Intelligent Control in 6G Open RAN: Security Risk or Opportunity?
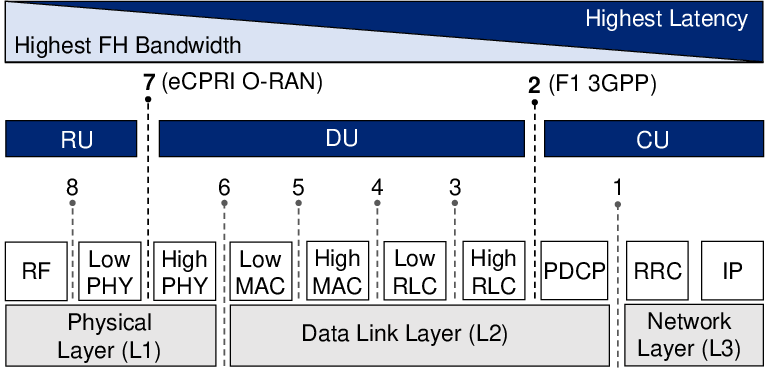
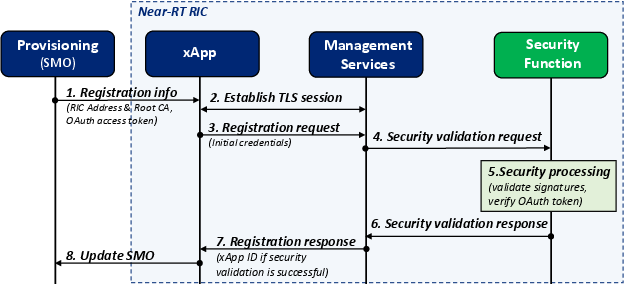
Abstract: The Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN) framework, emerging as the cornerstone for AI-enabled Sixth-Generation (6G) mobile networks, heralds a transformative shift in radio access network architecture. As the adoption of Open RAN accelerates, ensuring its security becomes critical. The RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) plays a central role in Open RAN by improving network efficiency and flexibility. Nevertheless, it also brings about potential security risks that need careful scrutiny. Therefore, it is imperative to evaluate the current state of RIC security comprehensively. This assessment is essential to gain a profound understanding of the security considerations associated with RIC. This survey combines a comprehensive analysis of RAN security, tracing its evolution from 2G to 5G, with an in-depth exploration of RIC security, marking the first comprehensive examination of its kind in the literature. Real-world security incidents involving RIC are vividly illustrated, providing practical insights. The study evaluates the security implications of the RIC within the 6G Open RAN context, addressing security vulnerabilities, mitigation strategies, and potential enhancements. It aims to guide stakeholders in the telecom industry toward a secure and dependable telecommunications infrastructure. The article serves as a valuable reference, shedding light on the RIC's crucial role within the broader network infrastructure and emphasizing security's paramount importance. This survey also explores the promising security opportunities that the RIC presents for enhancing network security and resilience in the context of 6G mobile networks. It outlines open issues, lessons learned, and future research directions in the domain of intelligent control in 6G open RAN, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic landscape.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.