- The paper documents rapid generative AI adoption (80% usage within two years) among Middlebury College students, highlighting early tech assimilation.
- It differentiates AI use for augmentation (61.2%) versus automation (41.9%), emphasizing varied impacts on student learning.
- The study reveals demographic and disciplinary disparities and underscores the need for clearer institutional AI policies to guide ethical use.
Generative AI in Higher Education: Evidence from an Elite College
Introduction
The paper "Generative AI in Higher Education: Evidence from an Elite College" explores the adoption and implications of generative AI among students at Middlebury College. It provides a vital quantitative analysis of how AI is integrated into academic settings, particularly focusing on the speed and nature of this adoption across various disciplines and demographics. The findings reflect the broader trend of rapid technological assimilation and its impact on higher education, presenting both opportunities and challenges for educational policies and student learning outcomes.
Adoption Patterns
Rapid and Widespread Adoption
The paper documents an exceedingly rapid adoption of generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT, among students at Middlebury College. Over 80% of students have adopted AI for academic purposes within two years of these tools' introduction. This adoption rate starkly contrasts with broader workforce adoption rates, indicating an academic environment more conducive to rapid technological integration. The data emphasize a near-universal acceptance of AI as a tool to enhance or streamline academic workloads among students.
Demographic Disparities
Adoption rates vary significantly across demographics and academic disciplines. The highest adoption rates are observed among Natural Sciences students (91.1%), while Literature and Language majors exhibit relatively lower rates. Male students and those with lower academic achievement are identified as more likely to adopt AI, hinting at AI’s potential to act as an equalizer in educational achievement.

Figure 1: Word Cloud of Student Motivations for Generative AI Use.
Usage Patterns
Augmentation vs. Automation
The paper differentiates between AI use for augmentation (enhancing learning) versus automation (completing tasks with minimal cognitive involvement). While 61.2% employ AI for augmentation, 41.9% use it for automation. This distinction is critical, as augmentation supports learning without replacing it, whereas automation might risk diminishing fundamental skills acquisition.
Student Perceptions
Students broadly perceive AI as beneficial for learning, with positive impacts reported on understanding course materials and learning abilities. However, fewer students believe AI directly improves their grades, suggesting a nuanced perception of AI's role in academic achievement.
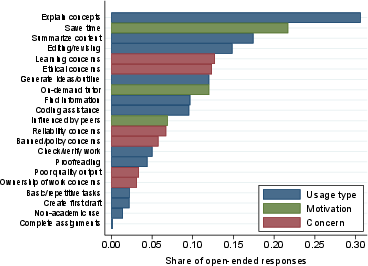
Figure 2: Frequency of Keywords in Student Motivations for AI Use.
Institutional Policy Implications
Policy Effectiveness and Challenges
Institutional policies play a crucial role in shaping AI usage. Prohibitive policies reduce AI use intention by 39 percentage points but introduce disparities, such as gender differences in compliance. There's a substantial information gap concerning AI policy awareness and access to institutional resources, which points to potential areas for policy refinement and better communication.
Need for Clearer Guidelines
Feedback from open-ended survey responses emphasizes the need for clearer AI policies and guidelines. Students demand explicit instructions and cite confusion over acceptable AI use as a barrier to more ethical and productive integration of AI tools.

Figure 3: Word Cloud of Student Feedback on Generative AI Policies.
Conclusions
The paper presents critical insights into how generative AI is transforming the academic landscape at elite institutions. By highlighting the rapid adoption rates, varied usage patterns, and significant effects of institutional policies, it underscores the need for educational institutions to proactively address the challenges and opportunities presented by AI. For future policies, a balanced approach that encourages beneficial AI use while mitigating potential drawbacks will be essential. Furthermore, providing training and clearer guidance on AI usage could fortify students' skills for both academic and professional success, ensuring that AI acts as an enhancer rather than a substitute for human learning.


