- The paper introduces a cross-domain diffusion framework for single-image 3D reconstruction, achieving robust multi-view consistency and high textural fidelity.
- It employs a multi-view cross-domain attention mechanism and cascaded mesh extraction pipeline to efficiently optimize mesh geometry and detail.
- Experimental results demonstrate improved Chamfer Distance and Volume IoU metrics on the Google Scanned Object dataset compared to prior methods.
Wonder3D++: Cross-domain Diffusion for High-fidelity 3D Generation from a Single Image
Introduction
Wonder3D++ introduces a cross-domain diffusion framework for single-image 3D reconstruction, targeting the generation of high-fidelity textured meshes with robust multi-view consistency and computational efficiency. The method leverages joint modeling of multi-view normal maps and color images, integrating a multi-view cross-domain attention mechanism and a cascaded mesh extraction pipeline. This approach addresses the limitations of prior SDS-based and feed-forward 3D generative models, which suffer from slow per-shape optimization, multi-view inconsistencies, and suboptimal geometric detail.

Figure 1: Wonder3D++ reconstructs highly-detailed textured meshes from a single-view image in only 3 minutes, using cross-domain diffusion and cascaded mesh extraction.
Methodology
Cross-domain Multi-view Diffusion
Wonder3D++ extends pre-trained Stable Diffusion models to jointly generate multi-view normal maps and color images, conditioned on a single input image and camera parameters. The core innovation is the domain switcher, which enables the diffusion model to operate on both domains without perturbing the pre-trained weights, and a cross-domain attention mechanism that enforces geometric and visual consistency between generated outputs.
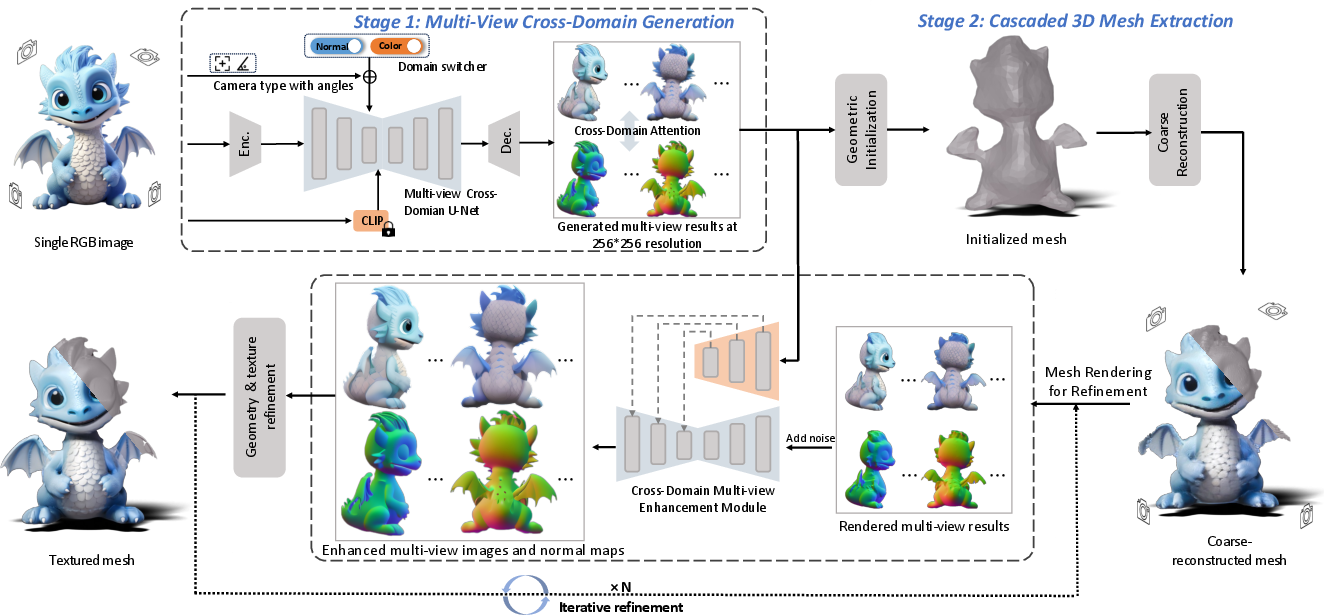
Figure 2: Overview of Wonder3D++. The pipeline conditions on image features, CLIP embeddings, camera parameters, and switchers to generate multi-view normals and colors, followed by cascaded mesh extraction.
