- The paper demonstrates SAP Joule’s main contribution by achieving 80.49% strict accuracy on the HumanEval-X JavaScript benchmark.
- It employs a standardized methodology with strict accuracy and manual execution via SAP BAS to evaluate code generation performance across 30 LLMs.
- The study highlights a weak correlation between model parameter count and performance, underscoring the importance of architecture and fine-tuning over size.
Evaluation of SAP Joule for JavaScript Code Generation
Introduction
This paper presents a systematic evaluation of SAP Joule, a proprietary generative LLM developed by SAP, focusing on its JavaScript code generation capabilities. The paper benchmarks SAP Joule against 29 contemporary LLMs using the HumanEval-X JavaScript dataset and employs strict accuracy as the primary evaluation metric. The analysis provides a comparative perspective on SAP Joule's performance relative to both proprietary and open-source models, with particular attention to the implications of model specialization, parameter count, and evaluation methodology.
Methodology
The evaluation framework is designed to accommodate the constraints imposed by SAP Joule's limited accessibility, specifically the absence of an API and the necessity for manual interaction via the SAP Business Application Studio (BAS) UI. The HumanEval-X JavaScript benchmark, comprising 164 programming problems, is selected for its manageable size and relevance. Strict accuracy is chosen as the evaluation metric, defined as the percentage of problems for which the model's single generated solution passes all associated unit tests.
Prompting is standardized by appending "Use JavaScript." to each prompt to mitigate language ambiguity. For proprietary models, batch APIs are utilized, while open-source models are executed locally via Ollama. All model outputs undergo a standardized cleaning process to remove non-code text, markdown formatting, extraneous function calls, and incomplete code, ensuring consistency in evaluation. Execution is performed using Node.js, and strict accuracy is computed as the proportion of problems solved without errors.
