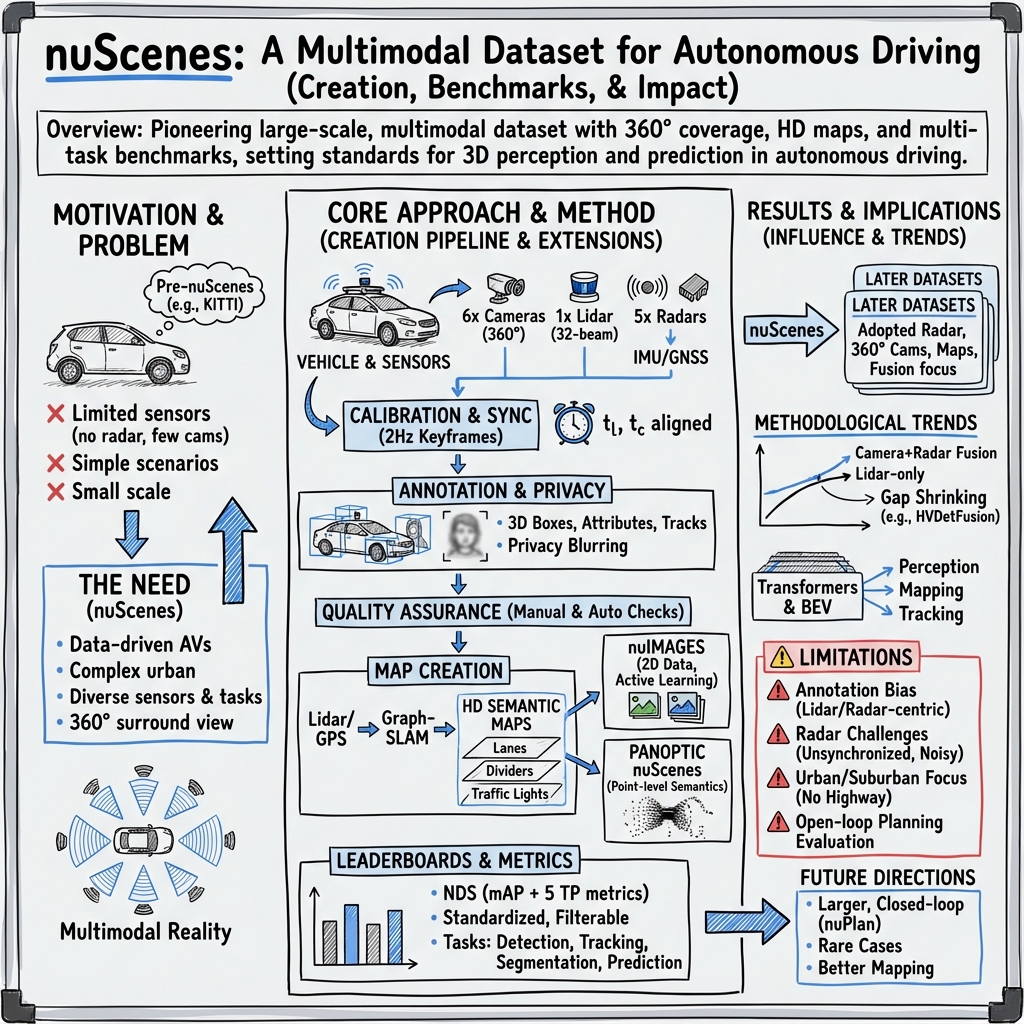
- The paper demonstrates how the nuScenes dataset enhances AV research through advanced multimodal sensor fusion and precise calibration techniques.
- It presents comprehensive data annotation methods and quality controls that ensure high accuracy in object detection, tracking, and localization.
- The study outlines benchmark challenges and dataset extensions, highlighting both progress and remaining obstacles in autonomous driving.
