- The paper introduces task distillation that compresses RL tasks into single-batch SL datasets using a meta-learning approach.
- It leverages a modified PPO called PPMO to synthesize efficient supervised datasets, achieving comparable performance with reduced training costs.
- Experiments on Cart-Pole, Atari, and MuJoCo validate its scalability, task generalization, and resource efficiency.
"Distilling Reinforcement Learning into Single-Batch Datasets" (2508.09283)
Introduction
The paper introduces a methodology termed task distillation, which leverages the concept of dataset distillation for the purpose of compressing reinforcement learning (RL) environments into highly efficient, single-batch supervised learning datasets. This enables not only the compression of data but also facilitates the transformation of learning modalities, from RL to supervised learning (SL), thereby paving the way for more resource-efficient training paradigms.
Methodology
The primary innovation in this work is the adaptation of dataset distillation to RL tasks, dubbed RL-to-SL distillation. This involves synthesizing supervised datasets from complex RL environments. The process uses a meta-learning approach with modified proximal policy optimization (PPO), termed Proximal Policy Meta-Optimization (PPMO), to compress the tasks effectively.
The training process consists of three nested loops: meta-epochs, policy epochs, and batched iterations. During meta-epochs, initialized learners are trained on synthetic datasets created by inner-learning processes. The algorithm updates the synthetic dataset based on the PPO policy loss, with the aim of maximizing the expected reward from the synthesized policy.
Experimental Setup
Cart-Pole Experiments
The cart-pole problem is expanded into multiple dimensions (ND cart-pole), allowing for controlled difficulty scaling. This facilitated experiments on k-shot learning and determining the minimum dataset size for successful task distillation.
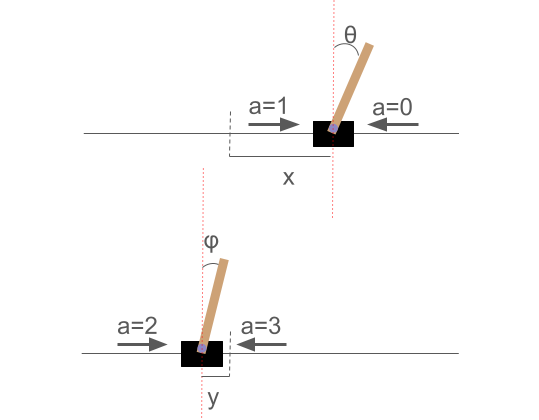
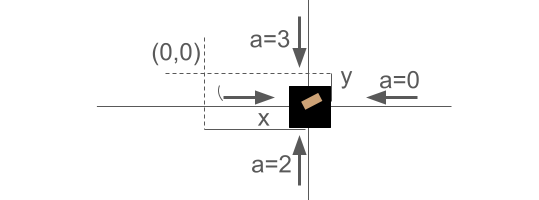
Figure 1: Two perpendicular side views of 2D cart-pole. The solid lines represent the degrees of freedom of the cart.
Atari and MuJoCo Environments
The paper demonstrates scalability by applying the distillation approach to more complex environments, including several Atari games and MuJoCo tasks. For Atari environments, encoder rollback is introduced as a technique to manage computational complexity, enabling partial distillations that act as intermediaries between direct-task RL training and full distillation.
Results
The experiments illustrate that task distillation can achieve performance comparable to standard RL training with significantly reduced computational costs for training additional models. Notably, the distilled datasets enable learners to achieve high performance in single-batch training steps.
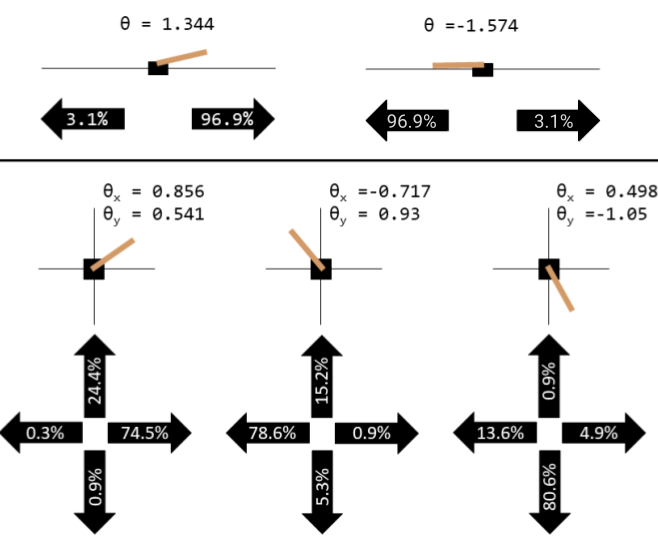
Figure 2: Visualizations of a distillation of 1D (above) and 2D (below) cart-pole with simplified information.
Trade-offs and Practical Implications
The distillation method presents an upfront computational cost that, although higher than individual RL training runs, offers substantial savings in scenarios requiring the training of multiple models, such as ensemble methods or neural architecture search. This approach effectively reduces the high exploration costs typical of RL, thereby making sophisticated tasks more accessible in low-resource settings.
Additionally, task distillation has potential applications in preserving data privacy, accelerating hyperparameter searches, and improving training efficiency in robotics and other real-world RL applications.
Conclusion
The research presents a robust framework for transforming RL tasks into compact SL tasks through task distillation, showcasing the ability to significantly cut training costs without compromising on performance. Future work should explore broader applications across different learning environments, further optimize the distillation process, and expand its applicability to other domains that demand efficient model training.




