- The paper presents DialTree-RPO, a reinforcement learning framework that formulates red-teaming as a sequential decision-making problem using dialogue tree rollout with pruning.
- It introduces adaptive masking and a specialized reward function with GRPO to stabilize training and prevent format collapse during multi-turn attacks.
- The framework achieves over 85% attack success rate on various LLMs, demonstrating strong transferability and systematic vulnerability discovery.
Tree-based Dialogue Reinforced Policy Optimization for Red-Teaming Attacks
The paper introduces DialTree-RPO, a reinforcement learning (RL) framework for automated multi-turn red-teaming of LLMs. The motivation stems from the observation that LLMs are significantly more vulnerable to adversarial attacks in multi-turn conversational settings than in single-turn scenarios. Existing red-teaming approaches either rely on manual expert intervention or automated template-based methods, both of which fail to systematically explore the vast space of multi-turn attack trajectories. The authors formalize red-teaming as a sequential decision-making problem, where an attacker agent strategically interacts with a target model to elicit harmful responses, treating each dialogue as a trajectory in a Markov Decision Process (MDP).
DialTree-RPO Framework
DialTree-RPO integrates three core innovations: (1) dialogue tree rollout with pruning, (2) a specialized reward function for non-verifiable outcomes, and (3) adaptive masking for stable multi-turn policy optimization.
Dialogue Tree Rollout and Pruning
The framework employs a tree-based exploration strategy, where at each turn, the attacker generates multiple candidate actions (CoT reasoning and attack queries), expanding the dialogue tree. Each branch is evaluated for format validity and topic adherence, with malformed or off-topic branches pruned to maintain search efficiency and trajectory quality.

Figure 1: Illustration of dialogue tree expansion with pruning, showing how candidate branches are generated and pruned at each turn to efficiently explore attack strategies.
Pruning is critical for preventing exponential growth and ensuring that only coherent, goal-directed trajectories are retained for optimization. The attacker policy is trained to maximize the probability of eliciting harmful responses from the target, subject to a KL regularization term to prevent policy drift.
Reward Function and Optimization
The reward function leverages HarmAug-Guard, a lightweight classifier that assigns a binary reward based on whether any turn in the dialogue elicits a harmful response above a threshold. The optimization objective is based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), which computes group-relative advantages for each trajectory and updates the policy using clipped surrogate objectives.
Adaptive Masking
A key challenge in multi-turn RL is format unlearning, where the attacker model loses its ability to generate structured outputs (CoT and query tokens) during RL updates. The authors introduce adaptive masking, which selectively masks format tokens from gradient updates in negative-advantage trajectories, preserving format-following capability without impeding policy learning.
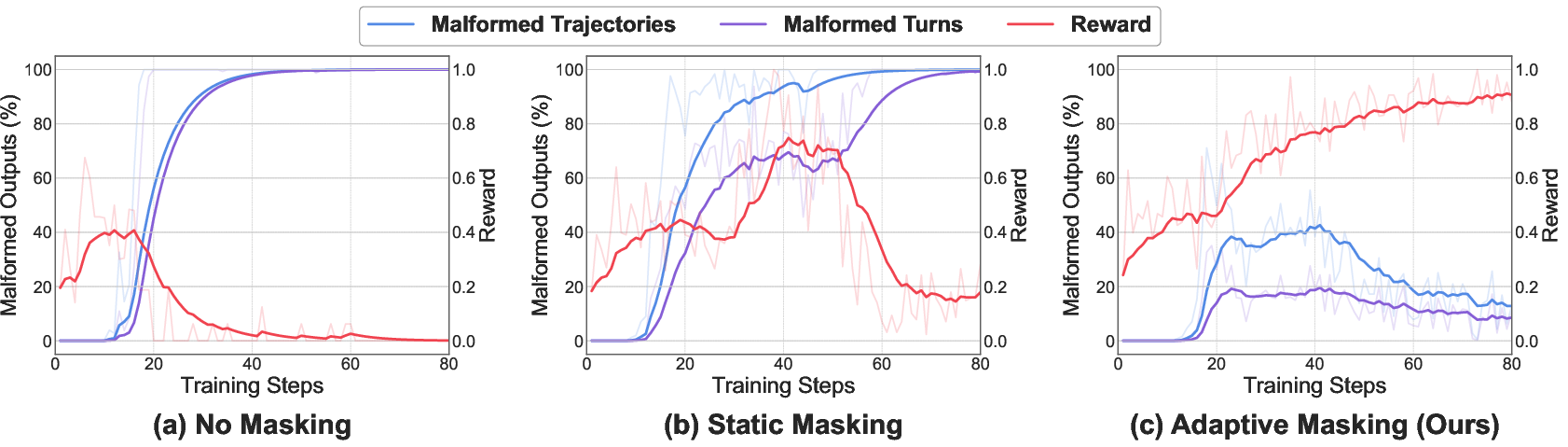
Figure 2: Pre-pruning malformed output rate and reward under three masking schemes, demonstrating that adaptive masking stabilizes training and prevents format collapse.
Experimental Results
DialTree-RPO is evaluated against ten target LLMs, including both closed-source (e.g., GPT-4o, Gemini-2.0-Flash) and open-source models (e.g., Llama-3.1-8B, Mistral-7B). The attacker is trained against a small frozen target model and tested for transferability to larger models. The main metric is Attack Success Rate (ASR), defined as the percentage of test cases where the target model produces a maximally harmful response.
DialTree-RPO achieves average ASRs of 85.0% (closed-source) and 85.5% (open-source), outperforming previous state-of-the-art methods by over 25% ASR. The method also demonstrates strong transferability, with policies trained on small models generalizing to much larger targets. Query efficiency is superior, with fewer queries required per successful attack compared to baselines.
Ablation Studies
Ablation experiments isolate the contributions of tree rollout, pruning strategies, tree depth, branching factor, and group size. Removing pruning mechanisms or tree rollout results in substantial performance degradation, confirming their necessity for effective exploration.

