- The paper presents a unified diffusion-based framework that integrates VLM-driven agents to achieve personalized and semantic image retouching.
- It introduces semantic replacement and parameter perturbation techniques to deliver precise, region-level control and improved aesthetic consistency.
- Experimental results show superior qualitative and quantitative performance compared to traditional methods, validating its practical efficacy.
PerTouch: VLM-Driven Agent for Personalized and Semantic Image Retouching
Introduction
The paper "PerTouch: VLM-Driven Agent for Personalized and Semantic Image Retouching" introduces an innovative framework aimed at overcoming the limitations inherent in traditional image retouching approaches. As photography becomes increasingly democratized, the demand for tools that enhance photo quality while respecting personal aesthetic preferences has grown significantly. Conventional tools such as Adobe Lightroom or Photoshop require substantial expertise, making professional-grade retouching inaccessible to average users. Deep learning techniques, while promising, often lack the capacity for subjectivity modeling, region-level control, and personalization in user interactions.
PerTouch proposes a unified framework relying on diffusion-based models to deliver semantic-aware, personalized image retouching. By leveraging vision LLM-driven agents (VLMs), PerTouch balances the intricacies of image aesthetic enhancement with user-specific intent. This introduces a novel approach to image retouching, emphasizing the balance between global visual consistency and fine-grained region-level editing.
Methodology
The PerTouch framework operates by integrating several key innovations:
Diffusion-Based Retouching: Diffusion models, specifically Stable Diffusion, are used as the backbone to address the need for high-quality, aesthetic image generation. These models are complemented by ControlNet to enable fine-grained region-level control (Figure 1).
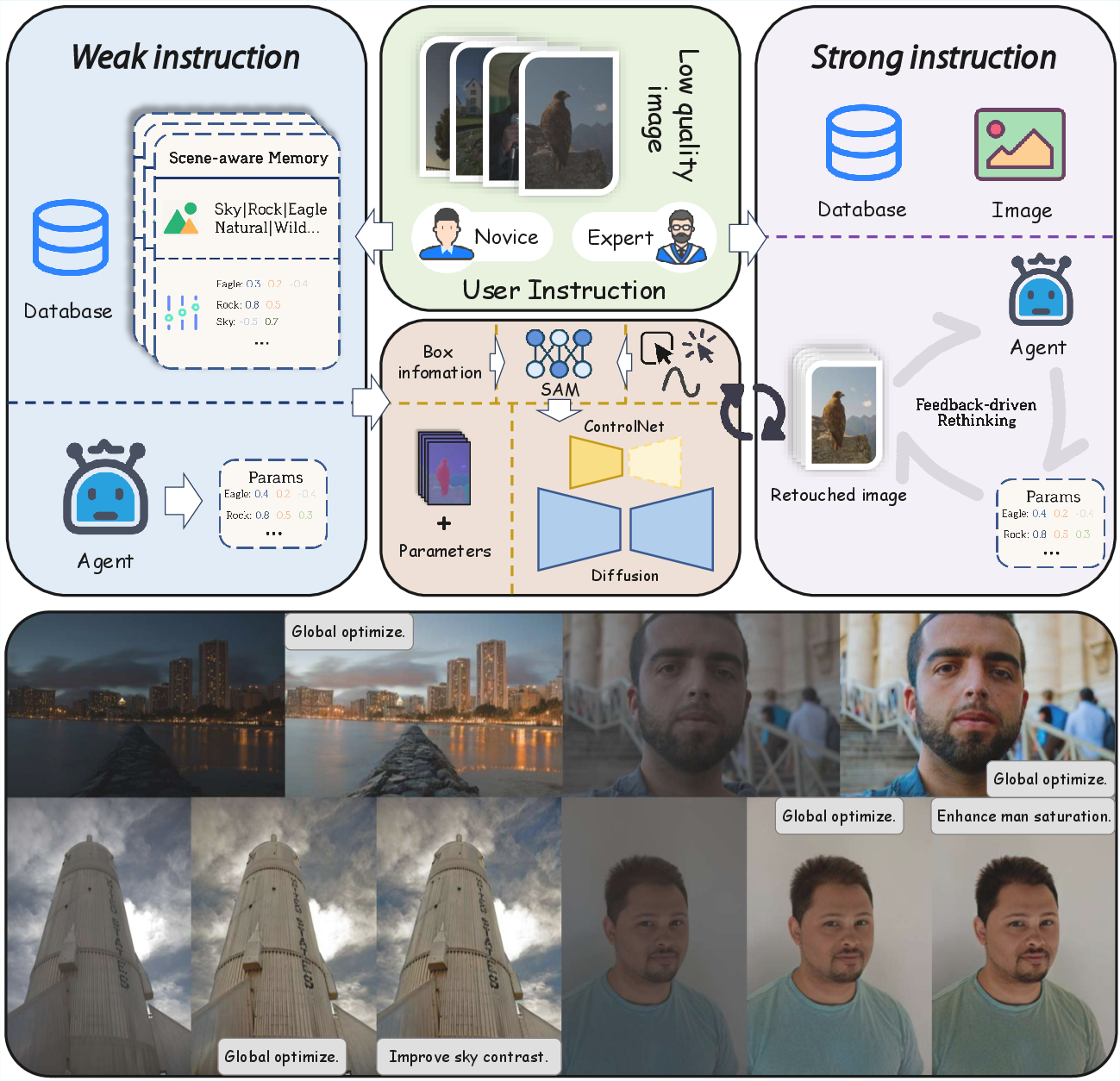
Figure 1: Overview of our PerTouch pipeline. Our method supports region-level personalized retouching with long-term user memory.
