- The paper introduces a multimodal dataset capturing human reactions during robot failures in collaborative tasks.
- The study employs intentional robotic failures and varied explanation strategies with 55 participants using comprehensive visual, audio, and facial analyses.
- The dataset paves the way for designing adaptive HRI systems and predictive models to enhance trust and resilience in human-robot collaboration.
REFLEX Dataset: A Multimodal Dataset of Human Reactions to Robot Failures and Explanations
Introduction
The "REFLEX Dataset: A Multimodal Dataset of Human Reactions to Robot Failures and Explanations" focuses on the critical aspect of Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), particularly when robots face operational challenges. Human collaboration with robots in various sectors necessitates the ability of robots to both recognize failures and provide explanations to maintain trust and effective cooperation. The REFLEX dataset provides a comprehensive resource for analyzing human responses to robot failures and the explanations provided for these failures in collaborative settings.
Objectives and Contributions
The dataset aims to facilitate research on human reactions to robotic failures, addressing both initial failures and their explanations. This will enable the development of robust and adaptive robotic systems capable of maintaining relationships even during repeated failures. Through this multimodal, richly annotated dataset, REFLEX intends to contribute to improving HRI systems by anticipating and managing such failure contexts effectively.
Dataset Overview
The REFLEX dataset captures human reactions in a typical Human Robot Collaboration (HRC) task (Figure 1).

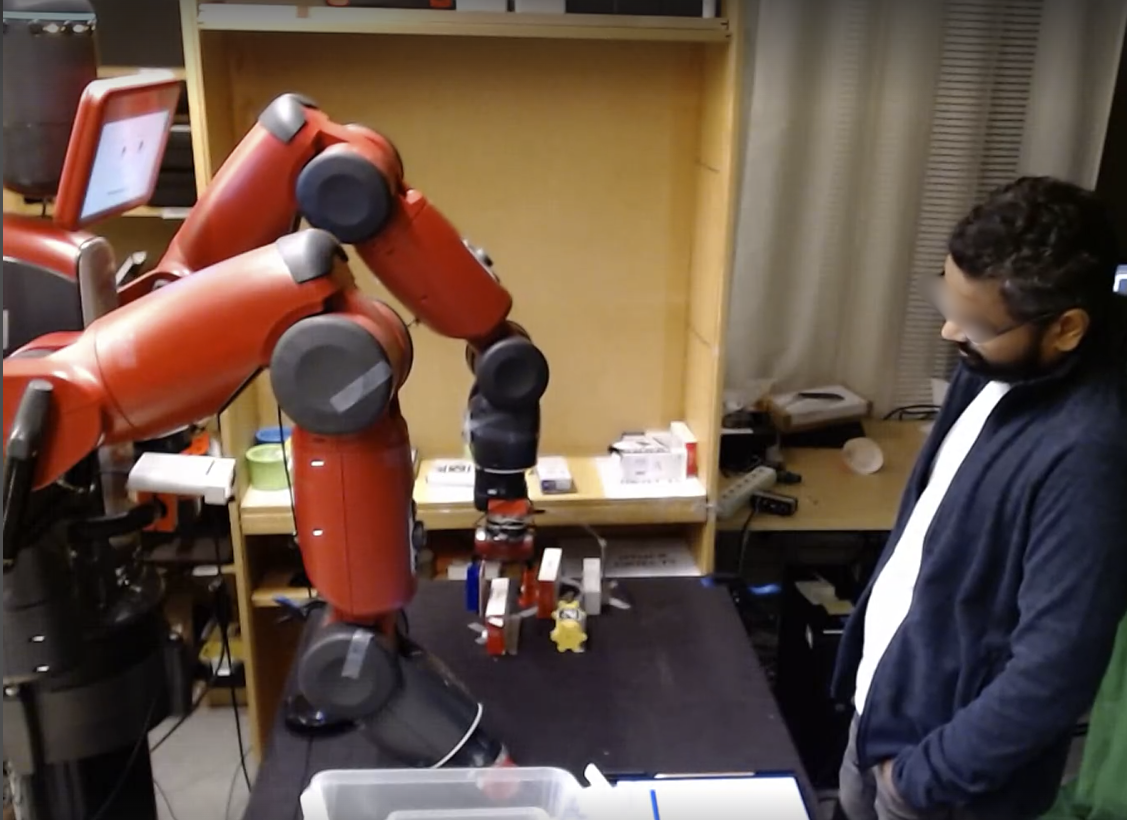
Figure 1: Human Robot Collaboration (HRC) task captured by 2 cameras: Camera 1 (left) focused on the user {additional_guidance} Camera 2.
