- The paper introduces ASFD, an automated face detection framework that leverages neural architecture search and novel loss functions to enhance detection accuracy and speed.
- It features the Auto-FEM module for multi-scale feature fusion and compound scaling to optimize network depth, width, and resolution.
- Experimental results show ASFD outperforming state-of-the-art detectors, achieving high mAP scores on benchmarks like WIDER FACE and FDDB with rapid inference speeds.
Automatic and Scalable Face Detector (ASFD): A Technical Overview
This essay provides an analysis of the "ASFD: Automatic and Scalable Face Detector" (2003.11228). The paper proposes an innovative approach to face detection, leveraging automated neural architecture search and novel loss functions to enhance both performance efficiency and accuracy. The proposed Automatic and Scalable Face Detector (ASFD) sets new benchmarks in face detection performance, particularly across challenging datasets such as WIDER FACE and FDDB.
Proposed Methodology
Automatic Feature Enhance Module (Auto-FEM)
The ASFD introduces an Auto-FEM designed through differential architecture search. This module aims to improve multi-scale feature fusion and context enhancement, crucial for face detection due to the diverse scales and poses of faces in varying lighting and occlusion conditions. Different from traditional hand-crafted feature enhancement techniques, Auto-FEM optimizes the feature module configurations, significantly enhancing detection capabilities.

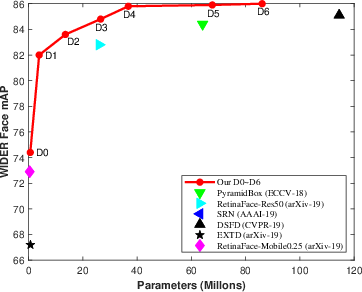

Figure 1: Illustration of the mean Average Precision (mAP) regarding the number of parameters, FLOPs, and GPU latency evaluated with single-model single-scale on the validation subset of WIDER FACE dataset. ASFD D0-D6 outperforms prior detectors in these aspects.
Distance-based Regression and Margin-based Classification (DRMC) Loss
The paper introduces the DRMC loss to tackle inaccuracies in bounding box prediction and enhance discriminative feature learning. Inspired by recent advancements in IoU-based losses, the DRMC combines distance-based regression components with margin-based classification losses, allowing for more precise localization and robust face-background discrimination.
Compound Scaling for Model Efficiency
Building upon methodologies such as EfficientNet and EfficientDet, ASFD employs compound scaling to proportionally adjust the network's depth, width, and resolution. This ensures optimized performance across different computational environments, from mobile devices to large-scale data centers.
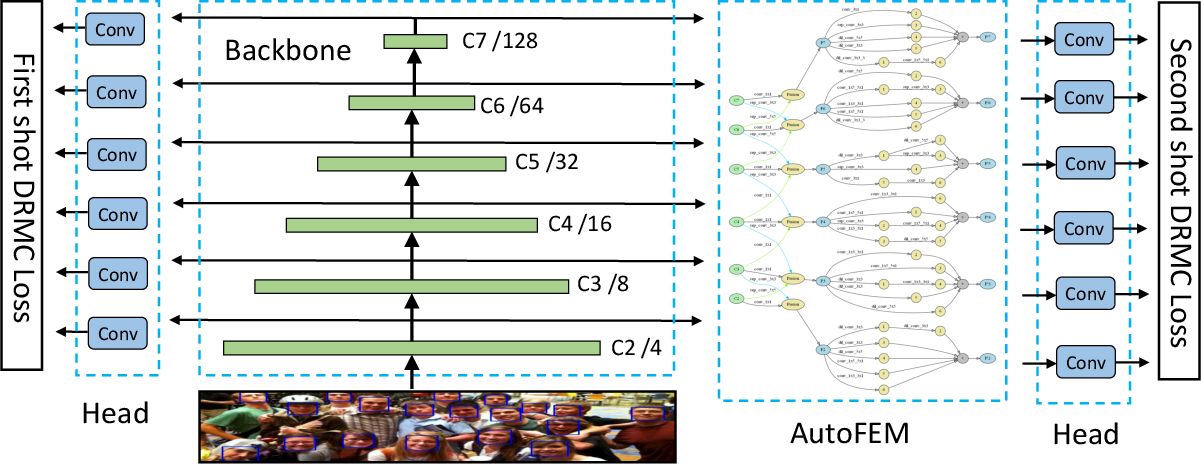
Figure 2: Illustration on the framework of ASFD, showing the placement of AutoFEM alongside a feedforward backbone.
Experimental Results
The ASFD models, specifically ASFD-D6, demonstrated superior face detection performance across standard datasets. On the WIDER FACE validation dataset, ASFD-D6 achieved mean Average Precision (mAP) scores of 97.2%, 96.5%, and 92.5% across Easy, Medium, and Hard subsets, respectively. Additionally, ASFD models maintained high inference speeds, with ASFD-D0 achieving over 120 FPS using a lightweight backbone such as MobileNet, underscoring the framework's efficiency.
Comparison with State-of-the-Art Detectors
ASFD significantly outperforms leading detectors like DSFD and RetinaFace, establishing new benchmarks in both mAP scores and FPS metrics. The integration of Auto-FEM and DRMC loss has been pivotal in realizing these performance gains, as evidenced by extensive experiments conducted on both WIDER FACE and FDDB datasets.
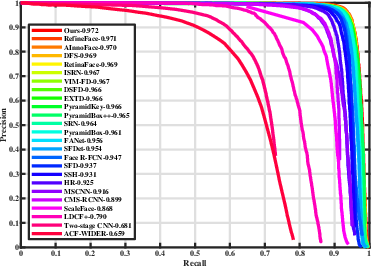