Summary of "nuScenes Revisited: Progress and Challenges in Autonomous Driving"
The paper "nuScenes Revisited: Progress and Challenges in Autonomous Driving" (2512.02448) presents a comprehensive revisitation of the nuScenes dataset, detailing its foundational role in advancing autonomous vehicle (AV) research. The authors explore the dataset's conception, its expansive influence on subsequent datasets, and the numerous standards it established within the AV community. This essay explores the dataset's structure, technical intricacies, and its extensions, while emphasizing its implications for AV research and the challenges it addresses.
Dataset Overview
nuScenes, a large-scale multimodal autonomous driving dataset, was designed to overcome the limitations of previous datasets such as KITTI. It comprises 1000 driving scenes from urban environments in Boston and Singapore, incorporating data from cameras, lidar, radar, and GPS/IMU systems. The dataset is pivotal for tasks like object detection, tracking, and localization, offering 360-degree sensor coverage and detailed annotations for 23 diverse object classes. The dataset's creation involved rigorous synchronization and calibration of sensors, emphasizing precision in data collection.
Sensor Setup and Calibration:
Two Renault Zoe vehicles equipped with a Velodyne HDL32E lidar, multiple cameras, and Continental ARS 408-21 radars were used for data collection. The calibration processes ensured high-quality data, crucial for accurate perception and planning tasks. The meticulous calibration is evident in the alignment of camera and lidar data, exemplified in high-quality synchronization and calibration efforts.

Figure 1: Overview of the sensors and their positions on the nuScenes vehicles.
Data Annotation and Quality Assurance
Annotation in nuScenes involves semantic labeling, instance identification, and bounding box delineation across a wide array of object classes, meticulously validated through multiple stages. The dataset employs privacy-preserving techniques, such as facial and license plate blurring, ensuring anonymity. Similarly, the annotation process includes validation steps that support attaining high-quality data, which is critical for AV applications.
Quality Control:
The quality assurance process in nuScenes is robust, utilizing manual and semi-automated checks to ensure annotation accuracy. This involves validating object scale, class, position, and orientation consistently across the scenes, surpassing typical outsourcing measures used in other datasets.
