- The paper finds that Chinese digital painters transitioned from initial resistance to a pragmatic and reflective stance toward generative AI over five years.
- The study employed annual surveys and semi-structured interviews with 17 participants to capture quantitative trends and qualitative narratives.
- Findings underscore the importance of AI systems that support artistic control while addressing ethical concerns like copyright and creative labor.
Longitudinal Evolution of Chinese Painters' Attitudes Toward Generative AI
Introduction
The paper titled "Tracing Generative AI in Digital Art: A Longitudinal Study of Chinese Painters' Attitudes, Practices, and Identity Negotiation" offers a five-year longitudinal analysis of how 17 Chinese digital painters have interacted with generative AI technologies. This work explores the evolution of painters' attitudes from initial resistance, through pragmatic adoption, to eventual reflective reconstruction influenced by peer pressure, emotional dynamics, and persistent ethical concerns, including copyright issues and the impact on creative labor.
Methodology
Participants and Procedure
The paper recruited 17 participants in 2021, requiring a commitment to a five-year investigation involving annual surveys and interviews. Participants included both professional digital painters and hobbyists, primarily from urban settings, with varying levels of education and years of drawing experience.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data was gathered annually through a combination of structured questionnaires and semi-structured interviews, allowing for a robust capture of both quantitative trends and qualitative narratives. The analysis aimed to trace longitudinal trajectories and the dynamics of identity negotiation through quantitative trend analysis and thematic qualitative coding.
Key Findings
Initial Resistance (2021-2022)
The initial phase saw painters expressing negative attitudes toward generative AI, primarily driven by skepticism about its aesthetic and creative legitimacy. Concerns about copyright and authorship underpinned their resistance, even as their familiarity with AI technologies grew.
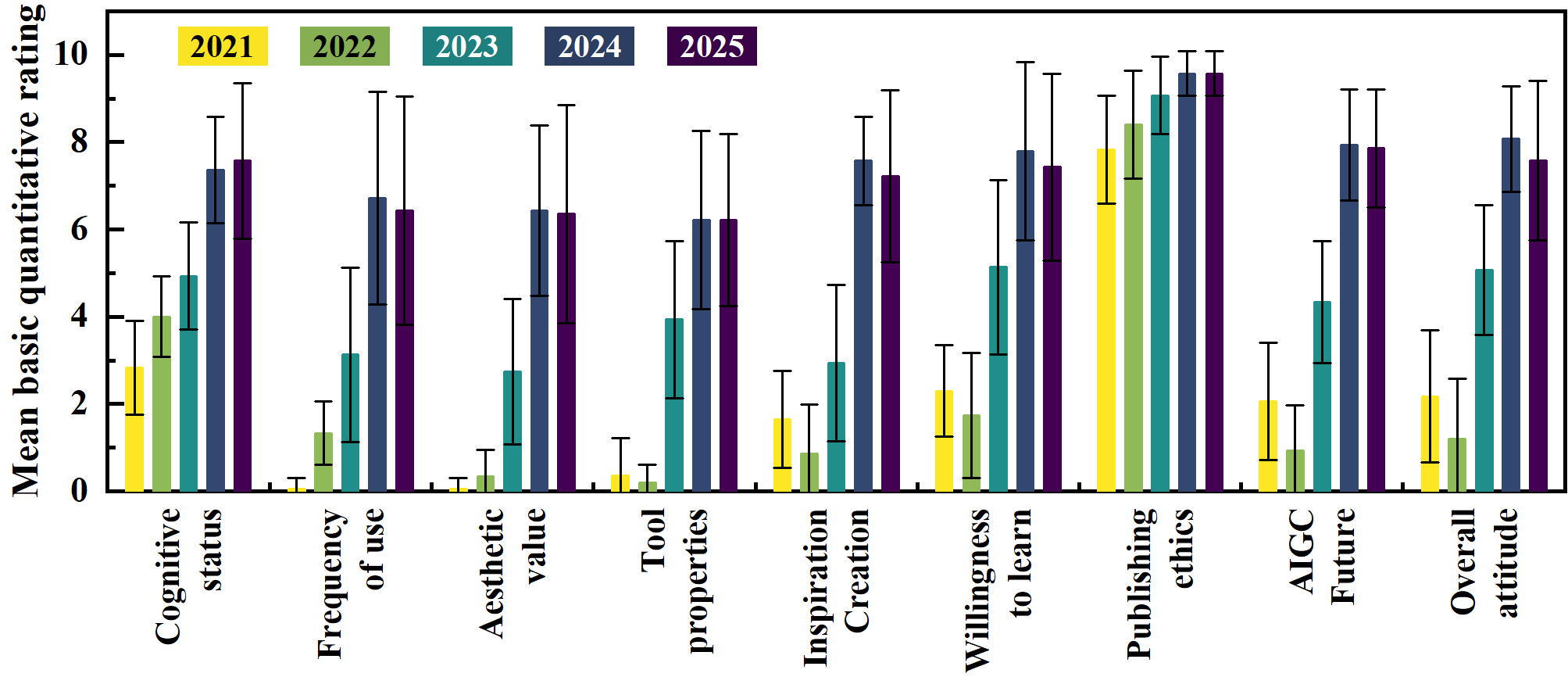
Figure 1: Mean and Standard Deviation of Participants’ Scores across Five Waves (2021--2025) on Nine Positively Scored Dimensions.