The multi-view cross-domain transformer block incorporates both multi-view attention (for inter-view consistency) and cross-domain attention (for inter-domain consistency), facilitating information exchange across views and modalities.

Figure 3: Structure of the multi-view cross-domain transformer block, enabling information exchange across views and domains.
Camera Type Switcher
To accommodate diverse input sources (e.g., real photos, synthetic images), Wonder3D++ introduces a camera type switcher, allowing the model to generate multi-view outputs under either perspective or orthogonal projection. This enhances robustness and mitigates distortions arising from mismatched camera assumptions.
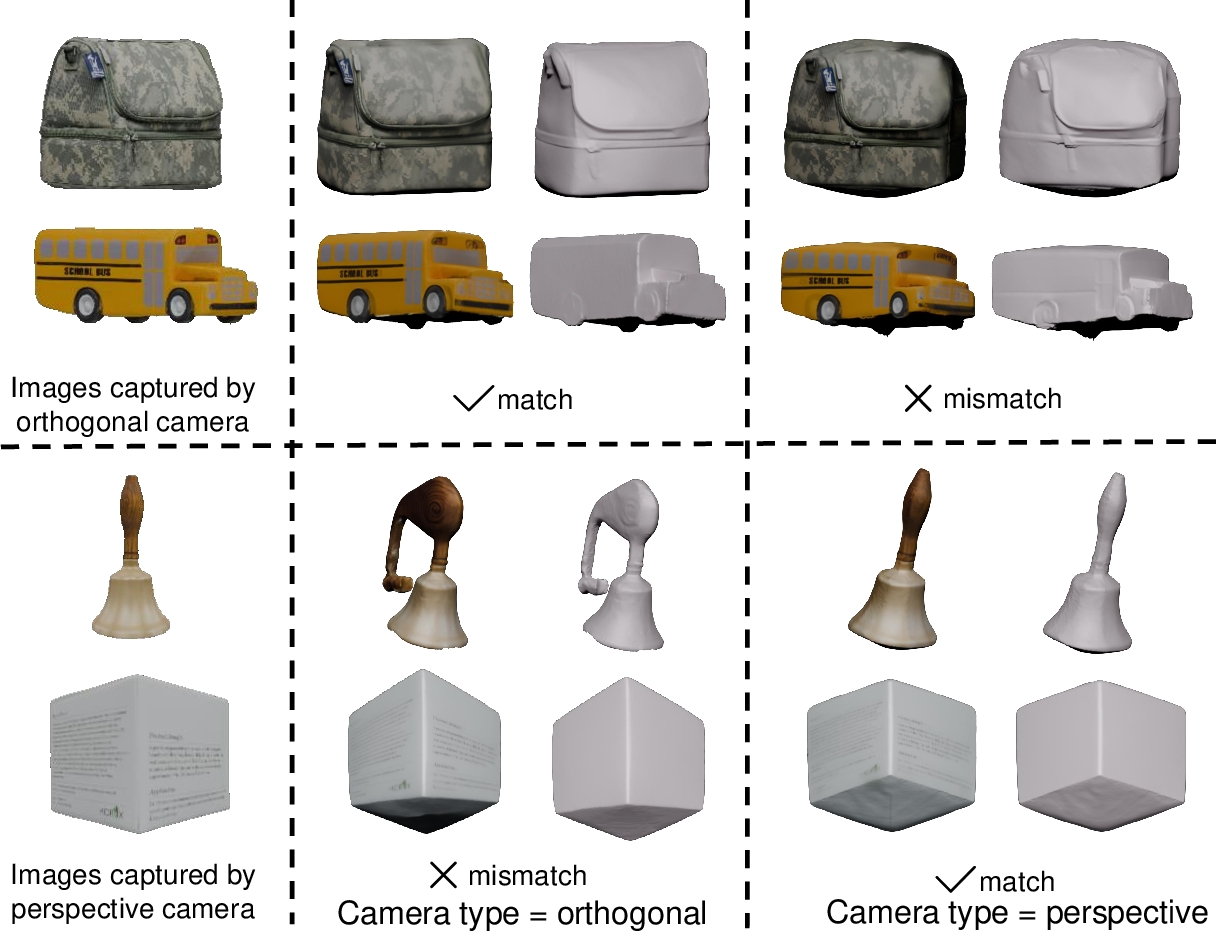
Figure 4: Ablation study on the camera type switcher, demonstrating improved robustness across projection types.