Results
SAP Joule achieves a strict accuracy of 80.49% on the HumanEval-X JavaScript benchmark, ranking fifth among the 30 evaluated models. The leading proprietary models, Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet and OpenAI GPT-4o, both attain 85.98% strict accuracy, followed closely by GPT-4 Turbo at 84.15%. The top-performing open-source model, Qwen2.5-32B, surpasses SAP Joule with 81.71%.
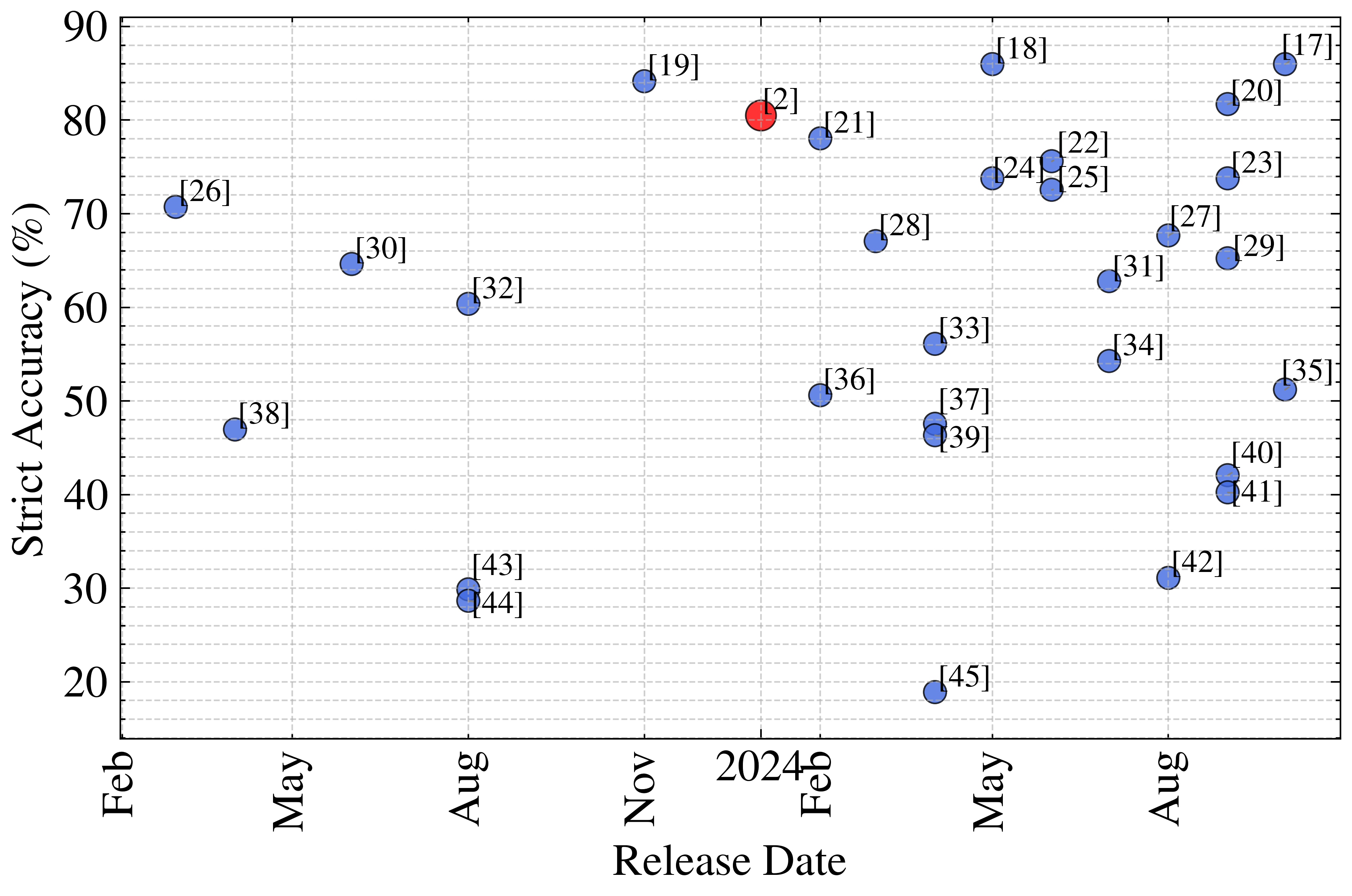
Figure 1: Measured strict accuracy performance over publication date of the investigated models. While even recent models vary wildly regarding strict accuracy performance, a slight trend towards better models can be observed.
The overall landscape reveals a mean strict accuracy of 60.6% with a standard deviation of 19%, indicating substantial variability in model capabilities. Notably, several open-source models, including DeepSeek-Coder-V2, Qwen2.5-Coder, Codestral, and Gemma2, achieve strict accuracy above 70%, demonstrating the efficacy of specialized code models even at lower parameter counts.
Analysis of Model Specialization and Parameter Count
A key observation is the weak correlation (r=0.23) between model parameter count and strict accuracy among open-source models. This suggests that architectural choices, training data quality, and task-specific fine-tuning exert a greater influence on code generation performance than sheer model size within the evaluated range.
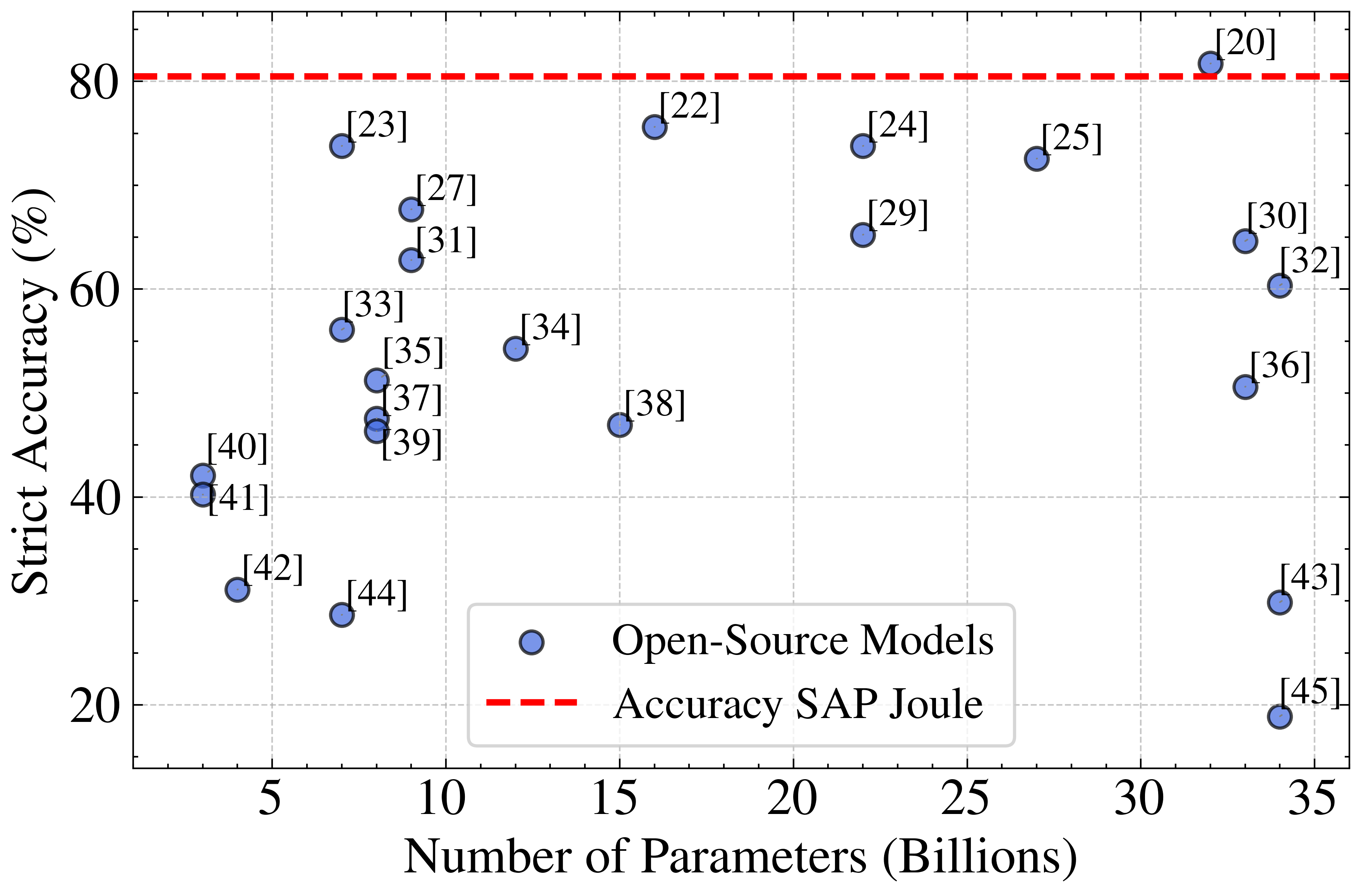
Figure 2: Performance in relation to the number of parameters for open source models. Since SAP Joule parameter count is unknown, the strict accuracy result is depicted independent of the parameter count.
