- The paper introduces InterSnap, which couples cryptographically signed cross-chain transaction receipts with need-based snapshot scheduling to ensure non-repudiation.
- It employs distributed peer selection, AES encryption, and IPFS decentralized storage to securely archive transaction data and facilitate dispute resolution.
- Performance evaluations show sub-second encryption and upload times with consistent snapshot throughput even under high ledger load in hybrid network settings.
Auditable Ledger Snapshot for Non-Repudiable Cross-Blockchain Communication
Motivation and Context
Blockchain interoperability underpins decentralized ecosystems, yet cross-chain transactions outside a single ledger remain fundamentally non-repudiable only within that ledger’s boundaries. Permissioned blockchains exacerbate this challenge by imposing asymmetric data access and restricted consensus verification across networks. Malicious behaviors—such as collusion, repudiation of legitimate claims post-failure, or asset transfer fraud—surface when external networks exploit these gaps. Existing solutions, including SATP, BUNGEE, and Fabric Snapshots, lack mechanisms for inter-chain transaction provenance, non-repudiable receipt archival, and verifiable snapshot sharing. The paper presents InterSnap: an architecture coupling cross-chain receipts and distributed snapshot transfer to enable auditability and enforce accountability in permissioned blockchain interoperability.
Architecture and Functional Components
InterSnap incorporates six principal pillars: cross-chain transaction receipts, need-based snapshot scheduling, distributed peer selection for snapshot generation, archive encryption, snapshot storage in decentralized systems (IPFS), and interoperable auditability.
Cross-Chain Transaction Receipts
For each cross-network transfer, InterSnap aggregates transaction endorsements by the sender network and mandates signed receipts from the receiver network, forming a cryptographically irrefutable bilateral transaction set. This protocol guarantees atomicity and non-repudiation of asset transfer agreements and effectively precludes fraudulent denial or double spending. Each completed transaction set is included in a ledger snapshot for subsequent verification and audit.
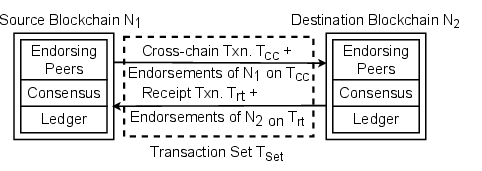
Figure 1: Cross-chain transaction receipts illustrating bilateral cryptographic endorsement for every cross-network transaction, serving as irrefutable proof against repudiation.
Workflow for Inter-Network Snapshot Archive Transfer
InterSnap employs a need-based snapshot scheduler, dynamically triggering archival upon significant ledger state changes (parameterized via block creation rate and interval threshold). The snapshot-generating peer is chosen based on maximum ledger height, addressing consistency and recency concerns while maximizing historical data integrity. Each snapshot, comprising ledger states and cross-chain receipts, is AES-encrypted for confidentiality and robust key management.

Figure 2: Workflow for secure cross-network snapshot archive transfer, leveraging decentralized storage and cryptographic guarantees.
Encrypted archives are uploaded to private IPFS, which provides efficient decentralized storage and retrieval through content-addressed references (CID). These CIDs and encryption keys are disseminated via interoperability chains or gateways (Hyperledger Cacti), enabling external auditors or foreign networks to verify transaction history, thus facilitating dispute resolution.
Need-Based Snapshot Archival
InterSnap optimizes both snapshot latency and archival size via a dynamic scheduling algorithm. Snapshots are archived when the block height increment exceeds a defined threshold, circumventing issues of periodic overwriting and loss of recency inherent to legacy systems.

Figure 3: Need-based snapshot archival process ensuring timely preservation of ledger state changes and maximizing audit readiness.
Inter-Network Communication Layer
InterSnap integrates relays, drivers, smart contracts, and identity interoperability protocols to effectuate secure, authenticated cross-network communication and data transfer. The design leverages dynamic service discovery protocols, identity exchange agents, and cryptographic proof exchange for automated and decentralized verification.