Multi-stage Training Strategy
The training pipeline consists of three stages:
- Multi-domain Pre-training: Fine-tunes the model for multi-view generation within each domain.
- Mixed-domain Fine-tuning: Enables generation of multi-view outputs in either domain from a single-view color image.
- Cross-domain Alignment Fine-tuning: Incorporates cross-domain attention for joint prediction of normals and colors, enhancing consistency.

Figure 5: Ablation study of the multi-stage training strategy, showing improved consistency and fidelity with multi-domain pretraining.
The mesh extraction process is divided into geometric initialization, inconsistency-aware coarse reconstruction, and iterative refinement. Geometric initialization uses Poisson reconstruction from integrated normal maps, with a topology-checking strategy to handle concave objects.
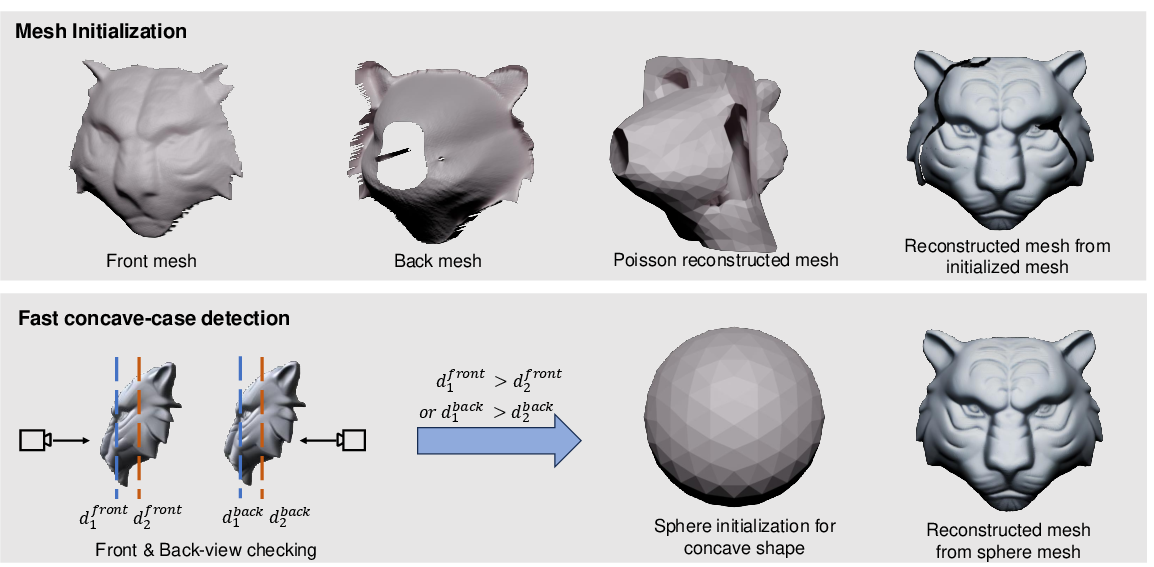
Figure 6: Geometric initialization using Poisson reconstruction and depth-based topology checking.
Coarse reconstruction optimizes mesh vertices via differentiable rendering, guided by multi-view normals and masks. A geometry-aware normal loss is introduced to mitigate inaccuracies in generated normals, enhancing surface detail.
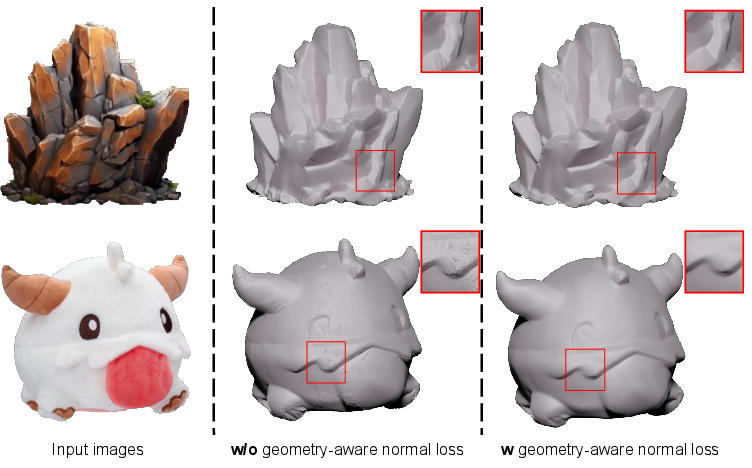
Figure 7: Geometry-aware normal loss improves surface detail by correcting normal inconsistencies.
