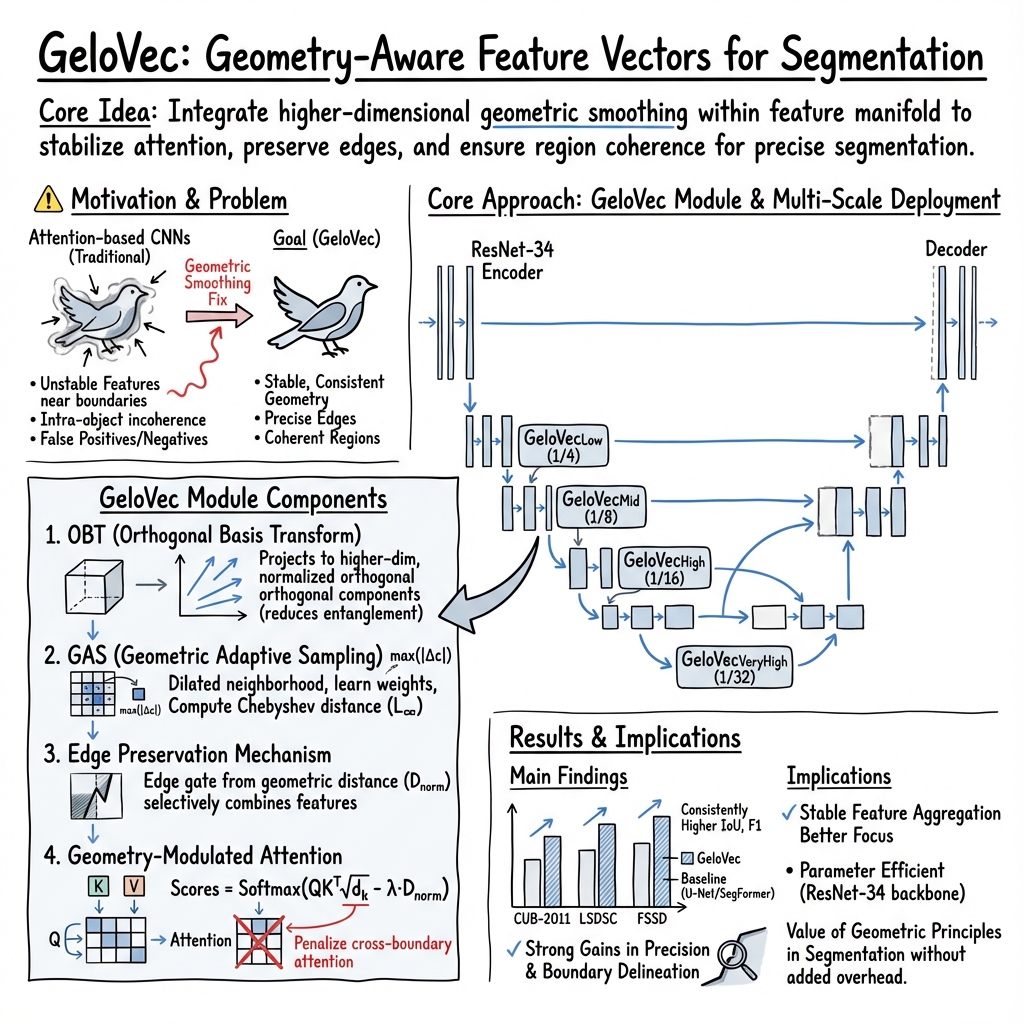
- The paper introduces a GeloVec module that integrates geometric smoothing into a UNet-based model, markedly improving feature coherence and boundary detection.
- It employs adaptive Chebyshev distances via Geometric Adaptive Sampling to preserve fine-grained image details and enhance segmentation precision.
- Experimental results show that GeloVec achieves an IoU of 83.6% and a precision of 92.1%, outperforming conventional models on benchmark datasets.
Introduction
The paper "GeloVec: Higher Dimensional Geometric Smoothing for Coherent Visual Feature Extraction in Image Segmentation" introduces a novel approach to image segmentation that leverages geometric smoothing techniques within a deep neural network framework. Image segmentation, the process of assigning a class label to each pixel in an image, is crucial in computer vision, with significant applications ranging from medical imaging to autonomous vehicles.
Throughout the evolution of segmentation techniques, CNNs have been pivotal, particularly the advancements achieved through architectures like the Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) and dilated convolutions. These approaches have been fundamental in dense prediction tasks, yet challenges persist in achieving consistent feature representation, especially around object boundaries. Traditional methods, including attention-based CNNs, often struggle with maintaining boundary integrity and intra-object homogeneity.
In response, GeloVec employs a higher-dimensional geometric framework to enhance the stability of feature extraction processes. The integration of geometric principles, such as those seen in non-Euclidean domains, has gained traction as a means to address the limitations faced by conventional segmentation strategies.
Methodology
Architecture Overview
GeloVec's architecture is anchored to a UNet-based encoder-decoder model, utilizing a ResNet-34 backbone for robust feature extraction with manageable computational requirements.

