- The paper demonstrates that integrating scaling laws with architectural factors like hidden size and MLP-to-attention ratio improves inference efficiency.
- It introduces conditional scaling laws to predict optimal architectural configurations under fixed computational budgets, validated by low MSE and high Spearman correlation.
- The lightweight architecture search framework achieves up to 42% higher throughput and enhanced task performance compared to baseline models.
Scaling Laws Meet Model Architecture: Toward Inference-Efficient LLMs
The paper "Scaling Laws Meet Model Architecture: Toward Inference-Efficient LLMs" investigates the intersection of scaling laws and architectural choices to enhance LLM efficiency, specifically aiming to optimize inference throughput while maintaining accuracy.
Architectural Factors and Inference Efficiency
Key Architectural Influences
This paper explores how architectural elements such as hidden size, the ratio of MLP to attention, and Grouped Query Attention (GQA) impact both inference efficiency and accuracy. The models trained range from 80M to 3B parameters, assessed across varying hidden sizes and MLP-to-attention ratios.
Inference Throughput
Larger hidden sizes and higher MLP-to-attention ratios have been shown to improve inference throughput. As depicted in Figure 1, these configurations decrease the total number of FLOPs required for inference, consequently improving the throughput.
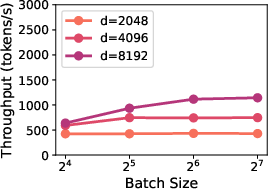
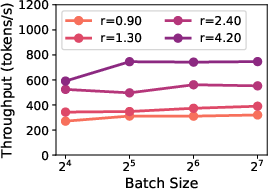
Figure 1: Inference throughput vs hidden size d=dmodel, showing increased throughput with larger hidden sizes for varying batch sizes.
Conditional Scaling Laws
Extending Chinchilla Scaling Laws
Building upon the Chinchilla scaling laws, this research introduces conditional scaling laws that incorporate architectural parameters, creating a framework for predicting optimal architectural choices under fixed computational budgets.
Predictive Validity
The validity of these conditional scaling laws is confirmed by their low mean squared error (MSE) and high Spearman correlation across models of varying sizes (80M to 1B), as showcased in Figure 2.
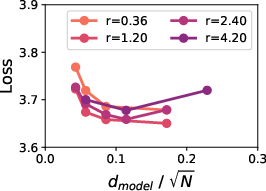
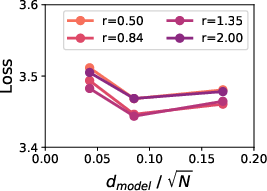
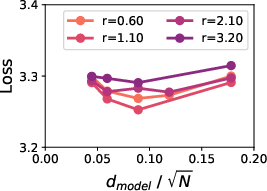
Figure 2: Predictive performance of conditional scaling laws, demonstrating consistent low MSE and high Spearman correlation across model scales.
Framework for Architecture Search
Optimization of Design
The paper outlines a lightweight framework for identifying model architectures that achieve a balance between inference efficiency and performance. This involves solving an optimization problem to maximize inference efficiency while satisfying a loss constraint, as supported by the conditional scaling law.
Experimentation and Results
Superior Model Configurations
The trained models, notably Panda-1B and Surefire-1B, demonstrated up to 42% higher inference throughput alongside improved accuracy over baseline models such as LLaMA-3.2. Specifically, Panda-1B and Panda-3B achieved higher task performance while maintaining or reducing training loss, verified through extensive downstream tasks evaluations listed in the supplementary tables.
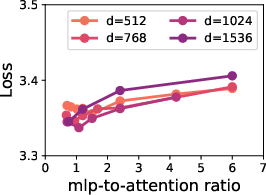
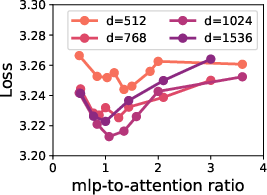
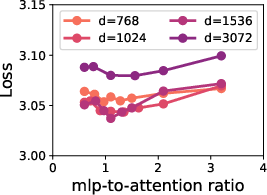
Figure 3: Results for 1B and 3B models showing Panda-1B following scaling law predictions for minimizing training loss and Surefire models achieving higher throughput than baseline models.
Comparisons and Explorations
The experimental results suggest that incorporating both empirical findings and scaling laws can effectively guide the creation of efficient LLM architectures, ensuring optimal resource utilization. Furthermore, the paper emphasizes the robustness of scaling laws in predicting performance improvements through architectural variations.
Limitations and Future Research
The analysis was predominantly focused on dense model architectures, with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models necessitating further exploration for scalability in inference efficiency. Future investigations should extend these findings to broader model classes and consider distinct hyperparameter requirements for differing architectures.
Conclusion
By leveraging conditional scaling laws and architectural influence, the paper establishes a comprehensive approach to optimizing LLMs for inference efficiency. This research sets a precedent for ongoing advancements in balancing computational cost with performance, critical for deploying scalable AI systems in real-world applications.









