- The paper introduces MVCustom, a method that integrates geometric latent rendering and dense spatio-temporal attention to achieve simultaneous multi-view consistency and high-fidelity subject customization.
- It leverages a pose-conditioned transformer block and depth-aware feature rendering to ensure accurate camera alignment and robust identity preservation across views.
- Experiments on CO3Dv2 and WebVid10M demonstrate that MVCustom outperforms baselines in multi-view consistency, customization fidelity, and pose accuracy.
MVCustom: Multi-View Customized Diffusion via Geometric Latent Rendering and Completion
Introduction and Motivation
MVCustom addresses the challenge of multi-view customization, a task that unifies camera pose control and prompt-based subject customization within generative models. Existing approaches either support multi-view generation without customization or enable customization without explicit viewpoint control, resulting in inconsistent subject appearance and surroundings across views. MVCustom is designed to overcome these limitations by enabling simultaneous multi-view consistency and high-fidelity customization, even when only a few reference images are available.

Figure 1: MVCustom achieves superior multi-view consistency and viewpoint alignment compared to prior methods, maintaining both subject and background coherence across diverse prompts.
Methodology
Multi-view customization is formalized as generating a set of images {Im}m=0M conditioned on reference images {Ii,πi}i=1N, a textual prompt, and target camera poses {ϕm}m=0M. The model must preserve subject identity, align with the prompt, and maintain geometric consistency across all views.
MVCustom leverages pose-conditioned transformer blocks, extending the architecture of CustomDiffusion360. The model consists of two branches:
- Main Branch: Generates target-view features, refined via self- and cross-attention conditioned on the prompt.
- Multi-View Branch: Aggregates reference-view features, synthesizing pose-aligned feature maps using FeatureNeRF and epipolar geometry.
The concatenated feature maps are projected into the backbone’s feature space, enabling explicit camera pose conditioning.

Figure 2: MVCustom architecture: (a) training pipeline with camera pose conditioning, (b) progressive attention mechanism for geometric consistency, (c) pose-conditioned transformer block integrating FeatureNeRF and projection layers.
Video Diffusion Backbone with Dense Spatio-Temporal Attention
MVCustom repurposes AnimateDiff’s video diffusion backbone, replacing 1D temporal attention with dense 3D spatio-temporal attention (STT). This extension enables the model to capture viewpoint-induced displacements and maintain spatial coherence across frames. The spatial attention field is gradually expanded during training to preserve stability and pretrained knowledge.
Inference-Time Geometric Consistency
Depth-Aware Feature Rendering
To enforce geometric consistency at inference, MVCustom constructs an anchor feature mesh Ma from an anchor frame’s feature and depth map. The mesh is rendered for each target camera pose, producing feature maps and visibility masks. During DDIM sampling, feature maps are updated by replacing masked regions with rendered anchor features, ensuring spatial alignment.
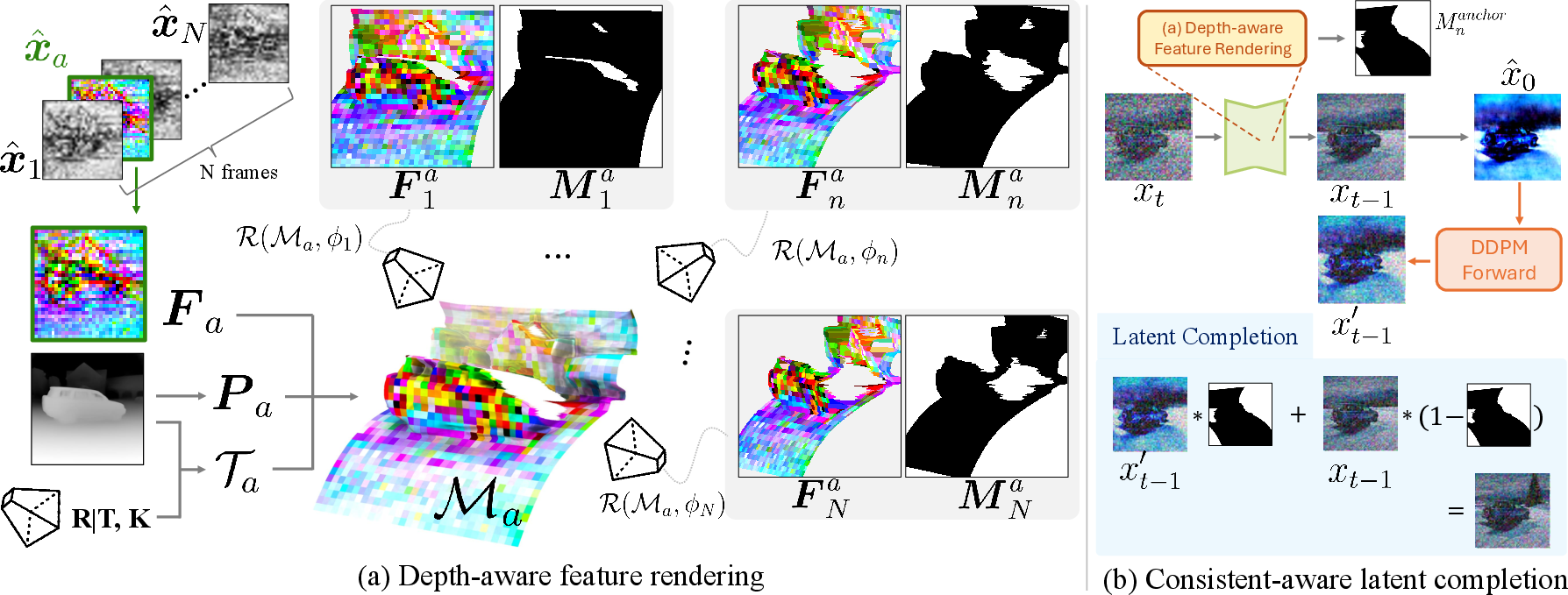
Figure 3: (a) Anchor feature mesh Ma constructed from feature and depth maps, (b) latent completion for newly visible regions.
Consistent-Aware Latent Completion
Disoccluded regions, not present in the anchor frame, are synthesized via stochastic latent perturbation. The model predicts an initial latent, reintroduces noise, and selectively replaces disoccluded regions, leveraging the temporal consistency of the video backbone for coherent synthesis.
Experimental Results
Quantitative and Qualitative Evaluation
MVCustom is evaluated on CO3Dv2 and WebVid10M datasets, compared against baselines including SEVA, CameraCtrl with DreamBooth-LoRA, and CustomDiffusion360. Metrics include camera pose accuracy, multi-view consistency (DreamSim, CLIP, DINO, Met3R), identity preservation, and text alignment.
MVCustom achieves the highest scores in both multi-view consistency and customization fidelity. Notably, it maintains accurate camera pose alignment and robust subject identity across diverse prompts and viewpoints, outperforming all baselines.

