- The paper introduces Step AG, an adaptive guidance strategy that selectively applies classifier-free guidance to reduce computational cost during critical denoising steps.
- It demonstrates that applying guidance only during the initial 30%-50% of steps maintains image quality and text alignment, yielding a 20%-30% reduction in inference time.
- The proposed approach is versatile, showing consistent performance improvements across both image and video diffusion models, paving the way for standardized acceleration techniques.
Revisiting Adaptive Guidance in Classifier-Free Guidance Text-to-Vision Diffusion Models
Introduction
The research presented in "How Much To Guide: Revisiting Adaptive Guidance in Classifier-Free Guidance Text-to-Vision Diffusion Models" (2506.08351) investigates the efficiency of adaptive guidance strategies in text-to-vision diffusion models, specifically focusing on classifier-free guidance (CFG). The study introduces Step AG, an adaptive strategy that achieves high-quality image generation with reduced computational costs. It offers an insightful analysis of why adaptive guidance works and demonstrates its universal applicability across different models, including video generation models.
Diffusion models [NEURIPS2020_DDPM, song2021DDIM] have become prominent for generative tasks like image, video, and audio synthesis. Classifier-free guidance [ho2022classifier] is a widely used conditioning method that requires twice the model forwarding steps compared to unconditional generation, leading to higher computational costs.
Previous research efforts to mitigate these costs include distillation techniques [meng2023distillation], training-free acceleration methods like caching [ma2024deepcache], and adaptive guidance strategies [castillo2023adaptive]. Unlike them, Step AG offers a simpler, universally applicable approach that does not rely on specific architectural dependencies or intricate hyperparameter tuning.
Adaptive Guidance Mechanism
The core concept of adaptive guidance is to decide whether the conditional or unconditional model predictions (scores) can be used at each denoising step to reduce computation without sacrificing output quality. The paper introduces Step AG, built on the understanding that during later denoising steps, the high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) renders classifier-free guidance less critical. This leads to a reduction in computational cost by limiting guidance application to the initial 30%-50% of steps.
Implementation and Results
The paper details an empirical evaluation across various diffusion models like Stable-Diffusion and PixArt-Σ, demonstrating an average inference time reduction of 20%-30%, while maintaining competitive image and text alignment metrics.
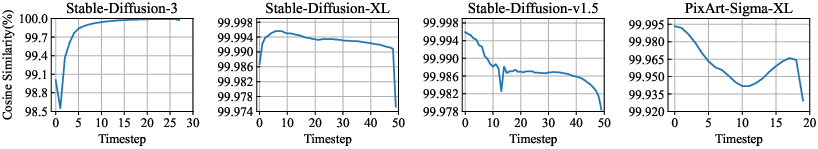
Figure 1: Cosine Similarity γt of different models. We calculate cosine similarity under their default inference step settings.
Notably, the proposed Step AG strategy consolidates the performance criteria for various generation tasks, providing a consistent improvement across models. This flexibility indicates the potential to standardize acceleration techniques in text-to-vision diffusion settings, making it highly adaptable to existing frameworks.
The effectiveness of Step AG compared to traditional CFG and other adaptive strategies like Similarity AG is highlighted by its empirical success across benchmarks. The scalability and implementation ease, due to the predictable computation cost reduction, make it a favorable choice for various applications. The study also discusses the influence of guidance scales and inference steps, asserting that appropriate tuning of these parameters alongside Step AG can enhance practical performance outcomes.

Figure 2: SNR of different diffusion models. This is calculated under training timestep setting. Inference bears a similar trend.
Video Generation Extensions
Step AG's applicability extends to video generation, as evidenced by tests on CogVideoX and ModelScope models, where it facilitated notable acceleration without compromising on the qualitative aspects of generated content. This paves the way for its deployment in more computation-intensive generative contexts.


Figure 3: Performance of Step AG of different video generation models. SPV(ratio) is compared with spv under p=1.0.
Conclusion
The introduction of Step AG in the field of adaptive guidance for diffusion models marks a significant stride in optimizing computational efficiency. Its universal applicability, ease of implementation, and consistent preservation of high-quality generation make it a viable strategy for enhancing the efficiency of existing diffusion-based generative systems. Future research could explore further optimizations and adaptations of Step AG for broader applications in real-time generative systems.



