- The paper introduces a CSC framework that divides customer conversations into five structured stages with specific communication strategies.
- It presents the CSConv and synthetic RoleCS datasets to enrich training data and improve model strategy adherence.
- Fine-tuning LLMs on RoleCS leads to significant gains in BLEU and BERTScore, proving the method’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
Evaluating, Synthesizing, and Enhancing for Customer Support Conversation
Introduction
"Evaluating, Synthesizing, and Enhancing for Customer Support Conversation" presents a novel framework for improving customer support dialogue systems. It primarily aims to bridge gaps in structured strategic guidance within available dialogue datasets, which hinders training models to adhere to professional communication standards. To rectify this, the paper introduces a Customer Support Conversation (CSC) task, specified by a structured framework based on COPC guidelines. The CSC framework delineates five conversational stages coupled with twelve strategic approaches to achieve quality communication in customer support.

Figure 1: An example dialogue between a service supporter (left) and a customer (right), showing support strategies (noted in parentheses) used by the supporter. The conversation is organized into five stages of the proposed CSC framework, shown in colored boxes.
CSC Framework and Datasets
The proposed CSC framework divides customer interactions into five stages: Connecting, Identifying, Exploring, Resolving, and Maintaining. Each stage incorporates specific strategies such as Greeting, Emotional Management, Information Delivery, and Feedback Request. This modular structure not only enables dynamic support flow but also promotes robust training of service agents.

Figure 2: Overview of the CSC framework's five stages, each paired with recommended support strategies (see Table~\ref{tbl:strategy}).
The paper introduces the CSConv dataset, comprising 1,855 curated and strategy-rich dialogues rewritten using LLMs to reflect strategic intentions. An innovative role-playing technique generates the RoleCS dataset, a synthetic collection that simulates complex support conversations through role-aligned agents. Fine-tuning LLMs on RoleCS demonstrates significant improvements, enhancing their ability to produce high-quality, aligned responses.
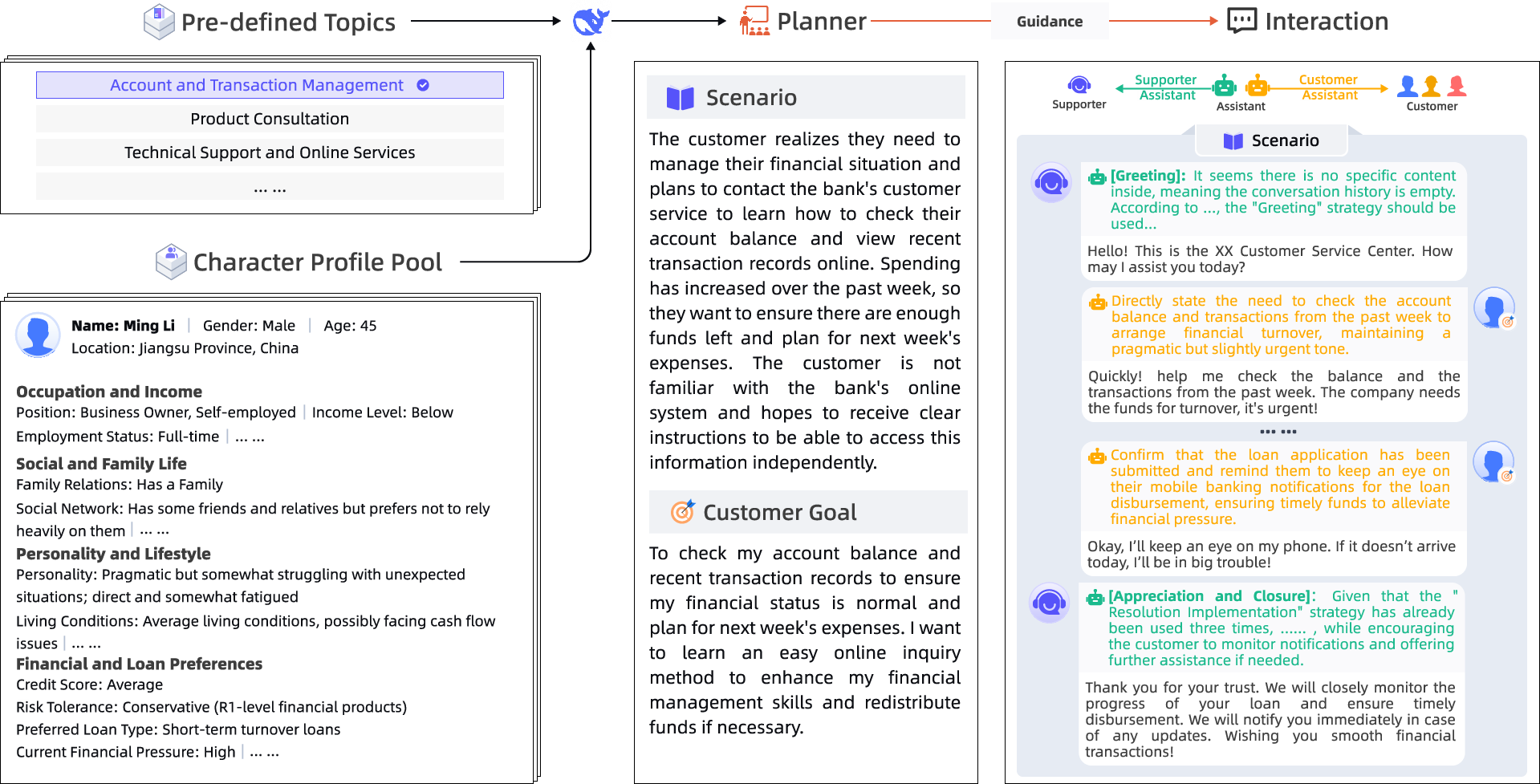
Figure 3: Illustration of synthetic conversation generation using role-playing agents.
Experimentation and Results
Extensive experiments with several LLMs, including GPT-4o and DeepSeek variants, reveal their performance boost when fine-tuned on the RoleCS dataset. The models showcased improved BLEU scores, BERTScore, and strategy adherence accuracy, proving the effectiveness of strategy-enriched synthetic data. Specifically, Qwen2.5-Instruct-72B achieved notable success, showing competitive performance to state-of-the-art models like DeepSeek-R1.
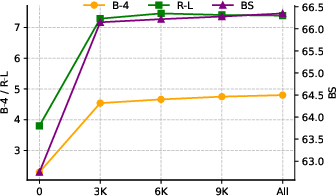
Figure 4: Performance comparison under different synthetic conversation dataset sizes.
Discussion
Utilizing the role-playing framework to generate RoleCS demonstrates the potential for diversified and realistic data creation. By mimicking real-world scenarios, this approach addresses limitations in dataset variability and domain-specific training scarcity. The impact of dataset size on model performance was also examined, indicating diminishing returns beyond a certain dataset magnitude. Additionally, the Oracle variant emphasized the critical role of precise strategy prediction in enhancing contextual responses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the paper makes substantial contributions in structuring customer support conversations through an innovative CSC framework and role-playing datasets. These efforts advance the training capabilities of LLMs, fostering efficient, empathetic, and strategically robust customer support systems. The approach lays groundwork for future explorations into AI's role in service-oriented dialogue management and highlights avenues for enhancement in emotional intelligence within AI-driven support systems.