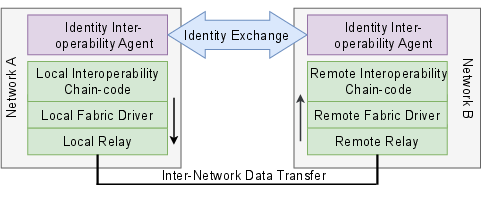
Figure 4: Layered inter-network communication diagram detailing the modular, interoperable architecture for distributed snapshot and transaction exchange using IPFS and Hyperledger Cacti.
Audit Model and Dispute Resolution
Snapshots are periodically transferred to independent auditors—a blockchain network comprised of trusted entities. Auditors can cryptographically verify historical contracts, resolve disputes, and maintain archived proofs irrespective of catastrophic failures or adversarial behavior in participating networks. The architectural model presumes honest participation but anticipates future enhancement via decentralized audit coordination.
Experimental Evaluation
A comprehensive evaluation was conducted on a hybrid testbed spanning on-premise, AWS, and private cloud instances interconnected via Docker Swarm. Performance metrics included archive encryption time, IPFS upload latency, snapshot throughput, peer bootstrap time, and cross-network archive transfer time under varying ledger heights and transaction payloads.
Strong numerical results include:
- Archive encryption and IPFS upload times remain sub-second for archives up to 12,000 transactions (Figures on latency and throughput).
- Snapshot throughput sustains above 100 snapshots per minute across ledger heights up to 20,000 (See respective histogram).
- Interoperable snapshot transfer times remain consistent (<2s increase beyond ledger height 15K), with total exchange time only marginally higher than encryption/upload phases.
- Recovery using IPFS-based snapshots incurs only negligible additional bootstrap latency (≈1s) compared to local restoration.
- Distributed resource consumption (CPU/memory) remains stable under sustained load (Figure 5).

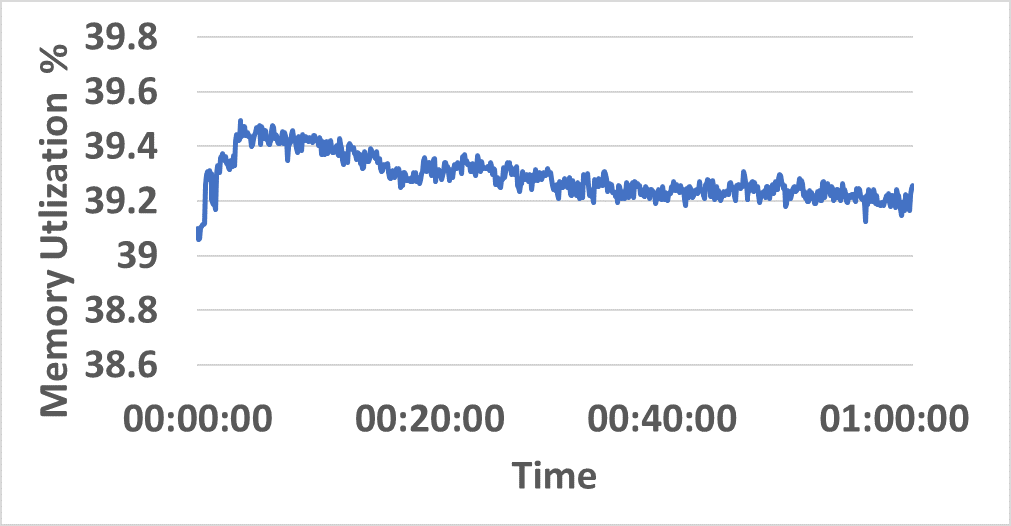
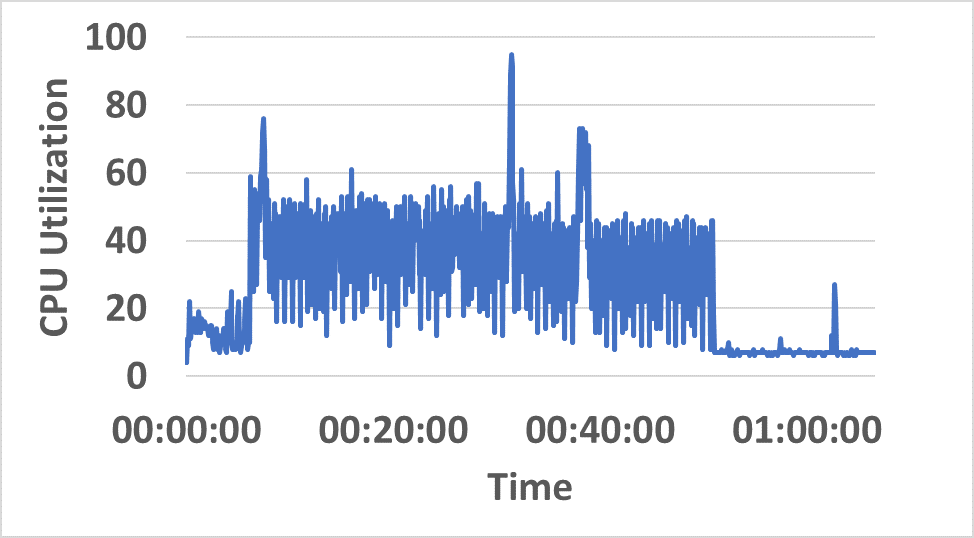
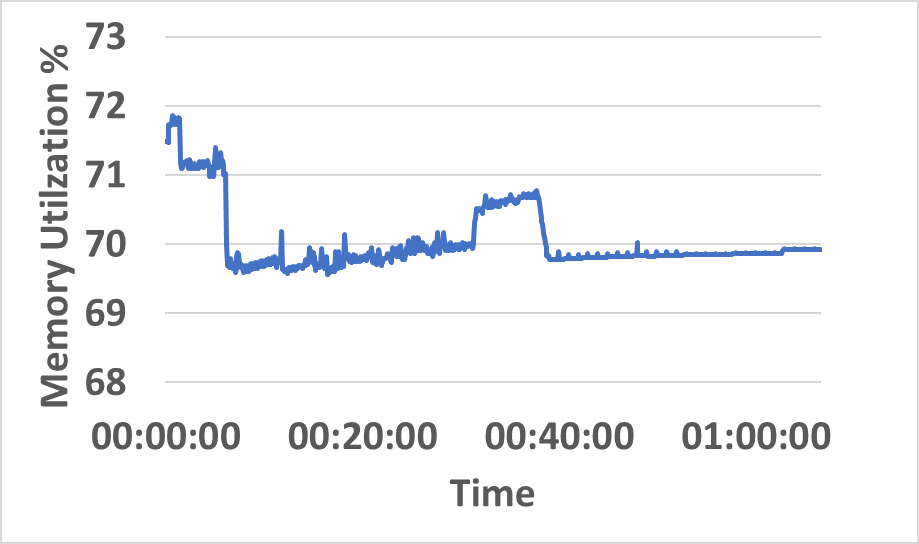
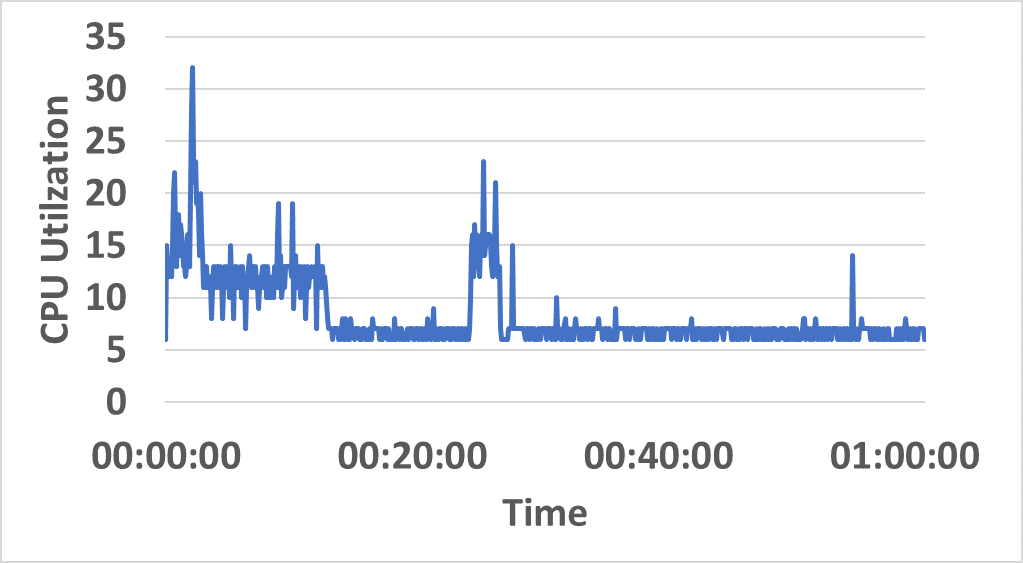
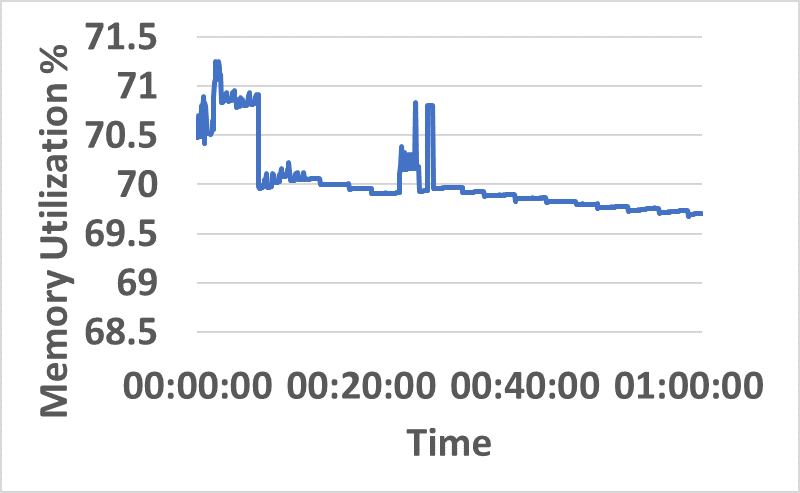
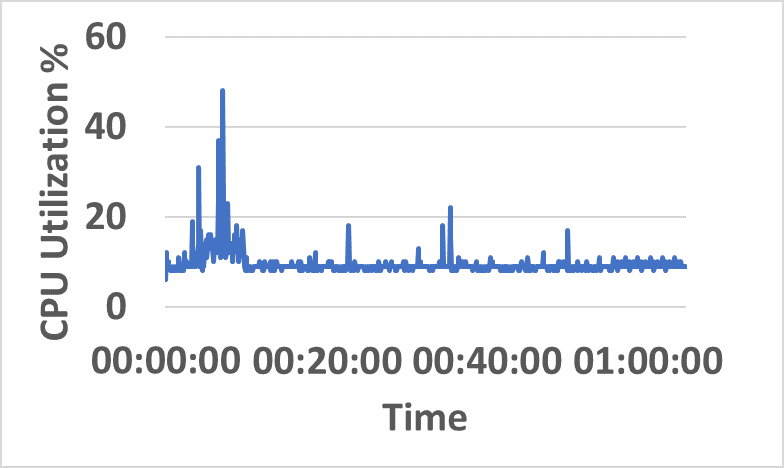
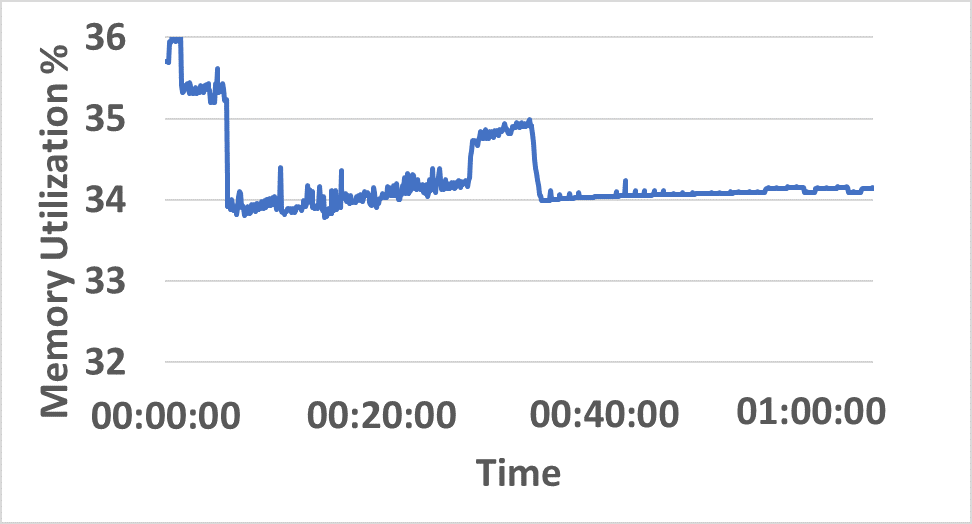