Texture generation is performed in UV space, using adaptive fusion and propagation strategies to maintain high texture fidelity. Iterative refinement leverages a cross-domain multi-view enhancement module (based on ControlNet) to upsample and enhance rendered outputs, further refining mesh geometry and texture.

Figure 8: Cascaded mesh extraction visualizes coarse-to-fine geometry refinement and error correction.
Experimental Results
Single-view Reconstruction
Wonder3D++ demonstrates superior performance on the Google Scanned Object dataset, outperforming SDS-based, multi-view, and feed-forward baselines in both Chamfer Distance and Volume IoU metrics. The method achieves efficient inference (∼3 minutes per object) and robust generalization across diverse input styles.
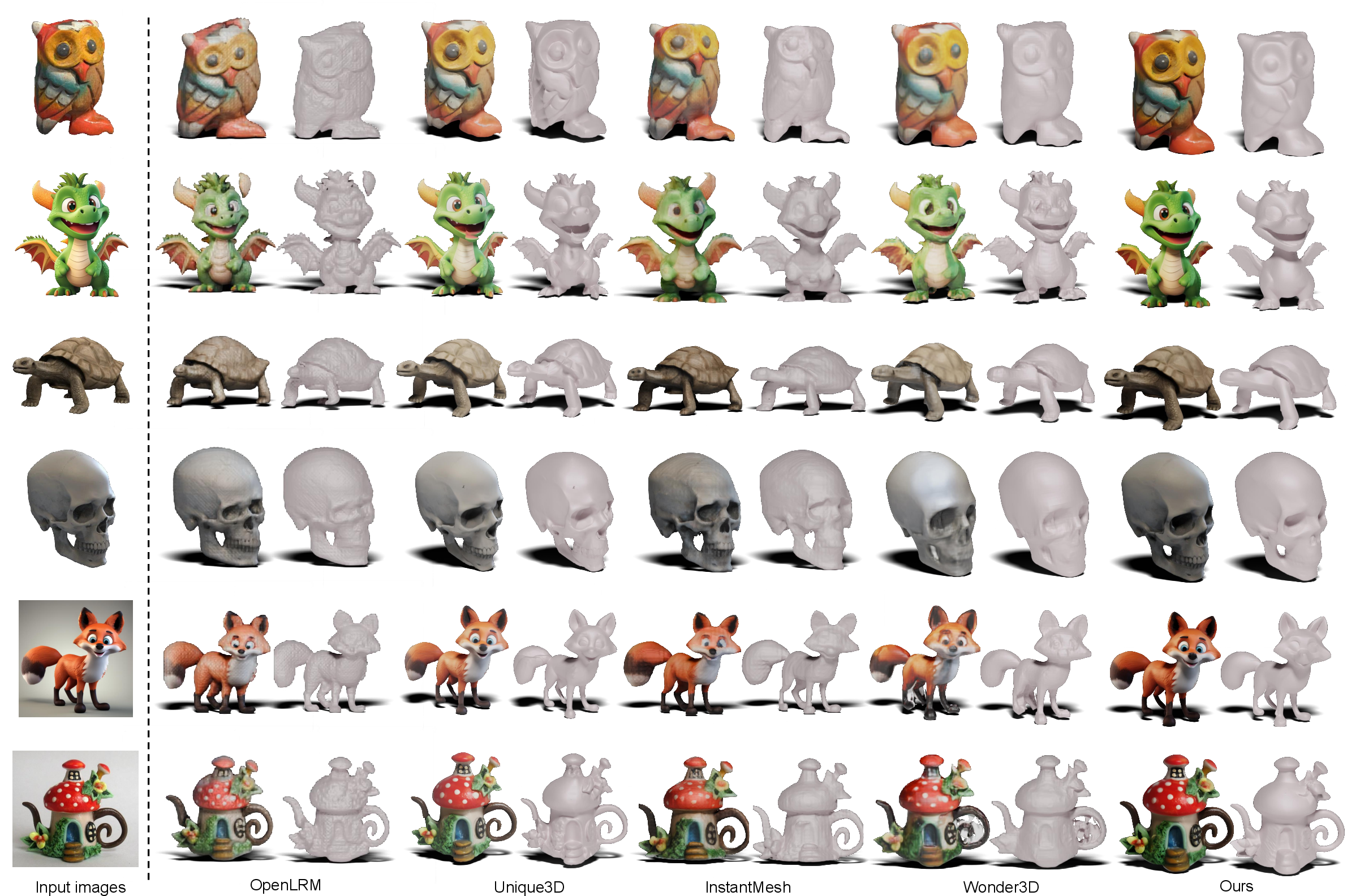

Figure 9: Qualitative comparisons with baselines on in-the-wild images for reconstructed textured meshes.
