- The paper presents PaperBridge, an AI-augmented system that synthesizes diverse publications into coherent research narratives.
- It employs a bi-directional analysis engine combining top-down structured prompts and bottom-up user inputs to generate inspiring narrative perspectives.
- Evaluation showed excellent usability and enhanced exploration support, highlighting its potential to transform academic narrative construction.
PaperBridge: Crafting Research Narratives through Human-AI Co-Exploration
The paper "PaperBridge: Crafting Research Narratives through Human-AI Co-Exploration" discusses a system called PaperBridge designed to aid researchers, particularly those in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), in organizing their publications into coherent research narratives. This effort addresses the complex challenge of synthesizing a diverse body of work into narratives that are meaningful across different communication contexts such as job talks, grant proposals, or public engagement scenarios.
System Design and Workflow
PaperBridge integrates human-AI collaboration by providing a bi-directional analysis engine powered by LLMs to support both top-down and bottom-up exploration strategies:
- Paper Management: The system starts by allowing the user to import their publications and categorize them based on thematic clusters relevant to their research goals.
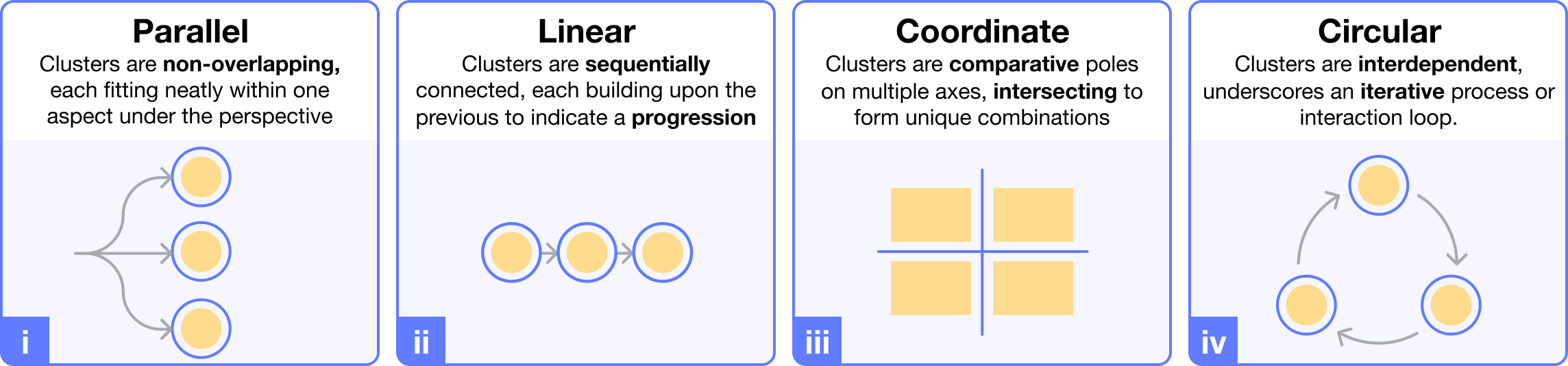
- Narrative Exploration: Users can explore different narrative frameworks (e.g., parallel, linear, circular, and coordinate) to see how their work can be interconnected to form various high-level structures.
- Frameworks and Perspectives: PaperBridge suggests multiple narrative perspectives for each framework, offering contribution statements and thematic clusters to help users frame their research story. The perspectives are provided as "sparks," which are keywords designed to inspire new ways of organizing papers.
- Organization and Rationale Exploration: Users can refine the system's suggestions by editing themes, re-assigning papers to different clusters, and exploring rationale strategies to justify the importance of their narrative stance.
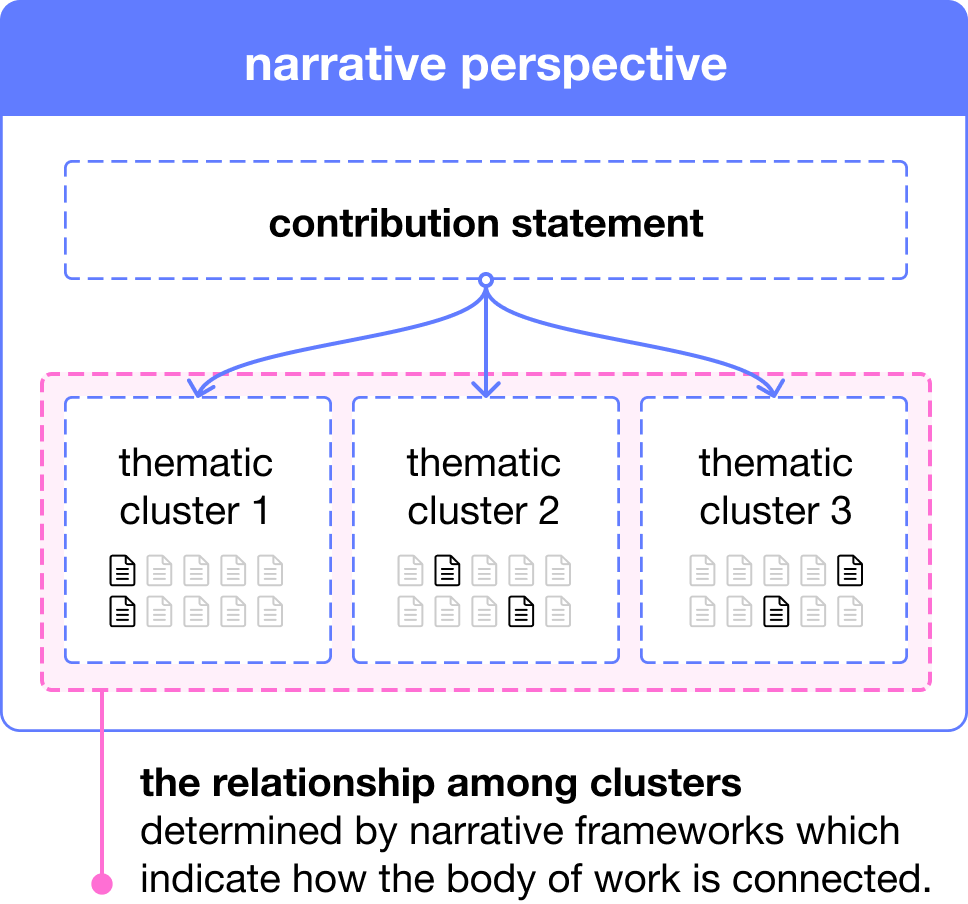
Figure 1: A narrative perspective is composed of three types of components: a contribution statement, thematic clusters, and individual papers, which are organized within the clusters to articulate the overarching themes.