Pragmatic Adoption (2022-2024)
As AI technology advanced, painters shifted towards pragmatic adoption, recognizing the efficiency and utility of AI tools, particularly in commercial settings. Despite lingering skepticism, the need to remain competitive in the industry drove many professional artists toward embracing AI for tasks like ideation and rapid prototyping.
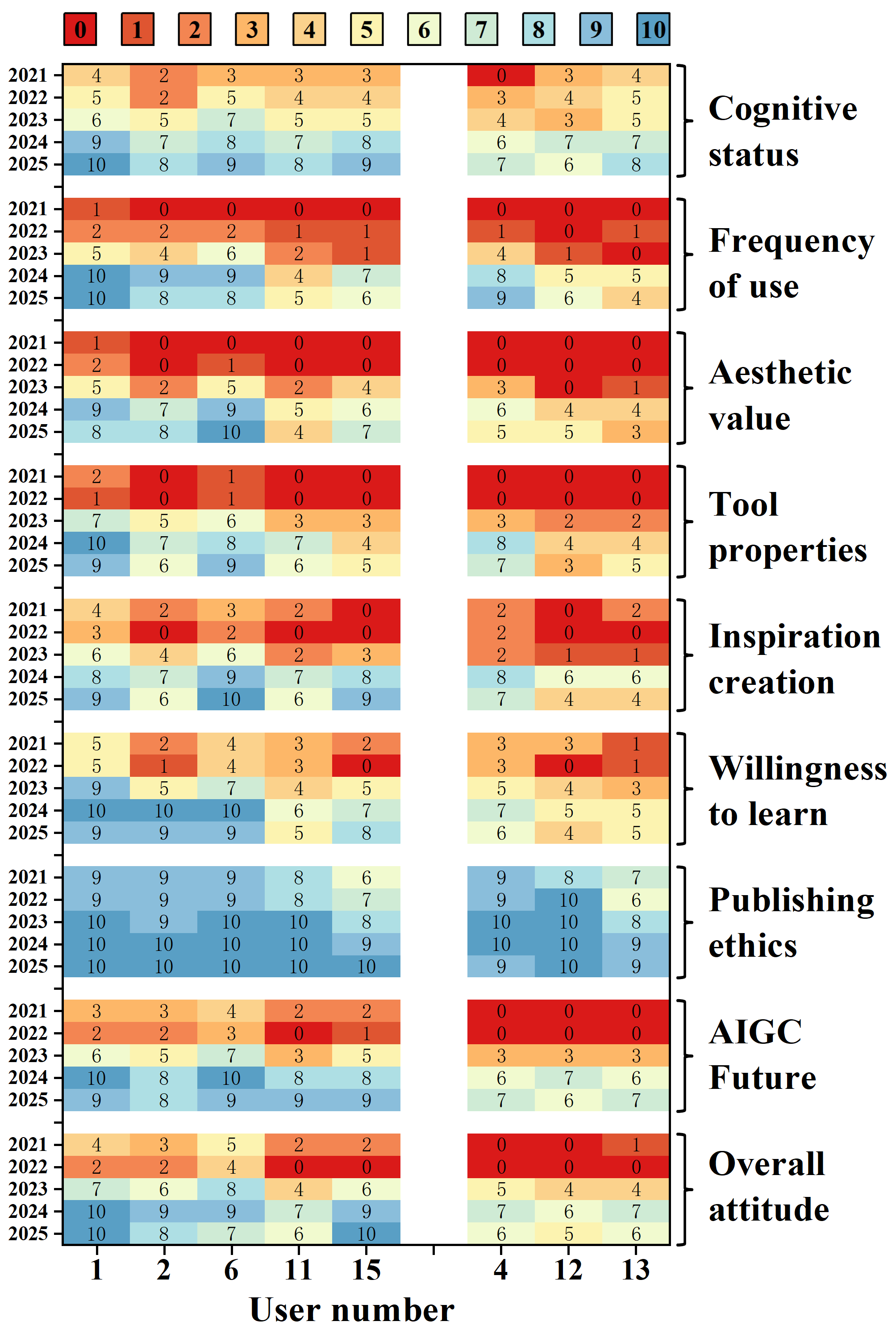
Figure 2: Attitudes of Professional (left) and Non-professional Artists (right) toward AI-assisted drawing on positively scored items.
Reflective Reconstruction (2024-2025)
In the final stage, attitudes stabilized, and participants engaged in reflective reconsideration of the role of AI in their work. While AI's utility was generally acknowledged, there was a renewed emphasis on identity negotiation and the importance of maintaining artistic control. Participants expressed concerns about the commodification of style and the implications for creative authenticity and professional identity.
