- The paper demonstrates that LLMs substantially enhance AIOps tasks by combining traditional system data with human-generated information for improved failure detection and diagnostics.
- It employs advanced prompt-based methods and fine-tuning techniques to extract structured insights from logs and other diverse data sources.
- The study identifies key challenges such as high computational costs and integration complexities, paving the way for future optimizations in automated IT operations.
A Survey of AIOps in the Era of LLMs
Introduction
The emergence of LLMs, in particular their robust natural language processing capabilities, has brought significant attention to their potential application in Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps). This paper offers a comprehensive survey of how LLMs impact AIOps tasks, spanning from failure detection to root cause analysis and automated remediation.
The rise of LLMs has expanded the data sources utilized in AIOps. Traditional system-generated data, such as metrics, logs, and traces, are complemented by human-generated data like software documentation and incident reports. A notable advancement is in processing traditional data sources, where techniques like log parsing have been augmented with LLMs to provide structured representations of log data. Studies have demonstrated that LLMs can successfully parse logs with high accuracy through methods such as prompt-based adaptive parsing, hierarchical candidate sampling, and the use of in-context learning.
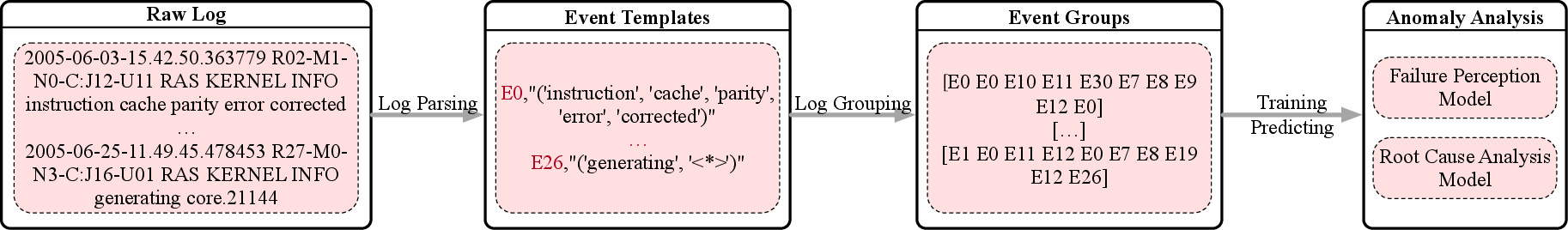
Figure 1: Log-based Failure Perception and Root Cause Analysis: The Common Workflow.
Moreover, new data sources have been integrated, such as configuration and source code, enhancing failure diagnosis through deeper semantic understanding and automated code analysis. This expanded data usage not only enriches diagnostic capabilities but also leverages LLMs' pre-trained knowledge for efficient anomaly detection and failure analysis.
Evolving Tasks in AIOps with LLMs
LLMs have significantly transformed traditional AIOps tasks. While failure perception tasks such as detection and prediction continue to evolve, new opportunities have arisen in root cause analysis through the use of LLMs for generating detailed root cause reports. This involves the synthesis of complex data into natural language explanations, assisting operators in understanding system failures more effectively than traditional methods, which often relied on predefined categorizations and simpler models.
