- The paper demonstrates that F-BFQ significantly improves LLM inference efficiency by dynamically switching between BFP quantization variants.
- The paper details a novel dynamic super-block vector processor that concurrently processes Q2 and Q3 BFP variants for efficient matrix multiplication.
- The paper validates F-BFQ on FPGA platforms, achieving 5.2 tokens per second and indicating potential expansion to support additional quantization methods.
F-BFQ: Flexible Block Floating-Point Quantization Accelerator for LLMs
Introduction
The paper "F-BFQ: Flexible Block Floating-Point Quantization Accelerator for LLMs" addresses the challenges of efficiently executing LLMs on resource-constrained edge devices. The proliferation of LLMs, exemplified by models such as LLaMA and GPT variants, has necessitated innovations to combat computational complexity and large memory footprints. One strategy, quantization, is pivotal for enabling the deployment of LLMs on lower-resource platforms while maintaining model accuracy. This paper proposes the Flexible Block Floating-Point Quantization (F-BFQ) accelerator which adeptly supports multiple BFP variants for improved inference performance across model layers without the need for reconfiguration.
Overview of Flexible Block Floating-Point Quantization
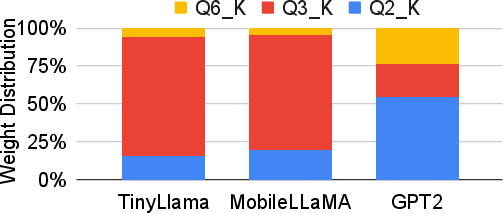
Quantization involves reducing the bit-width of weights and input tensors to lessen memory usage and computational demands. LLMs generally employ mixed BFP quantization across layers to balance accuracy loss with model efficiency. The F-BFQ accelerator introduces the capability to dynamically switch between BFP quantization variants, facilitating efficient matrix multiplication operations needed by BFP-quantized LLMs.
The F-BFQ accelerator, implemented on the AMD Kria board, demonstrates notable performance improvements by reducing inference time by 1.4× compared to execution on an Arm NEON-based CPU, while achieving 5.2 tokens per second.
Architecture of F-BFQ
The F-BFQ accelerator encompasses several key components:
These modules ensure operational efficiency and scalability, allowing the accelerator to handle diverse quantization tasks seamlessly.
FPGA Implementation and Evaluation
The evaluation employed the AMD KV260 board to benchmark the F-BFQ accelerator's performance across three LLMs: GPT2, MobileLLaMA, and TinyLlama. These models, previously quantized using llama.cpp's BFP approach, were subjected to matrix multiplication operations facilitated by the new accelerator design.

Figure 2: Overview of our F-BFQ accelerator design for Q2 and Q3 MatMul operations.
The performance analysis revealed a consistent speedup of 1.4× and improved token generation rates, underscoring the advantageous acceleration imparted by the F-BFQ architecture.
Future Directions and Implications
The study indicates significant potential for further development in flexible hardware accelerators supporting various quantization approaches. While the current version of F-BFQ is limited to specific BFP variants, extending the architecture to accommodate additional quantization methods—such as Q4 to Q8—could enhance performance across a broader range of LLMs.

Figure 3: Detailed view of the Dynamic Super Block Processor.
Such advancements would bolster FPGA-based solutions in edge AI applications, mitigating computational constraints inherent in mobile and IoT devices.
Conclusion
The proposed F-BFQ accelerator exhibits promising improvements in LLM inference efficiency, illustrating the utility of flexible quantization strategies in edge-based AI implementations. The ability to adapt across multiple BFP variants without reconfiguration marks a significant step in optimizing performance while maintaining model integrity. As AI deployments increasingly pivot toward edge-oriented applications, the need for such tailored hardware solutions will undoubtedly expand, prompting further exploration into adaptive quantization technologies.