Figure 3: Impact of tree depth, branching width, and group size on ASR, showing that increased planning horizon and exploration breadth improve attack success rates.
Increasing tree depth (number of turns), branching factor (number of candidate actions per turn), and group size (number of trajectories per optimization step) all lead to higher ASR, up to a point where reward sparsity becomes a limiting factor.
Analysis of Discovered Attack Strategies
Manual analysis of generated dialogues reveals that DialTree-RPO autonomously discovers sophisticated multi-turn attack strategies, including pretexting, gradual escalation, persistent gap-filling, policy-laundering keywords, privacy-defamation hybrids, risk-to-checklist conversion, tool elicitation, and cross-lingual evasion.

Figure 4: Case study of new attack strategies discovered by DialTree-RPO, illustrating pretexting and cross-lingual evasion in multi-turn interactions.
These emergent strategies exploit nuanced vulnerabilities in current safety mechanisms, demonstrating the necessity of multi-turn, context-aware defenses.
Practical and Theoretical Implications
The results indicate that current LLM safety guardrails are insufficient against strategic multi-turn attacks. Automated RL-based red-teaming frameworks like DialTree-RPO provide a scalable and systematic approach for vulnerability discovery, enabling more robust safety evaluation and alignment. The framework is adaptable to broader multi-turn strategic reasoning tasks, such as negotiation, persuasion, and debate.
From a theoretical perspective, the extension of GRPO and tree-based RL to non-verifiable, conversational domains represents a significant advance, highlighting the importance of structured exploration and reward design in complex interactive settings.
Future Directions
Potential future developments include the integration of process-based rewards to address reward sparsity in long-horizon dialogues, the application of DialTree-RPO to defensive alignment and countermeasure discovery, and the extension to other interactive AI domains requiring strategic planning and adversarial robustness.
Conclusion
DialTree-RPO establishes a new paradigm for automated multi-turn red-teaming of LLMs, combining tree-based exploration, reward modeling, and adaptive optimization to uncover vulnerabilities that elude single-turn and template-based methods. The framework demonstrates strong empirical performance, transferability, and efficiency, and uncovers novel attack strategies that challenge existing safety mechanisms. These findings underscore the urgent need for context-aware, multi-turn safety alignment in deployed LLMs and provide a foundation for future research in adversarial robustness and strategic dialogue optimization.