Semantic Replacement and Parameter Perturbation: To ensure semantic boundary precision in local edits, the framework employs semantic replacement and parameter perturbation. These techniques help mitigate overfitting to segmentation information and ensure consistent aesthetic quality across regions (Figure 2).
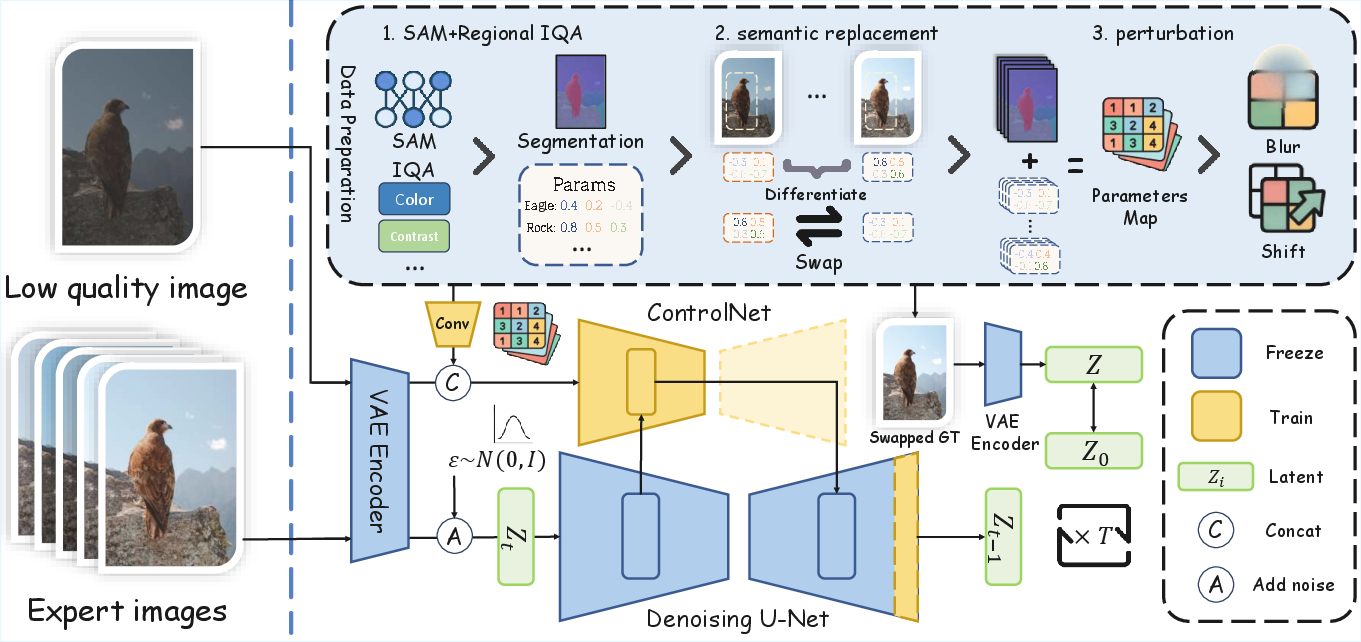
Figure 2: Dataset construction and training pipeline of PerTouch. Techniques include semantic replacement and perturbation to enhance boundary perception.
