- The paper demonstrates that AI-guided multimodal journaling scaffolds narrative construction and reduces linguistic and executive barriers for autistic adolescents.
- It details a structured dialogue system using the ABC-E model and a comic strip visualization to enhance narrative coherence and emotional expression.
- Results from a two-week field study show improved narrative skills, increased adolescent autonomy, and reduced parental moderation in journaling.
AI-Guided Multimodal Journaling for Autistic Adolescents: The Autiverse System
Introduction and Motivation
Autistic adolescents frequently encounter significant challenges in constructing and communicating coherent daily narratives, due to executive dysfunction, difficulties with open-ended prompts, and a reliance on visual rather than verbal processing. Traditional journaling, while beneficial for narrative development, imposes high linguistic and executive demands that can be prohibitive for this population. The paper introduces Autiverse, a tablet-based, AI-guided multimodal journaling system designed to scaffold narrative construction for autistic adolescents by leveraging conversational LLMs and visual supports. The system aims to lower the cognitive and linguistic barriers to journaling, foster autonomy, and facilitate richer parent-adolescent communication.
System Design and Architecture
Autiverse is grounded in formative research with autism experts and parents, which identified the need for structured scaffolding, visual aids, and minimized parental intervention. The system operationalizes these requirements through several key design principles:
- Structured Narrative Scaffold: Autiverse employs a stepwise dialogue based on the ABC-E (Antecedent, Behavior, Consequence, Emotion) model, guiding users to incrementally construct narratives.
- Multimodal Interaction: The system integrates conversational AI (text and speech) with a four-panel comic strip, providing visual representations of narrative elements to align with autistic adolescents' strengths in visual processing.
- Customizable AI Peer: The AI agent adopts a peer persona, with customizable name, voice, and appearance, to foster engagement and reduce the perception of didactic instruction.
- Parental Role: Parents are positioned as non-intrusive observers, ensuring safety while supporting adolescent autonomy.
The user flow is illustrated in (Figure 1), which details the main screens and sequential phases of the journaling process, from initial prompt selection to final review and reward.
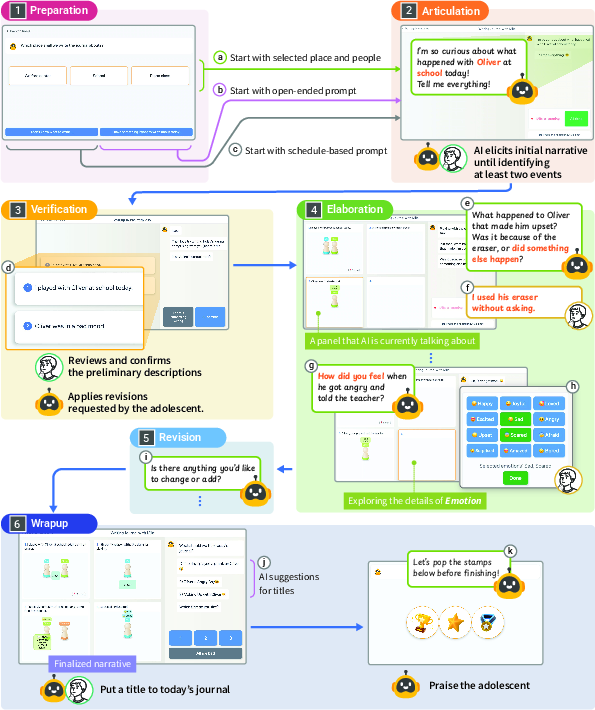
Figure 1: Main screens and usage flow of Autiverse, showing the structured, stepwise journaling process and multimodal supports.
Generative Pipeline and Implementation
The generative pipeline of Autiverse is modular and LLM-centric, comprising several components:
- Event Extractor: Identifies key events from user input.
- Question Generator: Produces contextually appropriate follow-up prompts, adapting to the adolescent's cognitive profile and conversational context.
- Story Analyzer: Evaluates narrative completeness, coherence, and adherence to the ABC-E structure.
- Description Reconstructor: Integrates user responses, maintains chronological order, and normalizes language.
