- The paper presents a framework that integrates uncertainty quantification and probabilistic rank sets to enhance algorithmic hiring.
- It employs local perturbations and entropy estimates to generate empirical candidate rankings, demonstrating improved robustness in synthetic tests.
- The approach promotes fairness by flagging uncertain candidate evaluations and supporting recruiter decisions with transparent model insights.
Humble AI in the Real-World: The Case of Algorithmic Hiring
Introduction to Humble AI
The paper "Humble AI in the real-world: the case of algorithmic hiring" (2505.20918) presents a method to incorporate Humble AI principles into algorithmic hiring systems. Humble AI is characterized by its cautious approach, emphasizing skepticism, curiosity, and commitment beyond performance metrics. The paper explores applying these principles to a real-world algorithmic hiring platform, addressing challenges of bias and stereotyping inherent in AI systems.
Methodology
The methodology involves operationalizing Humble AI principles through uncertainty quantification, entropy estimates, and user experience design. The critical innovation is the development of rank sets, which probabilistically determine candidate rankings rather than relying on deterministic outputs.
The rank sets are generated from empirical distributions of scores obtained via local perturbations around the candidate's feature vector. This involves using inference from an AI model in a black-box manner to determine a probability matrix that reflects the potential ranking positions of candidates. This approach facilitates the computation of metrics such as expected rank, entropy, and rank variance, enabling a nuanced understanding of candidate evaluations.
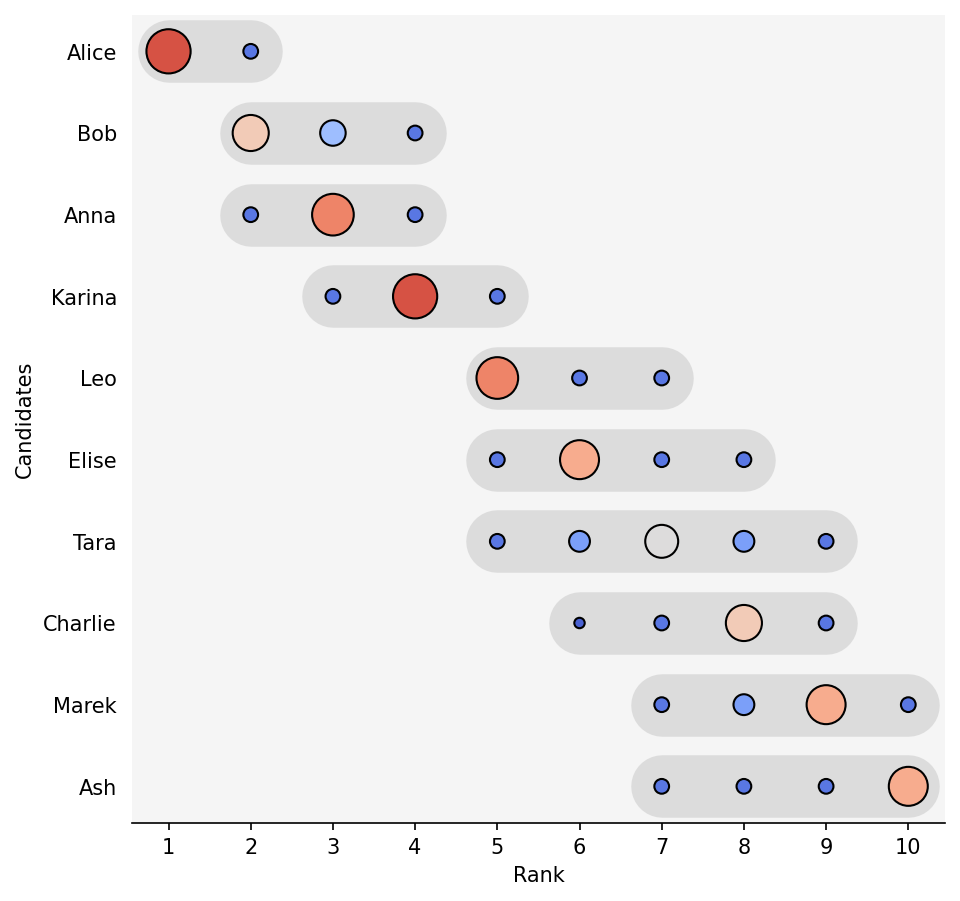

Figure 1: Low uncertainty regime where AI system is less uncertain on candidate rankings.
The implementation was tested using a widely-used HR platform, demonstrating how uncertainty quantification can flag candidates for further manual review. Empirical results from synthetic noise experiments establish that considering probabilistic information enhances the alignment of system rankings with presumed true candidate rankings.

Figure 2: Job listings.
The user's interface was designed to integrate seamlessly into the recruiter workflow, allowing toggling between traditional deterministic and humble AI-based rankings. This design ensures that recruiters are still able to work within familiar frameworks while gaining insights into the model's confidence levels.

Figure 3: Candidate matches (deterministic).
Synthetic experiments reveal that probabilistic rankings attained through rank set frameworks are more robust to noisy perturbations — a common characteristic of real-world hiring data. The Rank Biased Overlap (RBO) metric used for evaluation demonstrates that expected rank-based approaches more closely adhere to the ground truth rankings than point estimate approaches do.


Figure 4: Performance of ranking based on point estimates.
Discussion and Implications
The Humble AI approach has significant implications for increasing fairness and reducing inadvertent bias in AI-assisted hiring decisions. By quantifying and highlighting uncertainty, stakeholders are better equipped to make informed decisions about candidate rankings, promoting a more equitable hiring process.
Despite the positive outcomes demonstrated through synthetic data, a primary limitation is the lack of ground truth for candidate suitability in real-world applications. The paper acknowledges the challenge of validating uncertain outcomes without these benchmarks, though it suggests that these limitations reinforce the need for cautious AI deployment.
Conclusion
Humble AI introduces a viable framework to combat biases in algorithmic hiring. By considering model uncertainty and integrating it effectively into the hiring pipeline, the research provides a pathway towards developing trustworthy AI systems that align better with human values and ethical standards. Future studies should further explore real-world applications and refine methodologies to enhance scalability and applicability across different domains.
In conclusion, while challenges remain in operationalizing these principles at scale, the paper underscores the importance of acknowledging AI limitations and adopting a principled approach to AI deployment in sensitive domains like hiring.