Figure 4: Qualitative results: multi-view training data (blue) and inference results (pink) conditioned on new text and camera poses.
Ablation Studies
Ablation experiments demonstrate the impact of depth-aware feature rendering and consistent-aware latent completion. Depth-aware rendering enforces geometric consistency, while latent completion synthesizes realistic details in disoccluded regions. Dense spatio-temporal attention is shown to be critical for maintaining spatial coherence during feature replacement.

Figure 5: Ablation results: (a) effect of depth-aware rendering and latent completion, (b) spatial flow enforcement via spatio-temporal attention.
Diversity in Latent Completion
MVCustom’s latent completion mechanism introduces semantic diversity in disoccluded regions, as evidenced by variations across random seeds. This diversity is essential for realistic and varied content generation.

Figure 6: Diversity in consistent-aware latent completion: noise-driven variations in completed regions across seeds.
Implementation Details
MVCustom is built on a U-Net-based video diffusion backbone (AnimateDiff), chosen for compatibility with FeatureNeRF and per-frame feature map maintenance. The model is fine-tuned on 430K WebVid10M samples and customized using textual inversion and FeatureNeRF modules. Inference involves mesh construction, feature rendering, and latent completion, with efficient GPU utilization and memory management.
Limitations and Future Directions
MVCustom’s reliance on reference images with consistent object poses limits its ability to handle substantial pose variations. Future work may explore dynamic radiance field networks or hypernetwork-based approaches to enable pose-adaptive customization. Additionally, extending the framework to handle more complex scene compositions and larger-scale datasets remains an open research direction.
Practical and Theoretical Implications
MVCustom establishes a new paradigm for controllable multi-view generation, enabling applications in virtual prototyping, personalized asset creation, and immersive content design. The explicit integration of geometric constraints and latent-level completion provides a robust solution for data-scarce customization scenarios. The framework’s modularity and compatibility with existing diffusion models facilitate adoption in diverse generative modeling pipelines.
Conclusion
MVCustom introduces a principled approach to multi-view customization, integrating camera pose control, subject fidelity, and spatial consistency for both subjects and surroundings. Through dense spatio-temporal attention, depth-aware feature rendering, and consistent-aware latent completion, MVCustom achieves state-of-the-art performance in both multi-view generation and customization. The framework lays the groundwork for future research in controllable, customizable, and geometrically consistent generative modeling.