- Panel Scene Constructor: Translates structured narrative elements into a parametric JSON format for rendering the four-panel comic strip.
The pipeline is depicted in (Figure 2) and (Figure 3), highlighting the flow from dialogue analysis to visual scene generation.
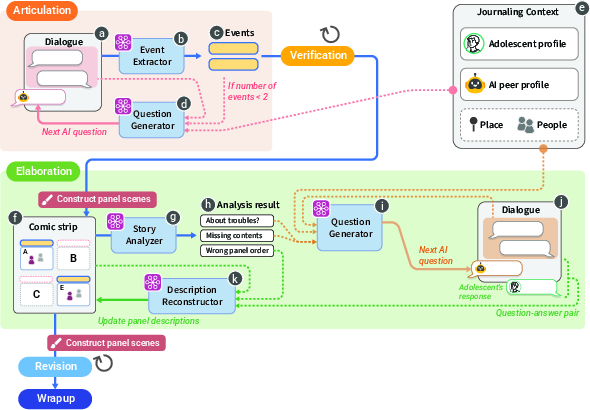
Figure 2: Generative pipeline flows of Autiverse, detailing the modular LLM-driven components for narrative extraction and scaffolding.
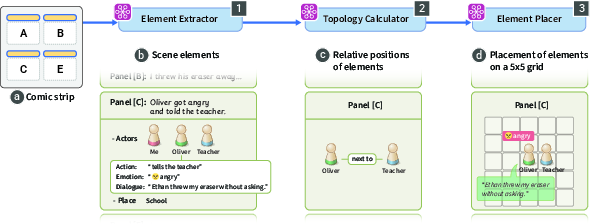
Figure 3: Generative pipeline for constructing panel scenes, mapping narrative elements to a structured visual grid.
The backend is implemented in Python (FastAPI), with OpenAI GPT-4.1-mini-2025-04-14 for LLM inference, and the client is a React Native app supporting both iPad and Android tablets. Speech recognition and synthesis are handled via CLOVA APIs, and all interaction data is logged for analysis.
Deployment Study: Methodology and Results
A two-week field deployment was conducted with 10 autistic adolescent–parent dyads in South Korea. Adolescents engaged in daily journaling sessions with Autiverse, while parents observed and provided daily and post-paper feedback.
Usage Patterns and Engagement
- Adherence: Four dyads used the system daily; no dyad skipped more than two consecutive days.
- Session Metrics: Mean of 12.2 journal entries per adolescent; average session duration 9m 43s; mean 46.9 conversational turns per session.
- Content Diversity: 68% of entries described routine places; 46% focused on leisure activities, 34% on daily life, and 20% on special events.
Narrative Construction and Multimodal Support
The structured, stepwise interaction scaffolded topic selection and narrative construction, with 66% of sessions initiated via selection-based prompts. The ABC-E format facilitated temporal organization and emotional reflection, with parents reporting improved narrative coherence and emotional expressiveness in their children.
Visual supports (comic strip) and speech interaction were rated highly by both adolescents and parents for aiding recall and expression. Adolescents preferred dialog-based comic journaling over self-writing or fully independent modes.
AI Peer Customization and Perception
80% of adolescents customized the AI peer, and the agent was widely perceived as a friendly, supportive companion. Adolescents reported a strong sense of ownership (mean 4.4/5) and autonomy (mean 4.2/5) over their journal entries, with only isolated cases of perceived lack of control due to output unpredictability.
Parental Impact and Communication
Parents reported significant improvements in their child's narrative skills, including increased topic focus, elaboration, and emotional range. Notably, the level of parental moderation decreased significantly over the paper (p = 0.001), as shown in (Figure 4), indicating increased adolescent independence.
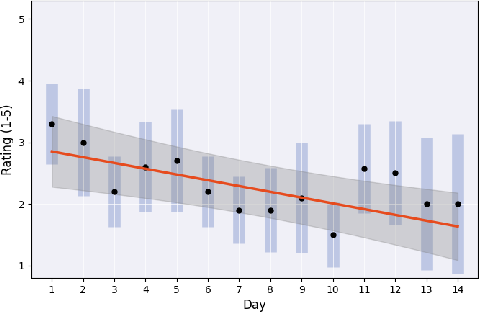
Figure 4: Daily trends in parental moderation, showing a significant decrease over the 14-day period.