Data Collection and Methodology
Data is collected through user studies involving 55 participants interacting with a robot capable of performing object-handling tasks. Cameras focused on both the user and the robot to capture reactions during the experiment. The robotic system was programmed to intentionally fail at certain tasks, such as Picking, Carrying, and Placing objects to observe human responses to these failures and how different explanation strategies affected user satisfaction.
Explanation Strategies
The robot employed various explanation strategies, which included fixed levels (Low, Medium, High) and decaying levels over successive interactions. The explanation scenarios are detailed to allow for analysis of human-robot trust dynamics over repeated failures (Table 1).
Multimodal Data Components
The dataset consists of the following components:
- Visual Representation: Anonymized video of the user and robot interaction.
- Speech Data: Transcriptions and prosodic analysis of user-robot dialogues.
- Facial Data: Extraction of facial landmarks and action units using OpenFace, providing a detailed view of user emotions and expressions.
- Gaze and Head Data: Eye and head movements provide insights into attention and engagement during tasks.
- Body Pose Data: Captures upper body movements to infer interaction nuances.
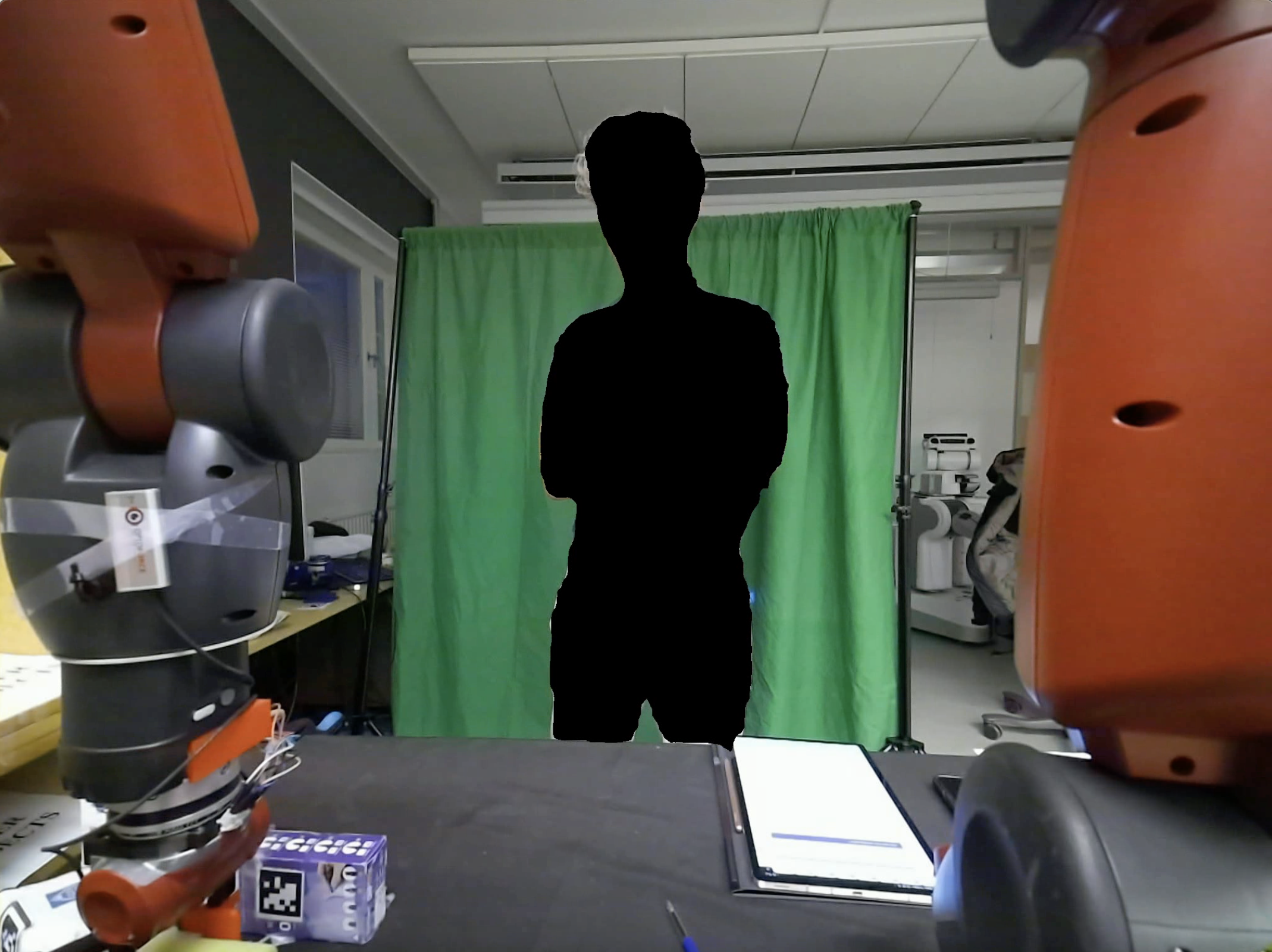
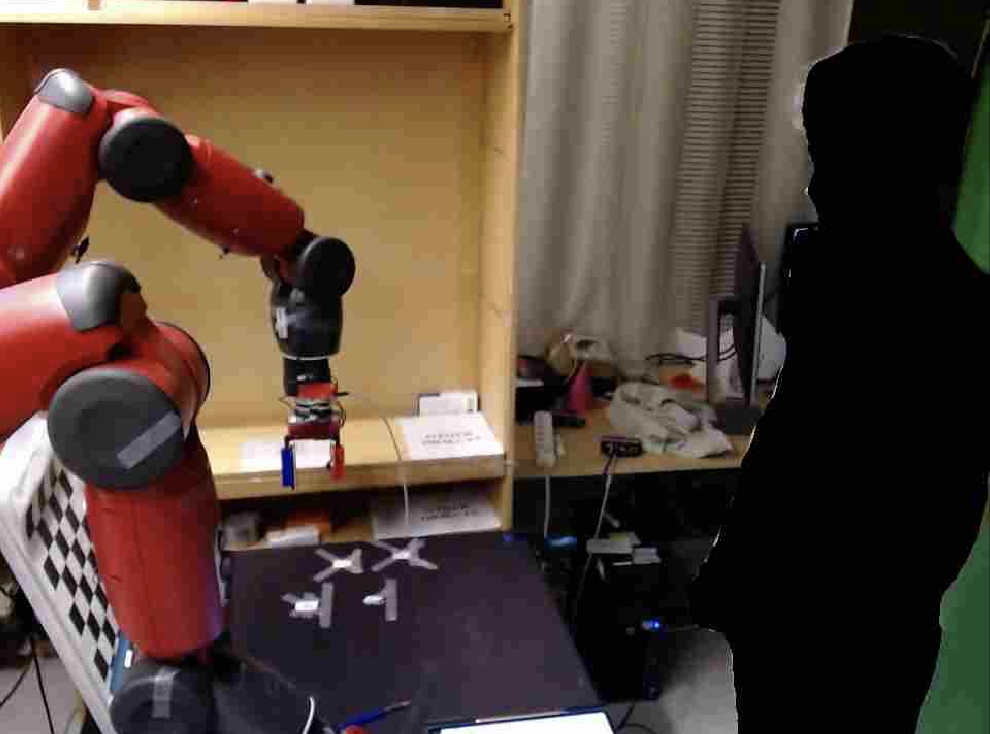


Figure 2: Visual Representation of the HRC Task, user-maskedd view: Camera 1 (left) focused on the user and Camera 2 (right).
Analyzing Human Reactions
REFLEX provides a nuanced analysis of human reactions categorized as Positive, Negative, and Skeptical emotions during and after robot failures, captured using facial emotion analysis tools. The dataset highlights variations in emotional responses to different failure types and resolutions (Figure 3), providing a basis for understanding the efficacy of various explanation strategies.
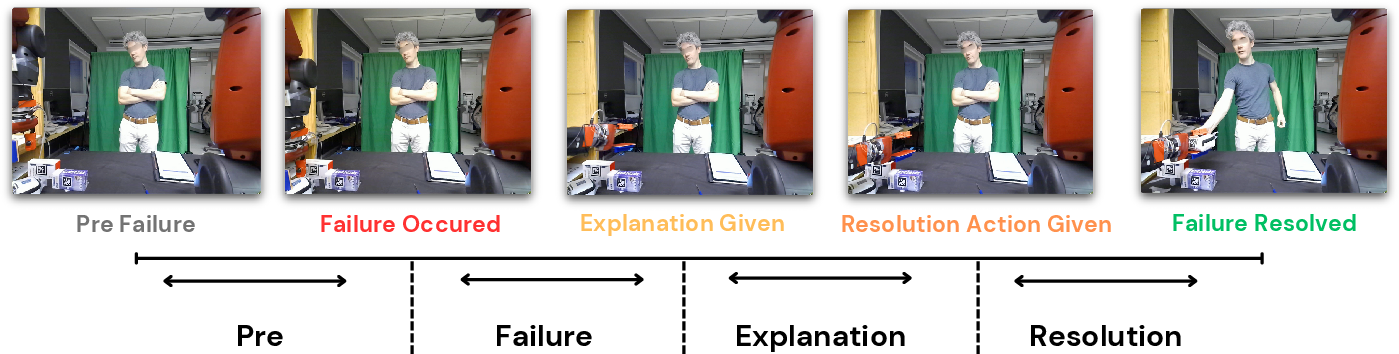
Figure 3: Human Reaction Modeling for Failure Explanation
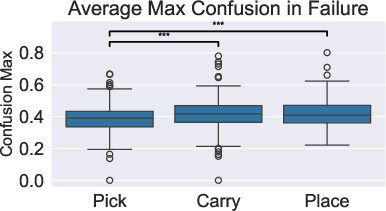
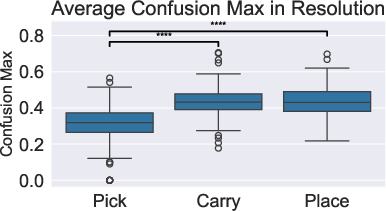
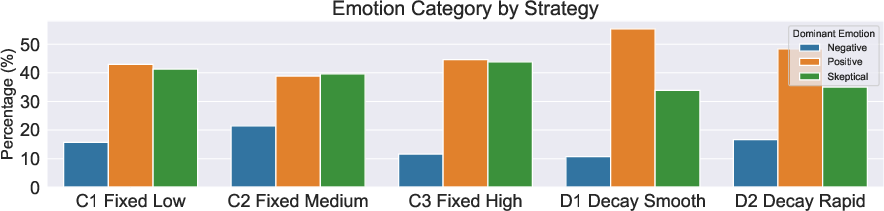