Bi-directional Analysis Engine
PaperBridge uses a bi-directional analysis engine capable of top-down and bottom-up processes:
Evaluation and Findings
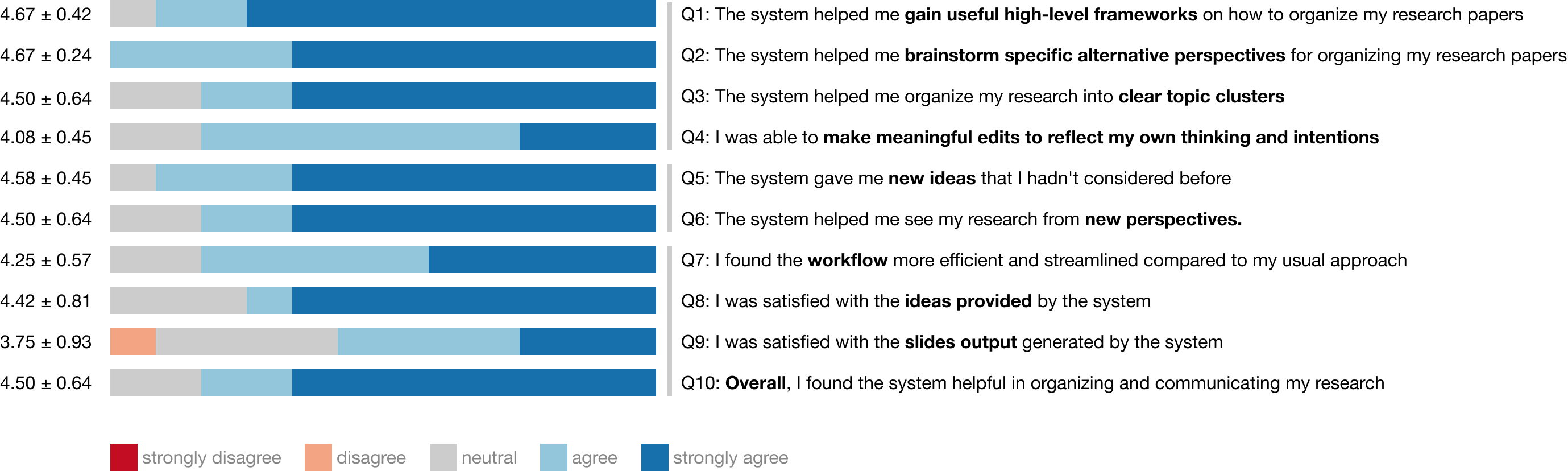
The evaluation included 12 HCI researchers and focused on usability and exploration support. Key findings were:
Discussion and Implications
The research highlights the potential of integrating AI with human creativity in academic workflows. The system's design reflects an understanding of the complexity involved in narrative construction for research communication:
- Frameworks as Cognitive Scaffolds: The defined frameworks serve not only as templates for organizing research but also as cognitive tools that guide users in abstracting and synthesizing their work.
- Narrative Ideation as Reflective Process: Exploration within PaperBridge sparked introspection, allowing researchers to conceptualize their contributions from fresh perspectives.
- Challenges: The breadth of papers vis-à-vis thematic coherence affects the generation of sparks, indicating a need for adaptive systems that can tailor suggestions based on the input's diversity.
Conclusion
PaperBridge exemplifies how AI can support the creation of research narratives by enabling structured exploration and reflection on academic work. By facilitating both top-down and bottom-up explorations, it empowers researchers to craft diverse and coherent narratives, adapting their scholarly output to varied audiences and communication needs. Future work can broaden its reach across disciplines, enhancing adaptability, and deepening AI-human interaction models in academic settings.