- The paper presents an end-to-end model achieving over 70% translation correctness and nearly 70% reduction in latency.
- Its duplex processing framework integrates a pretrained LLM with audio encoding and reinforcement learning to optimize real-time translation coherence.
- The system supports voice cloning to preserve speaker identity, outperforming benchmarks like SeamlessStreaming in quality and speed.
Seed LiveInterpret 2.0: End-to-End Simultaneous Speech-to-Speech Translation with Your Voice
Introduction to Seed LiveInterpret 2.0
Seed LiveInterpret 2.0 addresses the challenging task of Simultaneous Interpretation (SI) by proposing an end-to-end model with remarkable performance in simultaneous speech-to-speech translation. The model is designed to overcome prevailing challenges in the field, such as suboptimal transcription, translation quality issues, real-time speech generation difficulties, and multi-speaker confusion. Emphasizing high-fidelity and ultra-low-latency speech-to-speech generation, the model also supports voice cloning, enhancing user experience by preserving the speaker's identity across language barriers.
System Architecture and Training Methodologies
Seed LiveInterpret 2.0’s architecture relies on a duplex processing framework for simultaneous speech-to-speech translation. An initial LLM is pretrained as part of the Seed LLM family, which is then adapted to a multi-modal setting by integrating audio encoding capabilities for processing streaming audio inputs. This multi-modal model undergoes extensive multi-task continual training and supervised fine-tuning.
A significant innovation in Seed LiveInterpret 2.0 is its use of reinforcement learning (RL) to optimize performance under stringent latency constraints. The system employs a sophisticated reward mechanism balancing intra-segment consistency via single-turn rewards and inter-segment coherence through multi-turn rewards. The RL framework ensures that the model produces timely and semantically accurate translations, even under real-time operational demands.
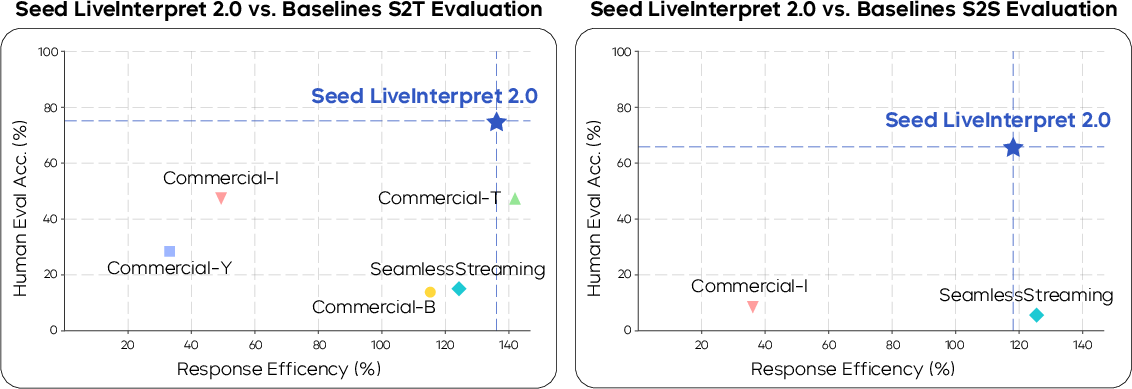
Figure 1: Evaluation of simultaneous interpretation systems: Translation quality scores vs. response efficiency for S2T and S2S modes.
The model’s performance is extensively validated using the RealSI benchmark, which reflects real-world simultaneous interpretation scenarios. Seed LiveInterpret 2.0 demonstrates superior translation quality compared to existing commercial SI solutions, achieving over 70% correctness as evaluated by human interpreters. The model significantly reduces latency, cutting the average delay of voice-cloned speech from nearly 10 seconds to approximately 3 seconds, representing a near 70% reduction in latency.
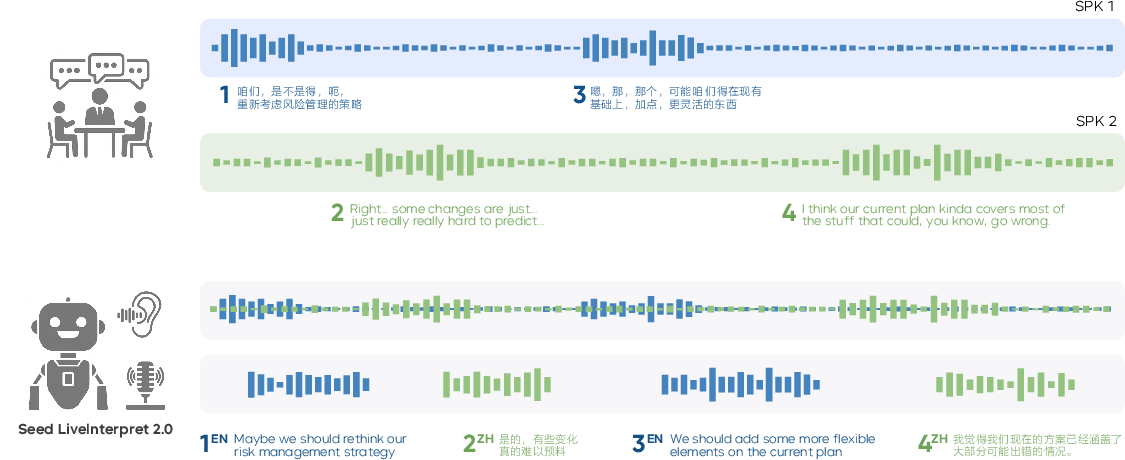
Figure 2: Illustration of Seed LiveInterpret 2.0 in multilingual conversation, demonstrating real-time translation and voice cloning capabilities.
Comparison with Baseline Systems
Seed LiveInterpret 2.0 competes favorably against other commercial and open-source systems, notably outperforming models such as SeamlessStreaming in terms of both translation quality and latency. Its unique ability to provide voice cloning alongside high-quality translation differentiates it from systems that do not support this feature or exhibit degraded performance, especially in long-form speech scenarios.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
The research introduces a unified, end-to-end architecture that sets a new standard for SI, particularly in speech-to-speech tasks. It advances the field by integrating LLMs with simultaneous translation capabilities, enhancing global communication channels across language divides. While the model presents advancements in latency and quality, future developments may seek to further scale the model's capabilities to support a wider range of languages and dialects.
Conclusion
Seed LiveInterpret 2.0 signifies a pivotal development in the field of simultaneous speech translation technologies, marrying low-latency performance with high fidelity and speaker identity preservation via voice cloning. The integration of sophisticated reward mechanisms in RL training further enhances the model’s efficiency, making it a viable solution for seamless, real-time multilingual communication in practical settings. Future work aims to refine its voice personalization features and expand its applicability across diverse linguistic landscapes.