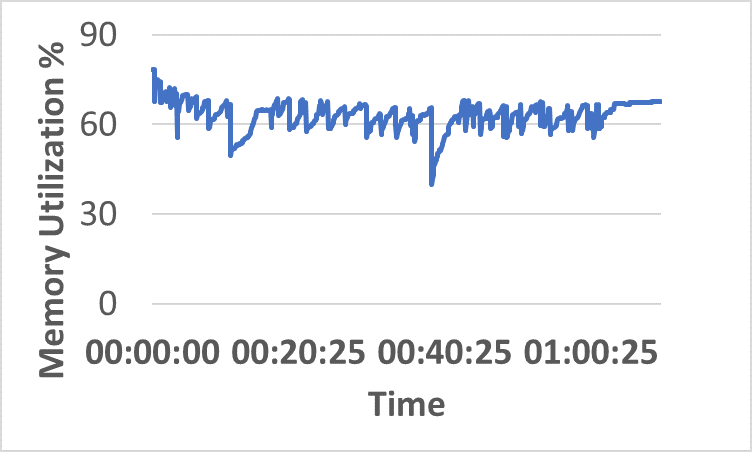
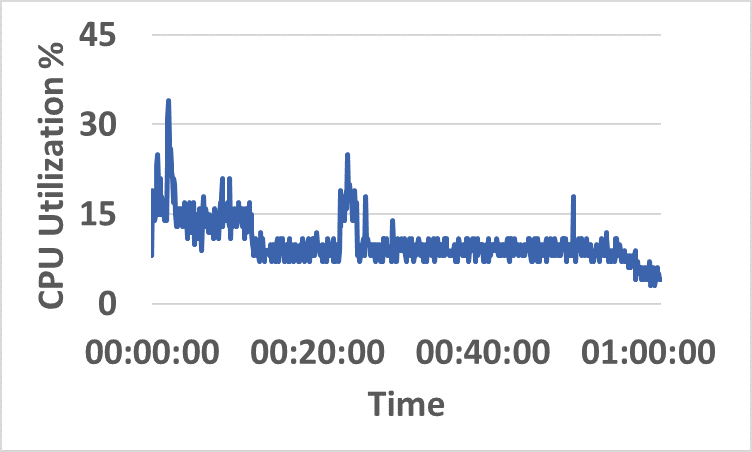
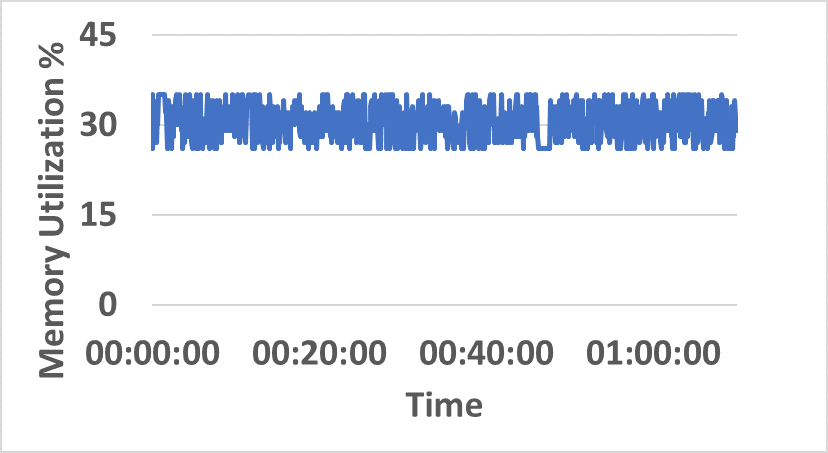

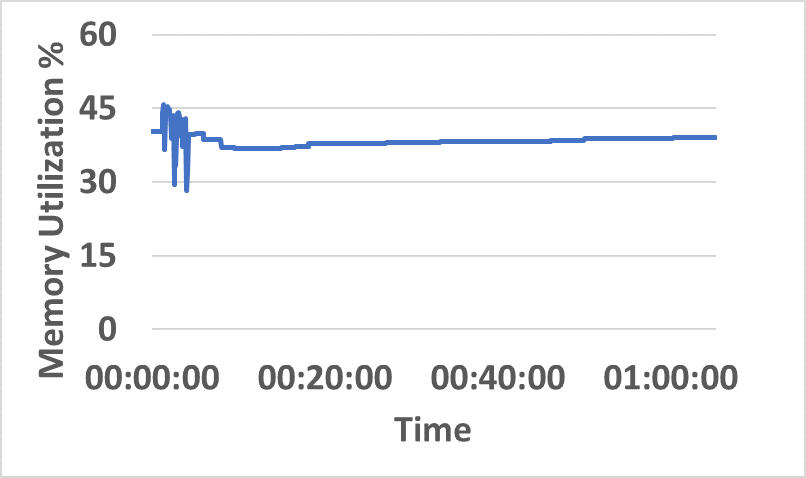
Figure 5: CPU and memory utilization traces across hybrid network resources during sustained InterSnap operation.
Comparison with Existing Techniques
InterSnap introduces distributed peer selection, periodic and need-based scheduling, irrevocable cross-chain receipt archival, and decentralized snapshot sharing. In contrast, reviewed frameworks (e.g., BUNGEE, SATP) lack receipt transactions and comprehensive dispute resolution via external audit, thus remain vulnerable to inter-chain fraud and data loss scenarios.
Security Analysis
InterSnap defends against network-level collusion, repudiation, ledger data loss, and fraudulent asset transfer. Combination of cryptographic endorsements/receipts ensures transaction atomicity and non-repudiation; encrypted archives and private IPFS networks secure confidentiality and integrity. The key management protocol and majority