- The paper demonstrates how instruction tuning significantly improves LLM alignment with user intents through supervised fine-tuning strategies.
- It employs data integration and LLM-generated outputs to construct diverse datasets, enhancing model adaptability across various domains.
- Efficient techniques like LoRA and QLORA, coupled with comprehensive evaluation frameworks, optimize tuning performance while minimizing resource usage.
Instruction Tuning for LLMs: A Survey
The paper "Instruction Tuning for LLMs: A Survey" (2308.10792) provides a comprehensive analysis of the evolving field of instruction tuning (IT) as applied to LLMs. It focuses on enhancing the capabilities and controllability of LLMs by bridging the gap between their training objectives and user requirements through instruction tuning, also known as supervised fine-tuning (SFT).
Introduction
The paper begins by highlighting the significance of instruction tuning in addressing the inherent mismatch in objectives between LLM training and user interaction. Most LLMs are trained to minimize contextual word prediction errors, which does not inherently align with user intents of following instructions helpfully and safely. Instruction tuning addresses this by training LLMs on datasets consisting of instruction-output pairs, thus aligning the model's responses more closely with human expectations.
Methodology
The general pipeline for instruction tuning is illustrated prominently (Figure 1). It involves constructing high-quality datasets and employing various fine-tuning techniques to enhance model performance.
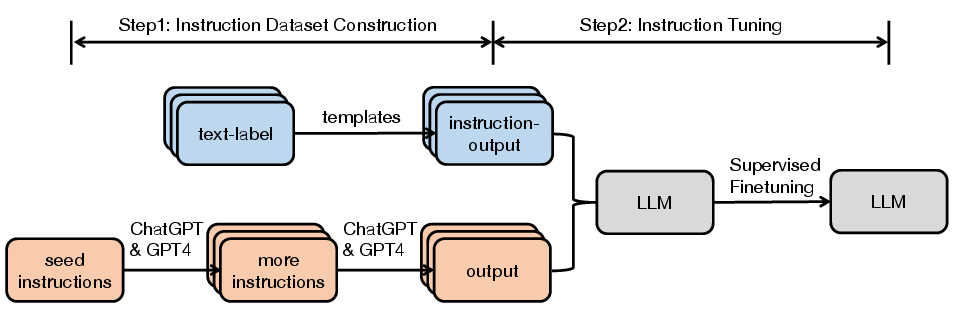
Figure 1: General pipeline of instruction tuning.
Instruction Dataset Construction
Datasets for instruction tuning consist generally of three components: instructions, optional input context, and expected outputs. There are two main approaches to constructing these datasets:
- Data Integration: This involves collecting (instruction, output) pairs from existing annotated natural language datasets, transforming them into the instruction format using predefined templates.
- LLM-Generated Outputs: Generating responses using state-of-the-art LLMs for pre-existing, manually written or machine-generated instructions to rapidly create diverse datasets.
Several renowned datasets such as Flan, P3, and Super-Natural Instructions leverage these methodologies and have significantly contributed to the adaptability and utility of instruction-tuned LLMs.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite its advantages, instruction tuning presents challenges such as crafting high-quality instructions, ensuring coverage, and addressing the concern that models may overfit to tasks heavily supported in the training data. Criticisms also extend to possible superficial alignment, where models learn surface patterns without deep comprehension, as discussed in the literature [Kung2023DoMR].
Multi-Modality and Domain-Specific Tuning
The application of IT extends to multiple modalities including image, speech, and video data, as well as specific domains. This adaptability enhances model performance across diverse sectors such as medical, dialogue systems, and code generation. Models like MathGenie (Figure 2) have shown significant improvements in domain-specific reasoning and complex task execution.
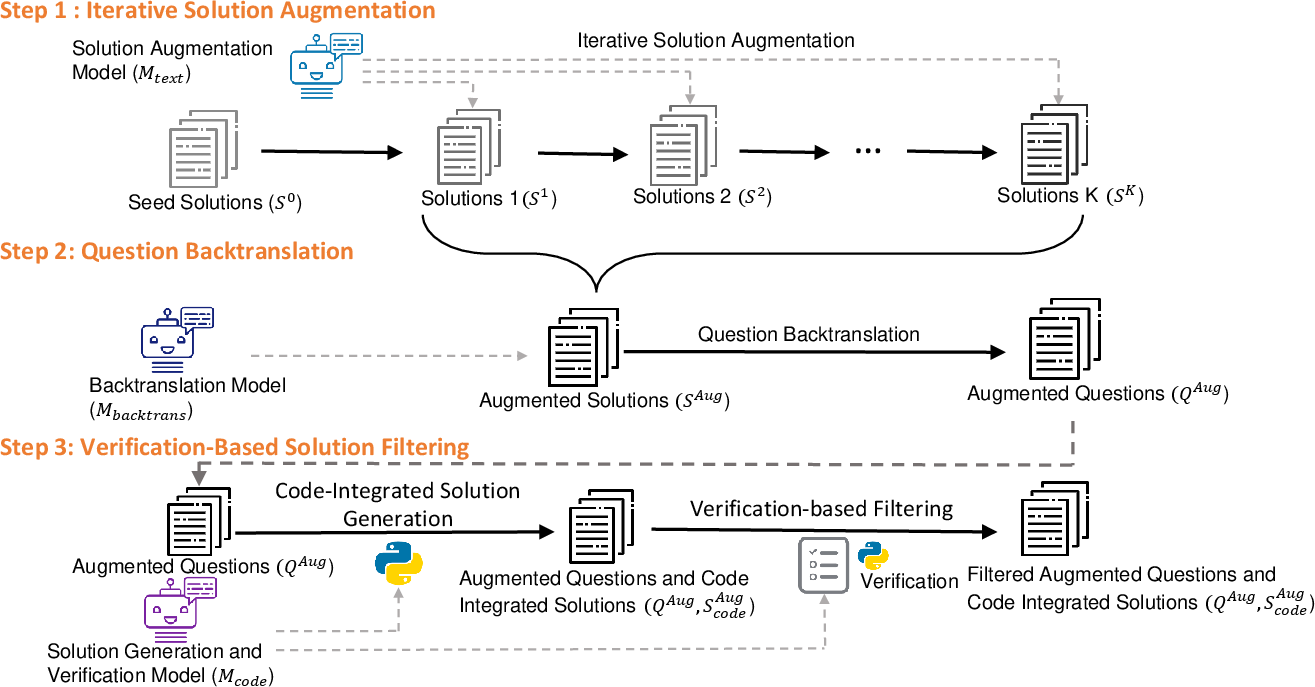
Figure 2: Framework of MathGenie.
Efficient Tuning Techniques
Several optimization techniques such as LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) [hu2021lora] and QLORA [dettmers2023qlora] are discussed for making instruction tuning more resource-efficient. These strategies focus on minimizing computational requirements while maximizing model performance during the tuning process, thereby enabling broader accessibility and deployment of tuned LLMs.
Evaluation and Analysis
The paper suggests comprehensive evaluation frameworks like HELM [Liang2022HolisticEO] and highlights various LLM evaluation strategies. These evaluations ensure robust understanding, capability measurement, and assessment of alignment strategies to enhance the reliability of LLM outputs.
Conclusion
The survey underscores the transformative potential of instruction tuning in aligning LLMs with human intentions more effectively. It encourages further research into inventive methodologies for dataset construction, explores novel fine-tuning techniques, and propagates deeper analyses to bridge current gaps, thereby enhancing both theoretical understanding and practical application in AI systems. Future work may focus on addressing criticisms regarding instruction tuning's superficial alignment and exploring modular tuning approaches for broader generalization and real-world deployment.