Figure 1: Architecture Overview.
The encoder pathway progressively downsamples the input image while increasing feature complexity using ResNet-34 blocks. GeloVec modules, designed to improve feature coherence via geometric smoothing, are integrated into the encoder pipeline. These modules refine feature maps before they are transmitted through skip connections to the decoder.
The encoder-decoder synergy enables detailed spatial information retention. Skip connections ferry geometrically enhanced feature maps from encoder layers to the decoder, enriching the segmentation output with context that preserves boundary detail and regional coherence.
GeloVec Module
Central to this approach is the GeloVec module, which introduces geometric-aware transformations to enhance segmentation precision. Deployed across several scales, these modules serve to balance fine-grained boundary detail with high-level semantic coherence:
- Orthogonal Basis Transform (OBT): Projects features into a space with orthogonally balanced components, enhancing discriminative capacity.
- Geometric Adaptive Sampling (GAS): Utilizes adaptive Chebyshev distance to inform attention mechanisms, preserving boundary and regional features by emphasizing differences in feature space.
- Edge Preservation Mechanism: Ensures continuity of boundary information through adaptive combinations of edge-focused and original feature maps.
Experiments and Results
GeloVec's efficacy was assessed across benchmark datasets including Caltech Birds-200, LSDSC, and FSSD. Across these datasets, GeloVec demonstrated superior performance, achieving mean Intersection over Union (IoU) scores that surpass state-of-the-art models by notable margins, substantiating its innovative design.
For instance, GeloVec attained an IoU of 83.6% on the CUB-200-2011 dataset, marking a significant improvement over established models like U-Net and DeepLabV3+. Additionally, a precision score of 92.1% underscores its robustness in accurately delineating complex boundaries.


Figure 2: Attention Values Distribution Comparison
Moreover, Figure 2 illustrates the effective concentration of attention within semantically rich regions, a contrast to the dispersed focus exhibited by traditional approaches. The precision in boundary delineation, especially across complex environmental transitions as seen in the FSSD dataset, further validates GeloVec's potential. The attention values distribution comparison reflects the model's enhanced capability to focus computational resources on relevant image areas, yielding more precise segmentation results.


Figure 3: FSSD Dataset Segmentation Results.
Conclusion
GeloVec represents a significant advancement in semantic image segmentation by integrating geometric principles into deep learning frameworks. The incorporation of methods such as adaptive Chebyshev distances and multispatial transformations results in a more stable and accurate feature extraction mechanism, significantly improving segmentation performance.
The GeloVec model paves the way for future exploration into geometric deep learning applications, asserting that the incorporation of spatial understanding can substantially refine segmentation tasks without incurring additional computational burdens. With its demonstrated success across diverse datasets, GeloVec stands as a promising avenue for future research and application in the domain of semantic segmentation.