endorsement thresholds uphold authenticity and resilience against Byzantine nodes. Safety and liveness guarantees are formalized: atomic transaction sets, time-bounded completion, persistent decentralized storage, and fault-tolerant recovery pathways collectively maintain operational viability and auditability.
Practical and Theoretical Implications
InterSnap's audit-oriented snapshot methodology decisively advances the state-of-the-art in permissioned blockchain interoperability:
- Ensures post-failure accountability and non-repudiation, crucial for complex multi-consortium environments (finance, supply chain, compliance).
- Enables automated, transparent dispute resolution via independent auditors.
- Lays foundation for modular extension to other protocols (Cosmos IBC, Chainlink CCIP, Polkadot XCMP) by abstracting endorsement and receipt mechanics.
- Introduces need-based snapshot scheduling for efficient archival and minimal overhead.
- Empirical results indicate scalability and negligible performance degradation under increasing network load.
Future Research Directions
Further work is indicated in decentralized auditing—inter-network protocols for transparent and coordinated snapshot verification. Incremental and selective snapshotting mechanisms could improve scalability on high-throughput blockchains. Integration with zero-knowledge proof systems and differential privacy could augment confidentiality guarantees for sensitive inter-chain contracts. Cross-protocol compatibility and standardization of inter-chain receipt mechanics remain open fields as global enterprise adoption widens.
Conclusion
InterSnap provides a comprehensive, auditable framework for non-repudiable cross-blockchain communication within permissioned environments. Its synthesis of receipt-based transaction sets, distributed snapshot archival, and decentralized dispute resolution marks a transition to reliable, scalable, and accountable inter-chain interaction—crucial to the practical realization of blockchain interoperability and automated governance.



















