- The paper introduces a novel DML framework that integrates derivative data with Monte Carlo estimates to drastically reduce MSE and improve computational efficiency.
- It transforms the integration problem into a regression task, enabling precise approximations of parametric mappings through blended value and gradient information.
- Extensive experiments demonstrate DML's superior performance and scalability in statistical functionals, Chebyshev expansions, and differential equation integrals.
Parametric Numerical Integration with (Differential) Machine Learning
Introduction
This paper presents a novel machine learning methodology for solving parametric integrals, enhancing classical approaches by integrating derivative information into the learning process. The study focuses on three core problem classes: statistical functionals, Chebyshev expansions for function approximation, and integrals associated with differential equations. The use of differential machine learning (DML) is a key innovation, significantly outperforming standard architectures in terms of mean squared error (MSE), scalability, and sample efficiency.
Methodological Framework
The paper introduces DML as a robust extension of traditional artificial neural networks (ANNs), leveraging single-realization Monte Carlo (MC) estimates combined with derivative data. This integration allows ANNs to approximate parametric mappings effectively, transforming the integration problem into a regression task. By training models on unbiased MC data with parameter-based gradients, DML inherits mathematical smoothness, reducing variance and enhancing generalization.
The authors propose a model where a loss function combines value-based and differential information, ensuring that models are both unbiased and efficient in variance reduction. The inclusion of derivative-based data significantly accelerates convergence compared to conventional ANNs.
Numerical Experiments
The study conducts extensive numerical experiments to validate the DML framework. These experiments encompass:
- Parametric Statistics: The paper demonstrates superior performance of DML models in approximating parametric moments and cumulative distribution functions (CDFs) across lognormal and chi-squared distributions. Figures highlight DML's precision even in regions of steep gradients or parameter boundaries.


Figure 1: Predictions vs.\ analytical moments for ANN (left) and DML (right) for X∼LogNormal(0,1) and m∈[−1,1].