Agent-Driven Interaction: The PerTouch agent processes natural language commands, distinguishing between strong and weak instructions for diverse user needs. Weak instructions rely on user history to automate retouching, while strong instructions provide professional users with fine-grained control (Figure 3).
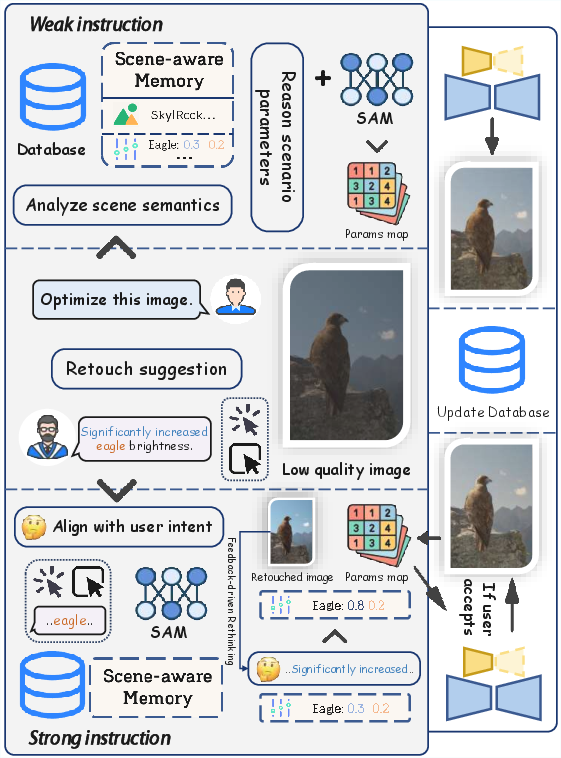
Figure 3: Agent workflow in PerTouch, highlighting adaptability in parsing varied user instructions.
Experimental Results
PerTouch demonstrates superior performance in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations against existing methods such as DiffRetouch and StarEnhancer. The system exhibits enhancements in PSNR and LPIPS scores across different expert-style outputs on the MIT-Adobe FiveK dataset, showcasing its efficiency in delivering high-quality, personalized retouching (Table 1).
Further, a user paper revealed significant preference for PerTouch retouched images, validating the system's efficacy in practical applications (Figure 4). This preference underscores PerTouch's ability to generate results that resonate with individual aesthetic tendencies.
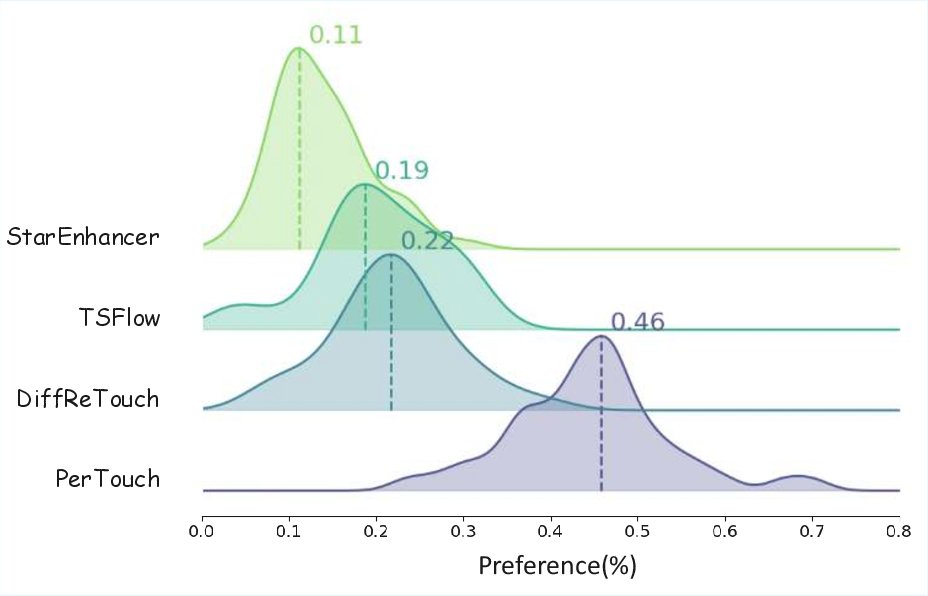
Figure 4: KDE plot of user paper. Comparison of high-quality image selection rates.
PerTouch's ablation studies confirmed the necessity of its modules, particularly the semantic replacement and perturbation mechanisms, for achieving localized editing precision and enhancing regional semantic control (Figure 5).
