Out of Distribution, Out of Luck: How Well Can LLMs Trained on Vulnerability Datasets Detect Top 25 CWE Weaknesses?
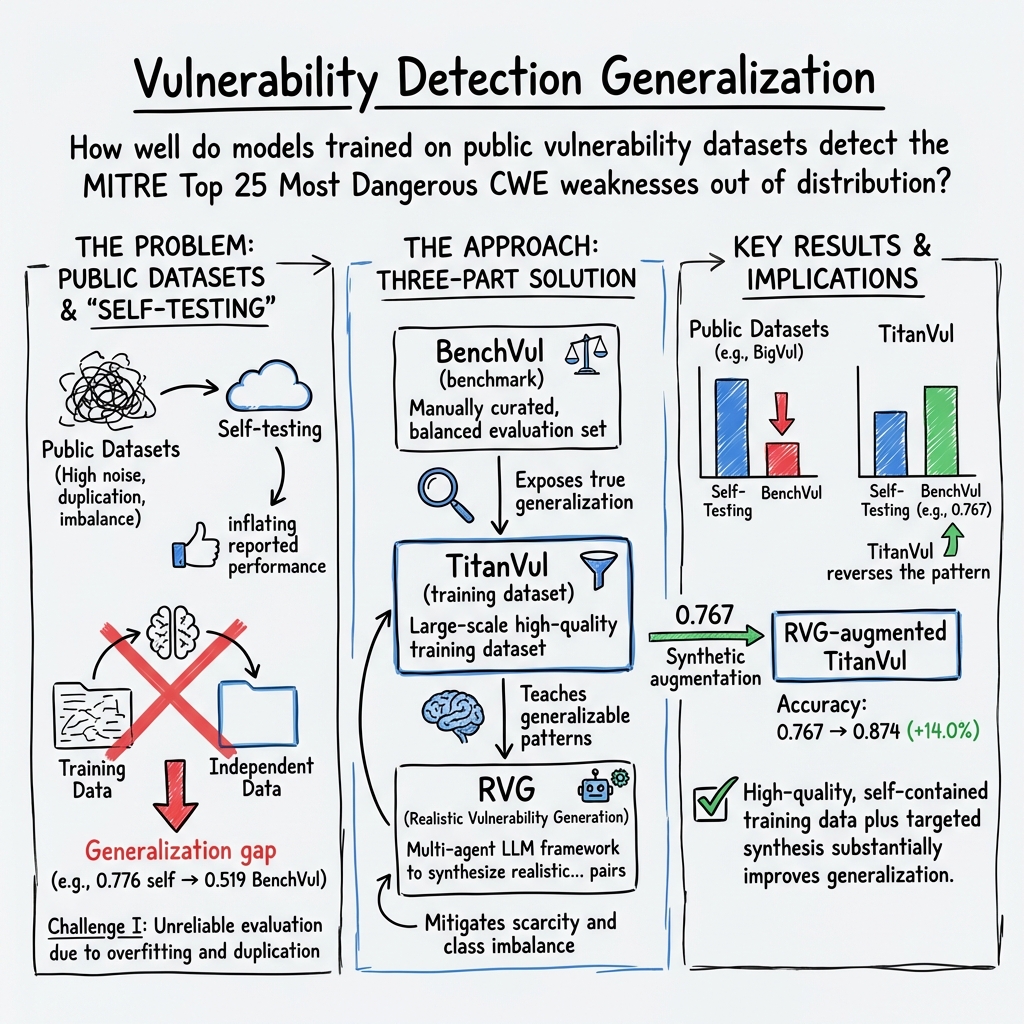
Abstract: Automated vulnerability detection research has made substantial progress, yet its real-world impact remains limited. Prior work found that current vulnerability datasets suffer from issues including label inaccuracy rates of 20%-71%, extensive duplication, and poor coverage of critical Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE). These issues create a significant generalization gap where models achieve misleading In-Distribution (ID) accuracies (testing on splits from the same dataset) by exploiting spurious correlations rather than learning true vulnerability patterns. To address these limitations, we present a three-part solution. First, we introduce BenchVul, which is a manually curated and balanced test dataset covering the MITRE Top 25 Most Dangerous CWEs, to enable fair model evaluation. Second, we construct a high-quality training dataset, TitanVul, comprising 38,548 functions by aggregating seven public sources and applying deduplication and validation using a novel multi-agent LLM pipeline. Third, we propose a Realistic Vulnerability Generation (RVG) pipeline, which synthesizes context-aware vulnerability examples for underrepresented but critical CWE types through simulated development workflows. Our evaluation reveals that In-Distribution (ID) performance does not reliably predict Out-of-Distribution (OOD) performance on BenchVul. For example, a model trained on BigVul achieves the highest 0.703 ID accuracy but fails on BenchVul's real-world samples (0.493 OOD accuracy). Conversely, a model trained on our TitanVul achieves the highest OOD performance on both the real-world (0.881) and synthesized (0.785) portions of BenchVul, improving upon the next-best performing dataset by 5.3% and 11.8% respectively, despite a modest ID score (0.590). Augmenting TitanVul with our RVG further boosts this leading OOD performance, improving accuracy on real-world data by 5.8% (to 0.932).
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.