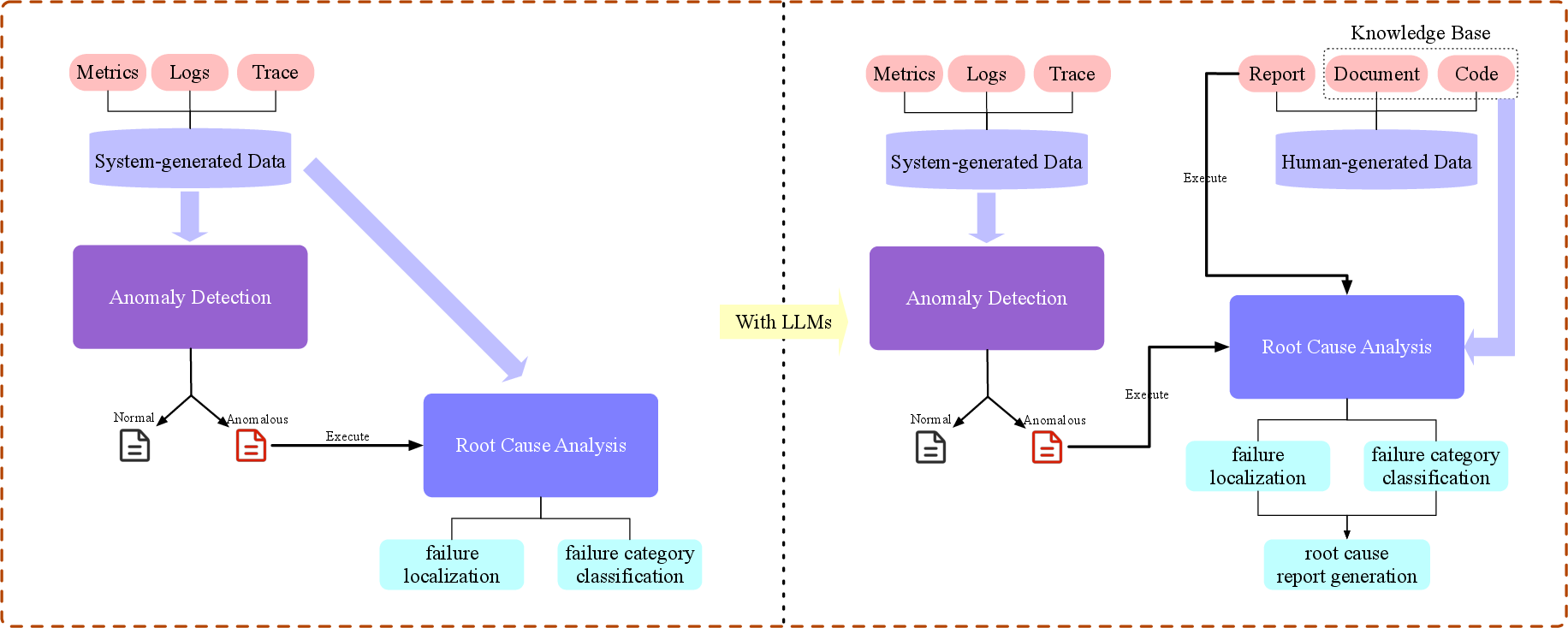
Figure 2: Evolution of Root Cause Analysis with the Rise of LLMs.
In the domain of Assisted Remediation, LLMs facilitate automated script generation and command recommendation, streamlining the remediation process. LLMs can generate, validate, and even execute remediation scripts, thereby increasing automation levels significantly compared to previous manual-intensive processes.
LLM-based Methods for AIOps
Various LLM-based methods have been developed, encompassing foundation models, fine-tuning approaches, and prompt-based methods. Foundation models provide pre-trained capabilities that can be adapted to specific AIOps tasks through full or parameter-efficient fine-tuning. Prompt-based approaches, leveraging in-context learning and task instruction prompting, enable LLMs to perform tasks without extensive retraining, utilizing carefully constructed prompts to guide model responses.