Novel View Synthesis
The cross-domain multi-view diffusion model yields high-fidelity, multi-view consistent outputs, as evidenced by PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS metrics. Joint modeling of normals and colors via cross-domain attention is shown to outperform sequential or independent domain generation strategies.

Figure 10: Qualitative comparisons with baselines on synthesized multi-view color images.

Figure 11: Ablation studies on cross-domain diffusion schemes, highlighting the benefits of joint prediction and cross-domain attention.
Ablation and Analysis
Ablation studies confirm the effectiveness of the geometry-aware normal loss, camera type switcher, and multi-stage training. The cascaded mesh extraction pipeline is shown to correct multi-view inconsistencies and enhance geometric detail iteratively.
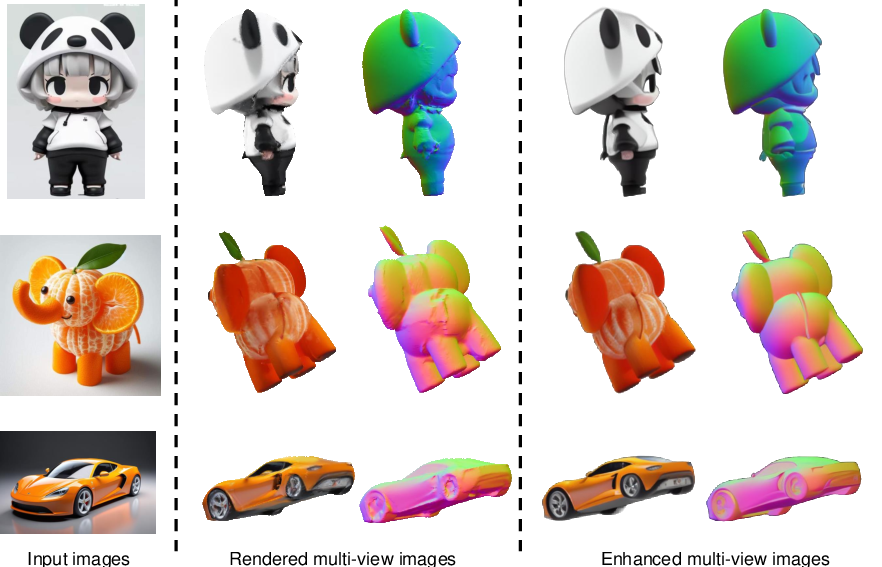
Figure 12: Visualization of the cross-domain multi-view enhancement method.

Figure 13: Visual comparison of textured meshes generated by Wonder3D++ against ground truth.
Implementation Considerations
- Computational Requirements: Training requires 8 high-end GPUs for several days; inference is efficient (∼3 minutes/object on a single A100).
- Scalability: The pipeline leverages 2D diffusion priors for zero-shot generalization, avoiding the need for large-scale 3D datasets.
- Limitations: Performance degrades for objects with highly complex geometry or severe self-occlusion due to sparse viewpoints and mesh-based optimization constraints.
- Deployment: The modular design allows integration with text-to-image models for text-to-3D generation, and supports both perspective and orthogonal camera settings.
Implications and Future Directions
Wonder3D++ advances single-image 3D reconstruction by integrating cross-domain diffusion and explicit mesh optimization, achieving state-of-the-art geometric and textural fidelity with practical efficiency. The joint modeling of normals and colors, combined with multi-view and cross-domain attention, sets a precedent for future 3D generative models. Potential future work includes scaling to more complex objects, increasing viewpoint diversity, and further improving mesh-based optimization strategies. The architecture's compatibility with text-to-image diffusion models opens avenues for high-quality text-to-3D asset generation.
Conclusion
Wonder3D++ presents a robust and efficient framework for high-fidelity 3D mesh generation from single images, leveraging cross-domain multi-view diffusion and cascaded mesh extraction. The method achieves strong quantitative and qualitative results, with demonstrated generalization and efficiency. While limitations remain for highly complex geometries, the approach provides a solid foundation for future research in 3D generative modeling and practical applications in graphics, vision, and robotics.














