prompt-agnostic deployment render it highly impactful for practical retrieval-augmented applications and motivate further exploration of activation-level interventions for robust AI alignment.