Figure 4: Analyzing Human Reactions by Detected Facial Emotions. Reaction to Different Robotic Failures by comparing likelihood of confusion in: (a) Failure Phase and (b) Resolution Phase, (c) Reaction to Different Robotic Explanations for Failures, Dominant emotional category seen across different explanation strategies in explanation and resolution phase.
Practical Implications
The dataset aids in designing HRI systems that adjust explanation levels according to user emotional states and helps strategize explanation strategies in long-term interactions, crucial for maintaining effective human-robot collaboration in environments with varied and complex tasks.
Conclusion
REFLEX introduces a rich dataset that is pivotal for advancing explainable AI and robust HRI systems by understanding nuanced human reactions to robotic failures and explanations. Its application extends to developing predictive models and adaptive strategies in real-world robot deployment, ensuring trust and positive interaction outcomes.
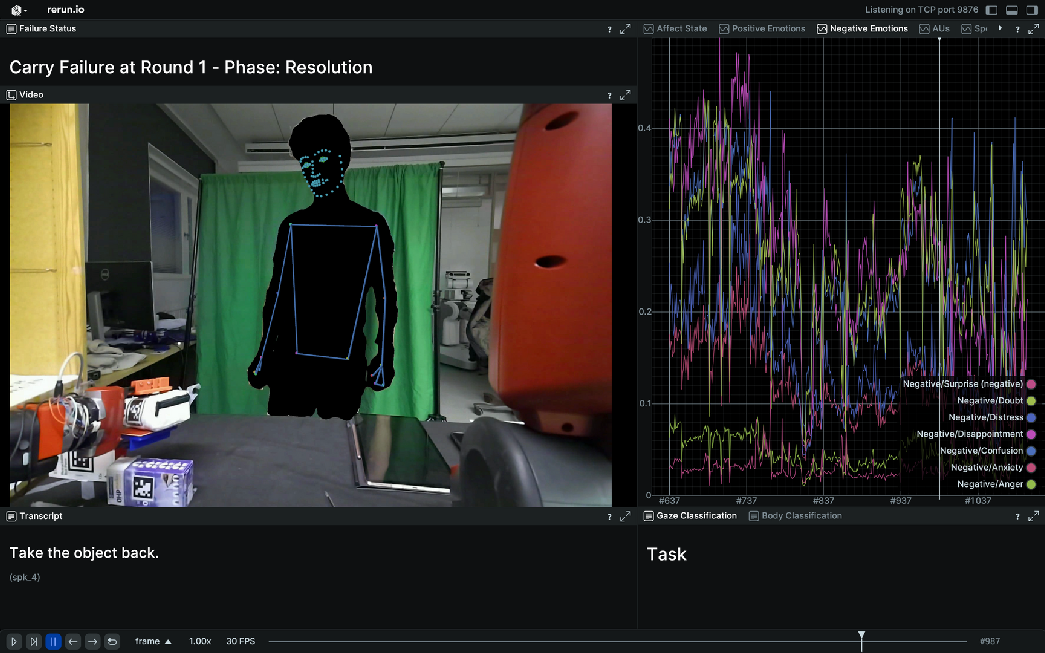
Figure 5: Multimodal Visualization of the Participant's Data










