Benchmarking GPT-5 in Radiation Oncology: Measurable Gains, but Persistent Need for Expert Oversight (2508.21777v1)
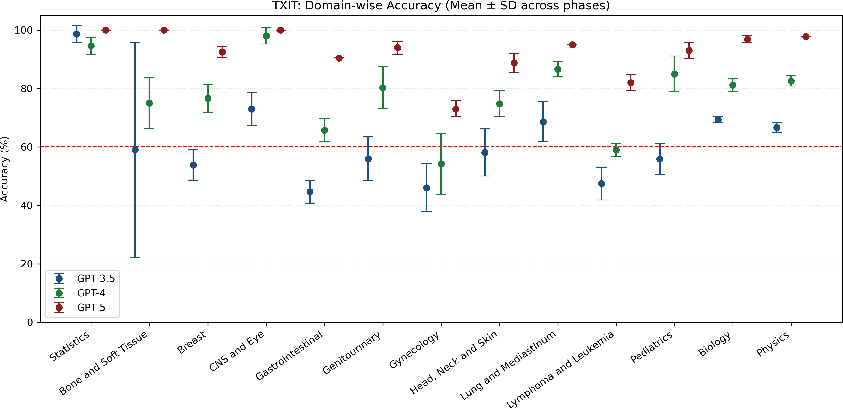
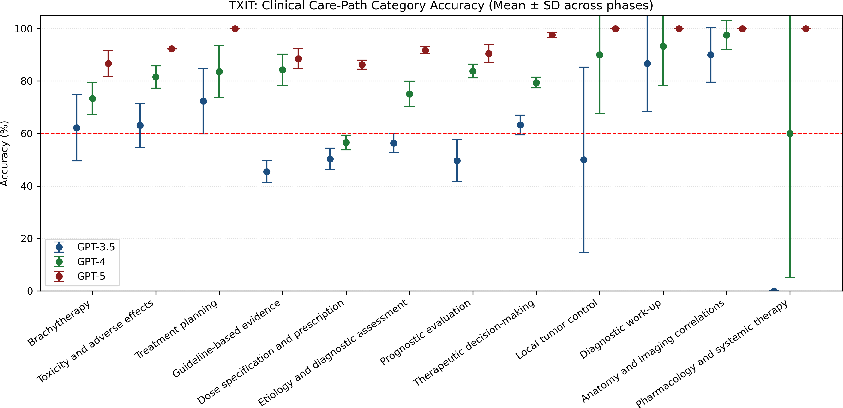
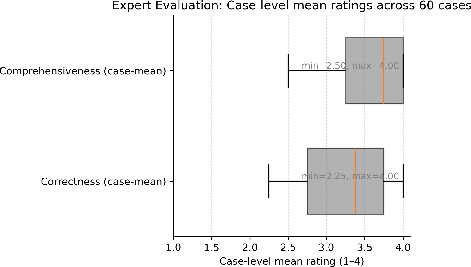
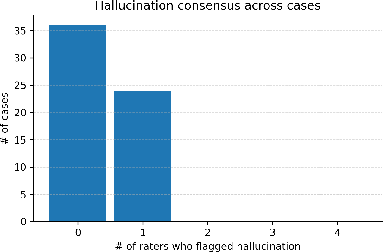
Abstract: Introduction: LLMs (LLM) have shown great potential in clinical decision support. GPT-5 is a novel LLM system that has been specifically marketed towards oncology use. Methods: Performance was assessed using two complementary benchmarks: (i) the ACR Radiation Oncology In-Training Examination (TXIT, 2021), comprising 300 multiple-choice items, and (ii) a curated set of 60 authentic radiation oncologic vignettes representing diverse disease sites and treatment indications. For the vignette evaluation, GPT-5 was instructed to generate concise therapeutic plans. Four board-certified radiation oncologists rated correctness, comprehensiveness, and hallucinations. Inter-rater reliability was quantified using Fleiss' \k{appa}. Results: On the TXIT benchmark, GPT-5 achieved a mean accuracy of 92.8%, outperforming GPT-4 (78.8%) and GPT-3.5 (62.1%). Domain-specific gains were most pronounced in Dose and Diagnosis. In the vignette evaluation, GPT-5's treatment recommendations were rated highly for correctness (mean 3.24/4, 95% CI: 3.11-3.38) and comprehensiveness (3.59/4, 95% CI: 3.49-3.69). Hallucinations were rare with no case reaching majority consensus for their presence. Inter-rater agreement was low (Fleiss' \k{appa} 0.083 for correctness), reflecting inherent variability in clinical judgment. Errors clustered in complex scenarios requiring precise trial knowledge or detailed clinical adaptation. Discussion: GPT-5 clearly outperformed prior model variants on the radiation oncology multiple-choice benchmark. Although GPT-5 exhibited favorable performance in generating real-world radiation oncology treatment recommendations, correctness ratings indicate room for further improvement. While hallucinations were infrequent, the presence of substantive errors underscores that GPT-5-generated recommendations require rigorous expert oversight before clinical implementation.
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.