Parents also gained new insights into their child's daily events and emotions, as visualized in (Figure 5), and reported enhanced parent-adolescent conversations.
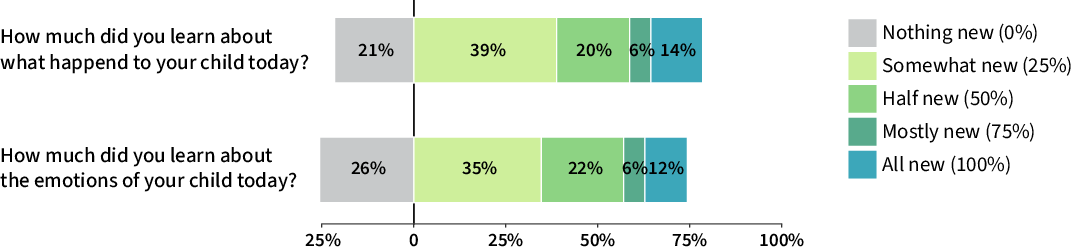
Figure 5: Distribution of parents' daily responses regarding new insights gained about their child's events and emotions.
User Acceptance
Adolescents rated Autiverse highly for ease of use (4.2), enjoyment (4.5), usefulness (4.6), and comic strip likability (4.5), but willingness to continue journaling was more variable, often reflecting general resistance to diary-keeping rather than system usability. Parents rated the system highly for utility, expressiveness, and recommendability (see Figure 6).
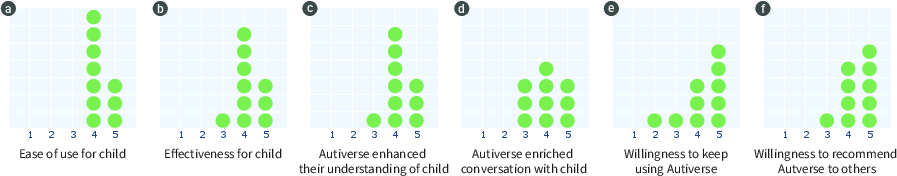
Figure 6: Distribution of parents' post-paper ratings for utilities and benefits of Autiverse.
Discussion and Implications
Adaptive Scaffolding and Transferability
The results demonstrate that structured, multimodal AI scaffolding can effectively lower the executive and linguistic demands of journaling for autistic adolescents, supporting both narrative development and emotional reflection. The observed transfer of narrative skills to everyday conversation, as reported by parents, suggests potential for broader social communication benefits, though longitudinal validation is needed.
The system's design, which minimizes parental intervention and positions the AI as a peer, was effective in fostering adolescent autonomy and engagement. However, the need for adaptive scaffolding—progressing from simple to complex narrative structures—was highlighted, with parents expressing a desire for both manual and data-driven control over system difficulty. The authors argue for a hybrid approach, combining parental insight with objective performance metrics.
Ethical and Developmental Considerations
The peer-like AI agent was effective in eliciting disclosure and engagement, but the risk of over-reliance and the ethical boundaries of AI companionship require careful design. The system should be positioned as a scaffold for social rehearsal, not a substitute for human relationships, and should incorporate guardrails for safety and privacy.
Limitations and Future Directions
The paper is limited by its small, culturally homogeneous sample and the use of an LLM not specifically optimized for Korean. Future work should explore cross-cultural generalizability, spectrum-wide applicability, and the integration of advanced gamification to sustain long-term engagement.
Conclusion
Autiverse demonstrates that AI-guided, multimodal journaling can scaffold narrative construction and emotional reflection for autistic adolescents, supporting both autonomy and parent-adolescent communication. The system's structured, visual, and conversational supports address core barriers to journaling in this population, and the deployment paper provides strong evidence for feasibility, acceptability, and preliminary efficacy. The work establishes a foundation for future adaptive, inclusive AI systems that augment neurodiverse strengths and bridge communicative gaps.