- Chebyshev Coefficients: The experiments further evaluate DML's ability to estimate Chebyshev coefficients for both smooth and non-smooth functions, confirming enhanced accuracy and efficiency. The results underscore DML's capability to handle high-dimensional parameter domains effectively.
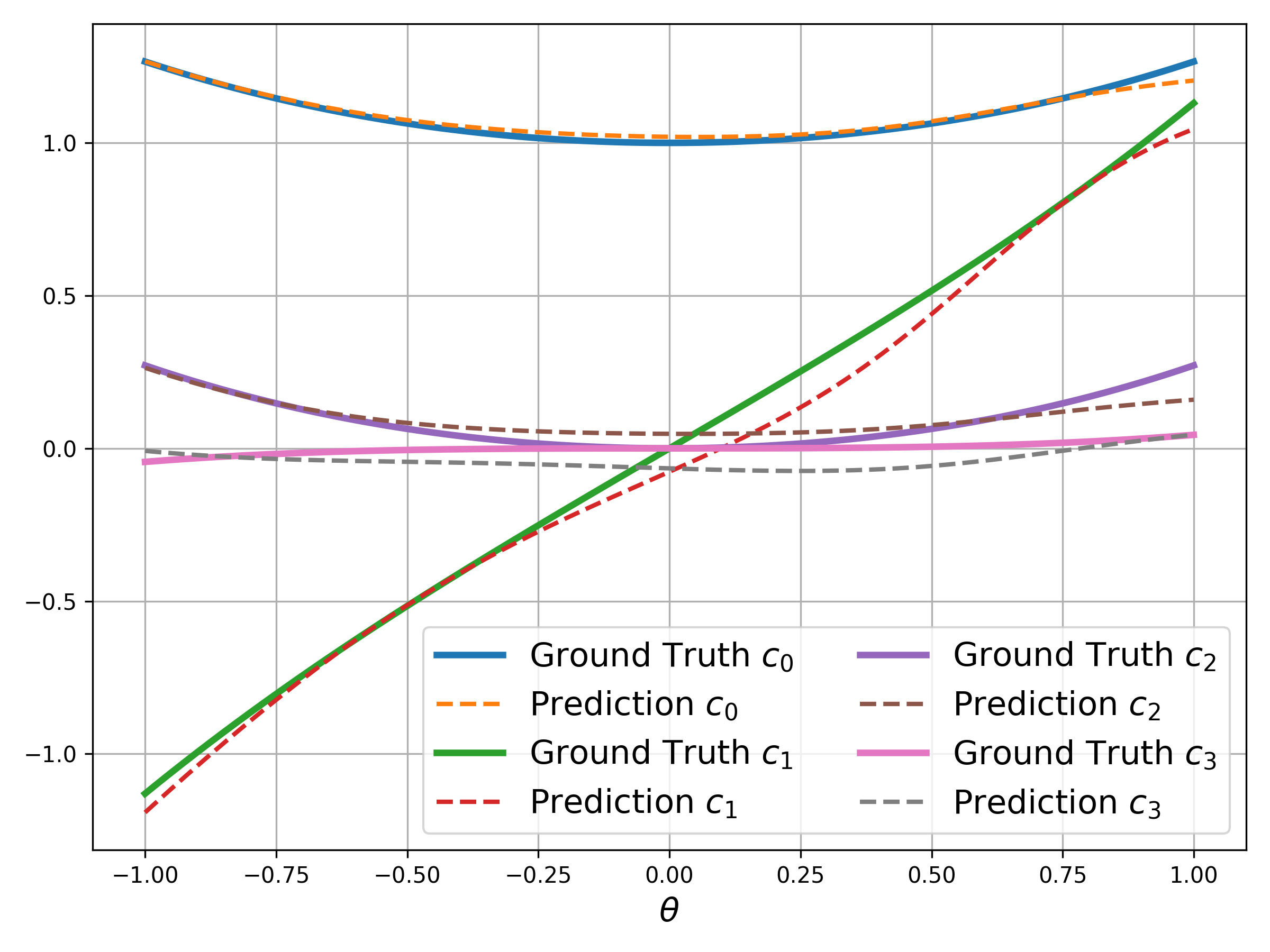
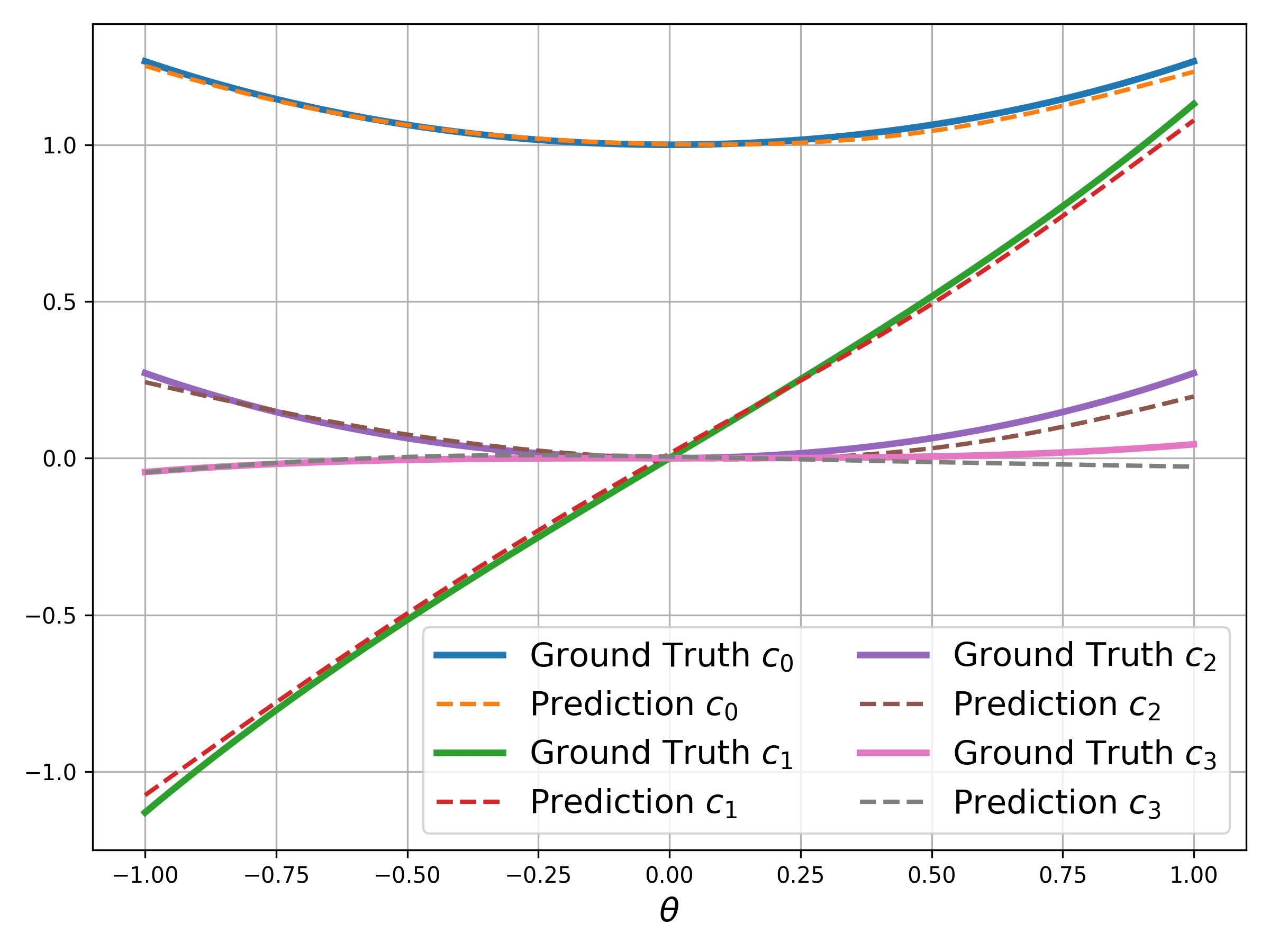
Figure 2: Predictions vs.\ analytical Chebyshev coefficients for ANN (left) and DML (right) for the exponential function with θ∈[−1,1] and L=15.
- Differential Equation Integrals: The final set of experiments addresses integrals arising from ODEs and PIDEs, such as those modeling nonlinear pendulums and stochastic processes with jumps. DML consistently yields high accuracy and reduced sample requirements, with scalability apparent as parameter dimensionality increases.
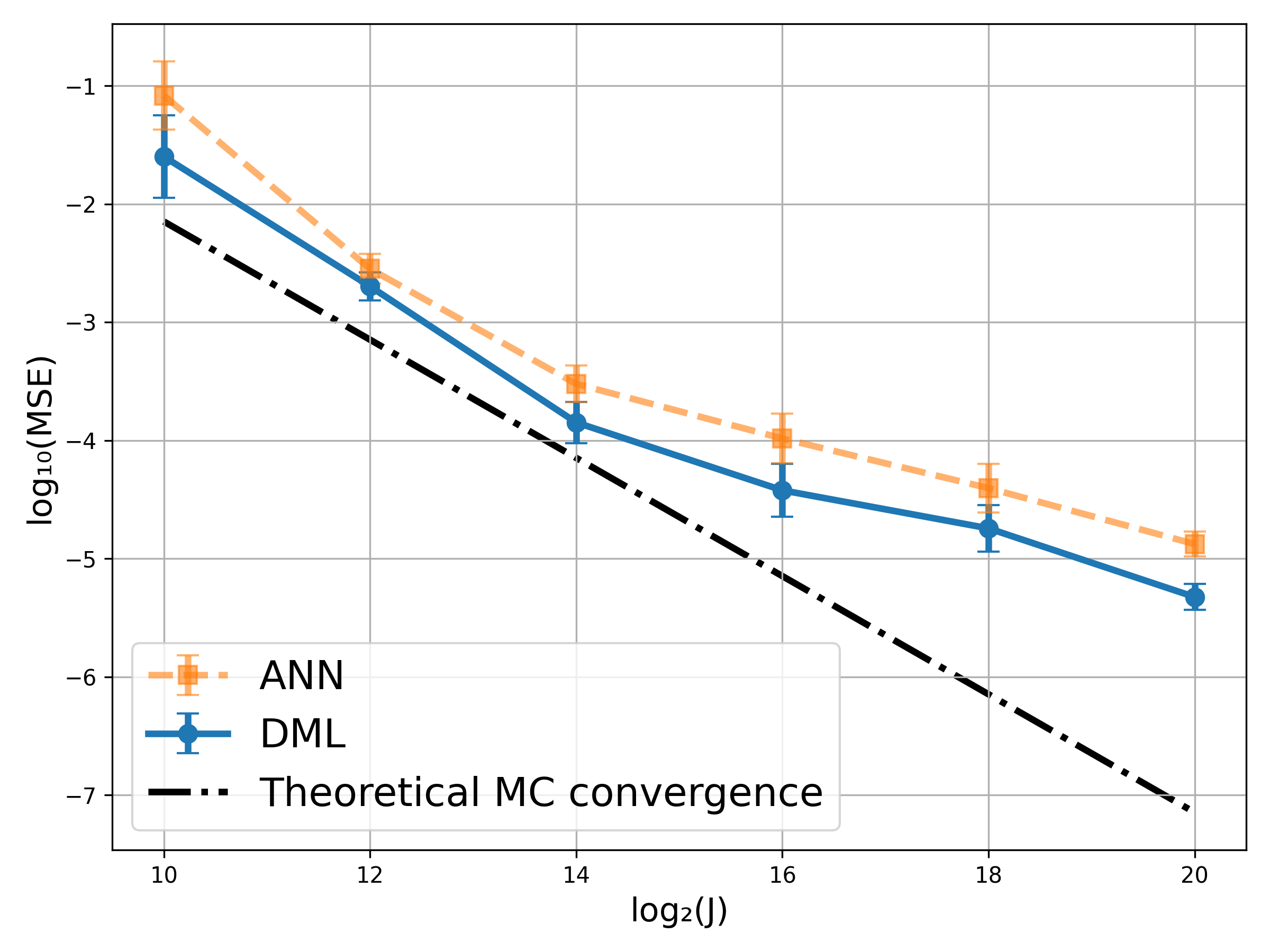
Figure 3: MSE vs.\ training set size for the Legendre elliptic integral with b∈[0.01,π/2] and θ∈[0,0.99].
Implications and Future Directions
The DML approach presented in the paper offers substantial improvements over conventional methods, particularly in handling complex, high-dimensional parametric integrals. By efficiently integrating derivative data, DML models promise enhanced accuracy and computational efficiency. This technique has broad applicability across scientific computing, financial modeling, and uncertainty quantification.
Future research could explore the application of DML in other complex integrals and multidimensional parameter spaces. Additionally, investigating the integration of DML with more advanced architectures could further improve efficiency and accuracy.
Conclusion
The paper establishes DML as an effective, scalable approach for parametric numerical integration. By bridging Monte Carlo simulations with advanced neural network training protocols, the framework adeptly addresses the challenges of high-dimensional integration tasks, offering significant advancements in numerical methods. The findings set a compelling precedent for integrating derivative information into machine learning models, heralding a new era of precision in computational analysis.
Figures prominently throughout the study provide clear visual validation of the results, emphasizing DML's strengths in various applications. This work sets the stage for more sophisticated approaches to numerical integration, opening pathways to enhanced computational techniques and broader scientific insights.