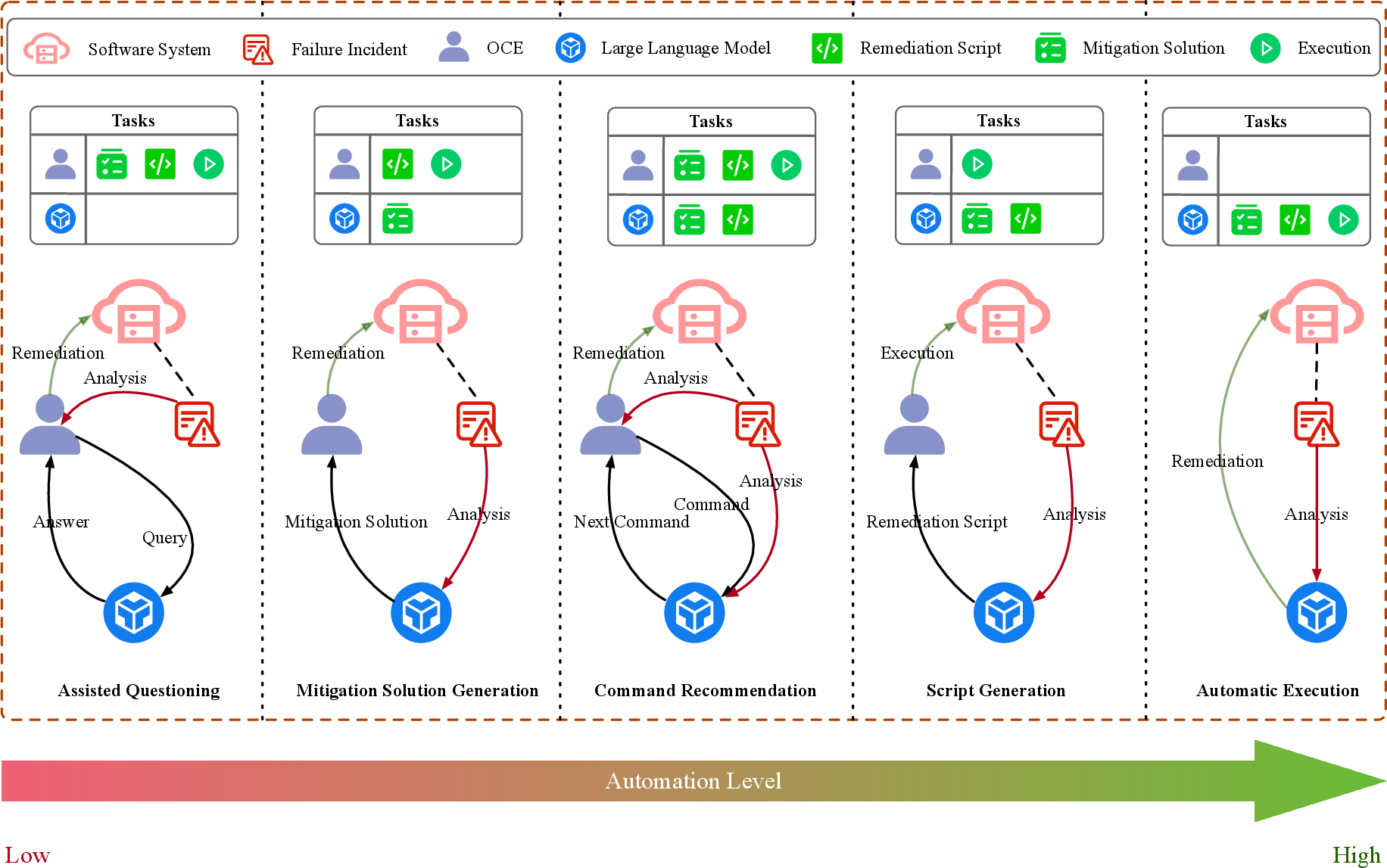
Figure 3: Various Types of Auto Remediation Approaches.
Embedding-based methods transform AIOps data into semantic representations amenable to LLM interpretation, while knowledge-based approaches integrate historical data retrieval and tool augmentation to enhance model reasoning and decision-making.
Evaluating LLM-based AIOps
The integration of LLMs in AIOps has necessitated new evaluation methodologies, including emergent metrics for generation tasks and manual evaluation for interpretative tasks demanding human judgment. While traditional metrics persist for classification tasks, manual evaluations now play a critical role in assessing generation quality and contextual relevance in LLM-driven solutions.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the remarkable progress, challenges such as high computational costs and the integration of more diverse data sources remain. Further research is needed to optimize LLM computational efficiency and develop methods for incorporating traces data effectively. Additionally, enhancing LLM's generalizability during software evolution and integrating them within existing AIOps toolchains are crucial for advancing automated IT operations management.
Conclusion
The application of LLMs in AIOps holds substantial promise for enhancing IT operations through improved anomaly detection, diagnostics, and automated remediation. Nonetheless, addressing existing challenges and optimizing the synergy between LLMs and traditional approaches will be pivotal for realizing their full potential in operational settings.