SAP Joule's parameter count remains undisclosed, precluding direct comparison on this axis. However, its performance is competitive with both large proprietary and specialized open-source models, indicating effective model design and training for code generation tasks.
Implications and Future Directions
The results underscore the rapid advancement of LLMs in code generation, with strict accuracy scores for top models converging in the 80–86% range. SAP Joule's strong performance, despite its general-purpose orientation and limited developer tool integration, highlights the potential for enterprise-focused LLMs to deliver robust code generation capabilities.
The paper also demonstrates the viability of strict accuracy as an evaluation metric in scenarios where automated, large-scale sampling is infeasible. However, the inherent variance and potential bias of single-sample metrics warrant caution in broader generalization.
Given SAP Joule's recent extension to ABAP code generation, future research should assess its performance in this domain, particularly given the scarcity of public ABAP datasets and the unique requirements of SAP-centric development environments. The ongoing internal evaluations by SAP in this area are likely to yield further insights into the adaptability and specialization of enterprise LLMs.
Conclusion
This evaluation establishes SAP Joule as a competitive LLM for JavaScript code generation, achieving 80.49% strict accuracy and ranking among the top five models on the HumanEval-X JavaScript benchmark. The findings highlight the narrowing performance gap between proprietary and open-source models and emphasize the importance of model specialization over parameter count. Future work should extend this analysis to ABAP and other SAP-specific languages, as well as explore the integration of LLMs into enterprise software engineering workflows.