Extensions and Leaderboards
nuScenes has fostered the evolution of extensions like Panoptic nuScenes and nuImages, extending its utility to point-level annotations and 2D image tasks, respectively. These extensions enable detailed study into environmental interactions and traditional 2D detection challenges, broadening the scope of AV research possibilities.
Benchmark Challenges:
nuScenes hosts various benchmark tasks, such as 3D detection, tracking, and lidar segmentation, providing standardized metrics like the nuScenes Detection Score (NDS). This fosters a competitive and collaborative environment, enabling methodological advancements in AV systems.
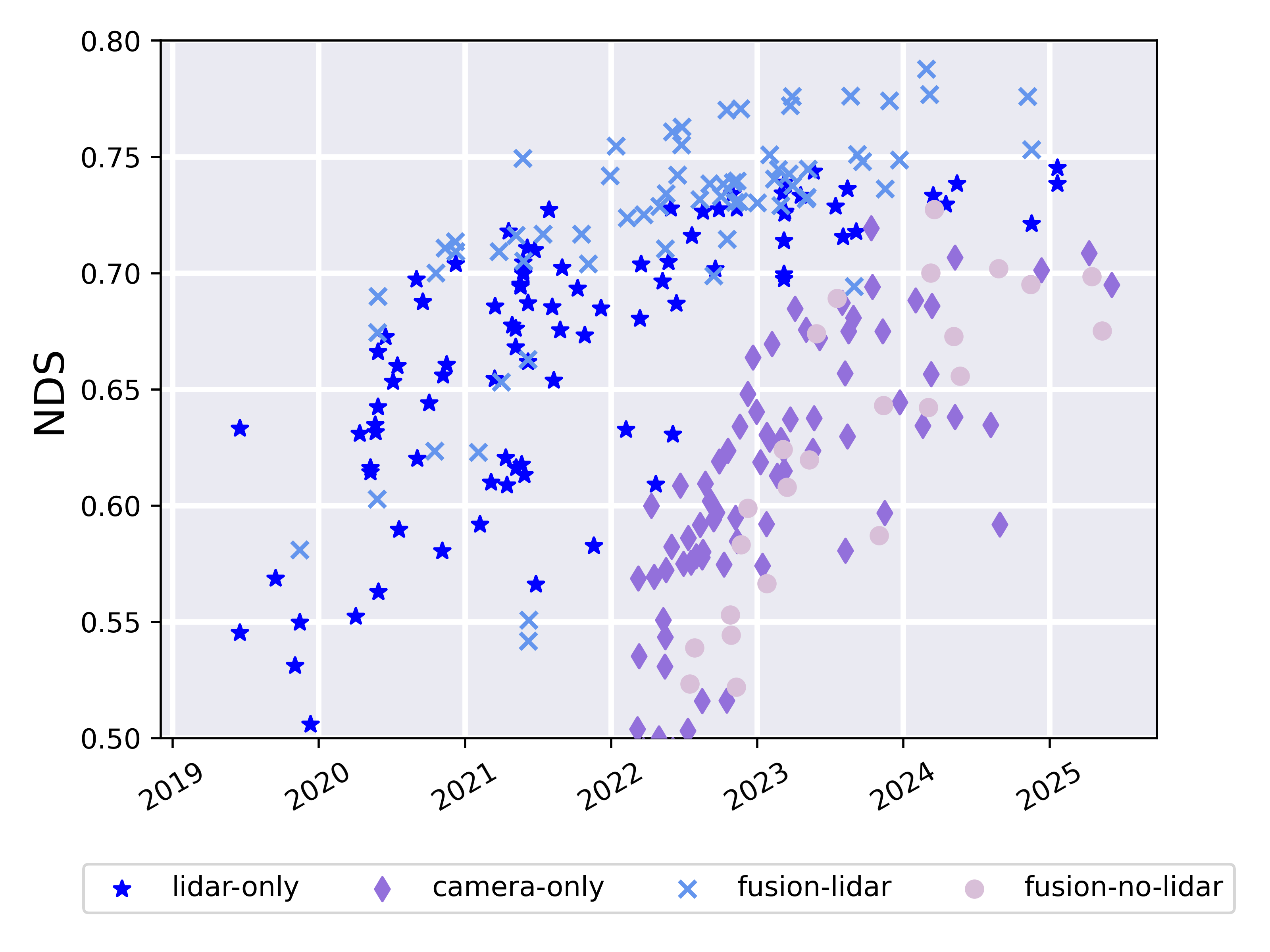
Figure 2: Results on the nuScenes detection leaderboard.
Radar and Mapping Developments
nuScenes was pioneering in integrating radar data, marking a shift towards robust sensor suites in adverse weather conditions. Despite the inherent challenges in radar data processing, it offered a significant advantage in velocity estimation and environmental perception, leading to broader radar dataset developments in the field.
Mapping Innovations:
The dataset's high-definition maps are integral for precise localization, offering geometric and semantic information crucial for AV operations in complex urban landscapes. These mapping features have inspired subsequent datasets to expand on map granularity and utility, enhancing navigation and planning capabilities.

Figure 3: Semantic map annotations overlayed on a front camera image from a driving scene in Boston-Seaport.
Conclusion
The nuScenes dataset has had a monumental impact on AV research, setting benchmarks for multimodal data collection, annotation quality, and sensor fusion techniques. Its extensions and influence on subsequent datasets underscore its foundational role in the field. However, challenges such as sensor synchronization, data density, and geographic diversity remain pivotal areas for improvement. Future iterations and datasets, like nuPlan, focus on closed-loop simulation frameworks, addressing open challenges in perception and planning.
nuScenes continues to facilitate advancements in autonomous driving technologies, promoting robust and comprehensive AV solutions across diverse operational scenarios.