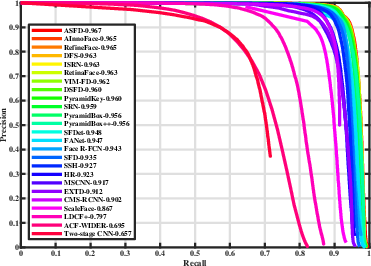
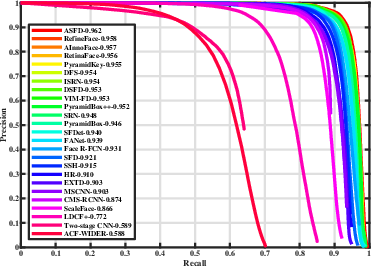

Figure 3: Precision-recall curves on WIDER FACE, indicating the superior precision of ASFD models.
Scalability and Efficiency
The ASFD's design allows it to be scaled for different application scenarios without compromising accuracy, a key advantage over conventional detectors. By tailoring the network width and depth, ASFD optimizes resource consumption according to specific deployment needs.
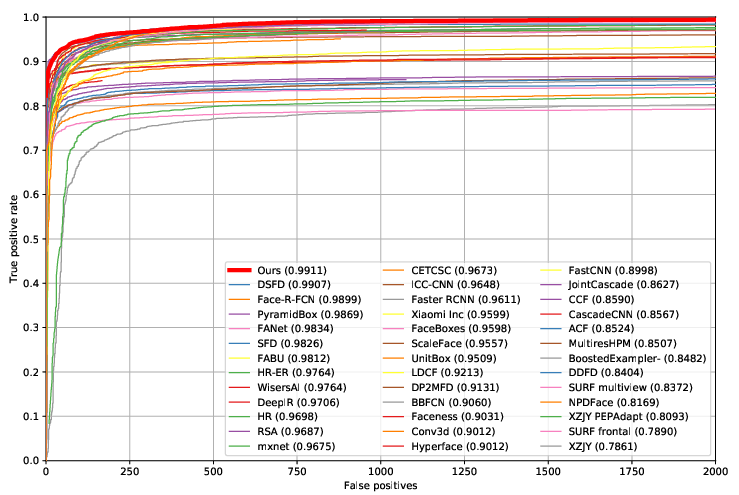
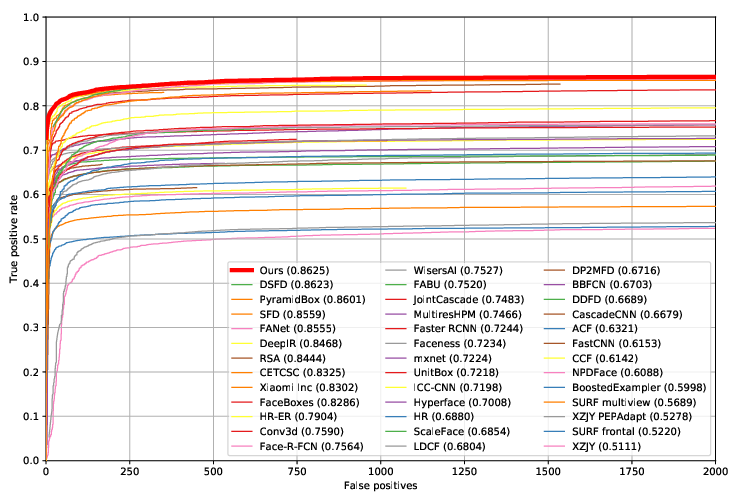
Figure 4: ROC curves on the FDDB dataset, showcasing ASFD's strong performance in face detection challenges.
Conclusion
The ASFD framework marks a significant advancement in the field of face detection, presenting a comprehensive solution that balances accuracy and computational efficiency. Through the introduction of the Auto-FEM, DRMC loss, and compound scaling, the ASFD model achieves state-of-the-art results on challenging benchmarks while maintaining high-speed inferencing capabilities.
The implications of this work are vast, offering practical applications in surveillance, autonomous vehicles, and various real-time AI deployment scenarios. Future research may explore further enhancements in neural architecture search algorithms and loss function designs to build upon the foundational work established by ASFD. The significant strides made by this model establish it as a pivotal contribution to the ongoing development of robust face detection systems.