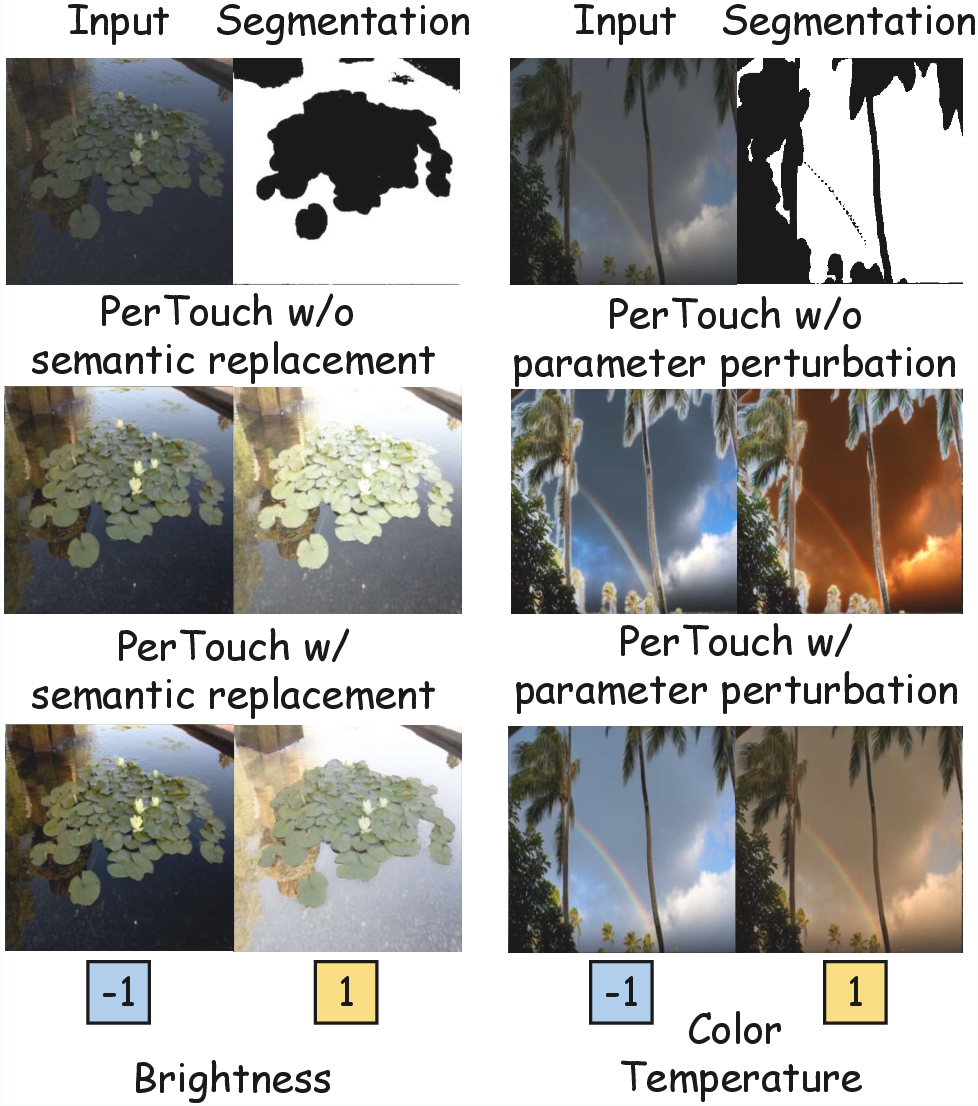
Figure 5: Ablation studies on key components of PerTouch, showing improvements in semantic region control.
Implications and Future Directions
PerTouch advances the field of image retouching by integrating user-driven semantic control with high-performance diffusion models, pushing towards adaptive and personalized enhancements. The practical implications of such technology include better accessibility for non-professional users and more efficient workflows in context-aware retouching scenarios.
Future developments may explore expanding PerTouch's attribute control capacities, further integrating feedback loops to refine user intent interpretation, and enhancing system adaptability across diverse photo contexts. These directions promise to refine and expand the potential applications of image retouching technologies in burgeoning fields of personal digital media and professional photography.
Conclusion
PerTouch represents a substantial contribution to image retouching methodology, merging state-of-the-art diffusion models and VLM-driven agents for personalized semantic editing. The framework's ability to effectively parse natural language instructions and perform context-aware aesthetic adjustments places it at the forefront of user-centric image enhancement technologies. The demonstrated effectiveness of PerTouch validates its promise in driving future innovations in personalized digital photography solutions.