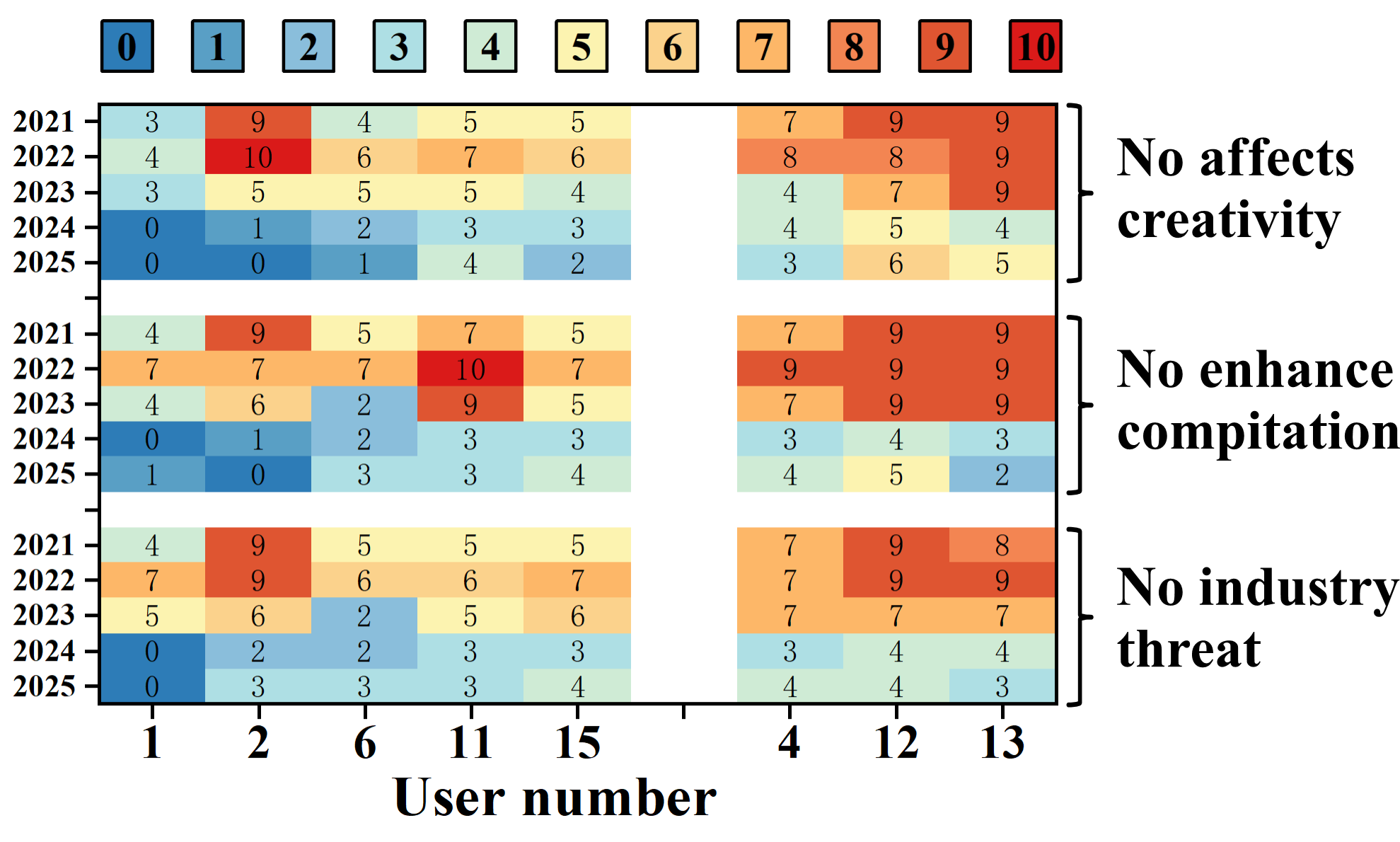
Figure 3: Attitudes of Professional (left) and Non-professional Artists (right) toward AI-assisted drawing on negatively scored items.
Implications and Future Directions
Design Implications
The findings underscore the necessity of designing AI systems that provide user control, support diverse modes of collaboration, and preserve the potential for creative divergence through serendipity and failure. Ensuring transparency and respecting user agency are crucial for fostering productive human-AI collaboration.
Theoretical Contributions
This paper contributes a nuanced understanding of technology adoption as a dynamic process of identity and value negotiation. It challenges the notion of linear adoption curves and offers insights into the socio-emotional dynamics underpinning human-AI interaction.
Limitations and Future Research
Future work should expand the investigation to include larger, more diverse samples and explore the impact of generative AI across different cultural contexts and creative domains. Additionally, there is a need to further investigate the interplay between technological advancements and identity negotiation in creative professions.
Conclusion
This longitudinal paper provides a comprehensive view of how generative AI reshapes digital painting practices over time. The insights gained highlight the complexities of adopting new technologies in creative fields and offer valuable guidance for the design and implementation of future human-AI collaborative systems. Through a deeper understanding of artists' evolving relationships with technology, this work advances both academic discourse and practical applications in the field of creative technologies.


