Scaling Image and Video Generation via Test-Time Evolutionary Search (2505.17618v1)
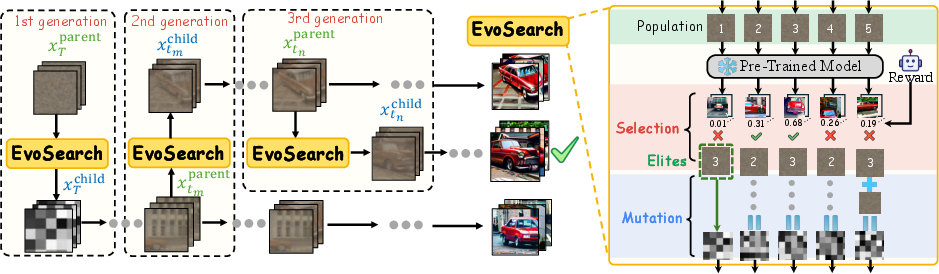
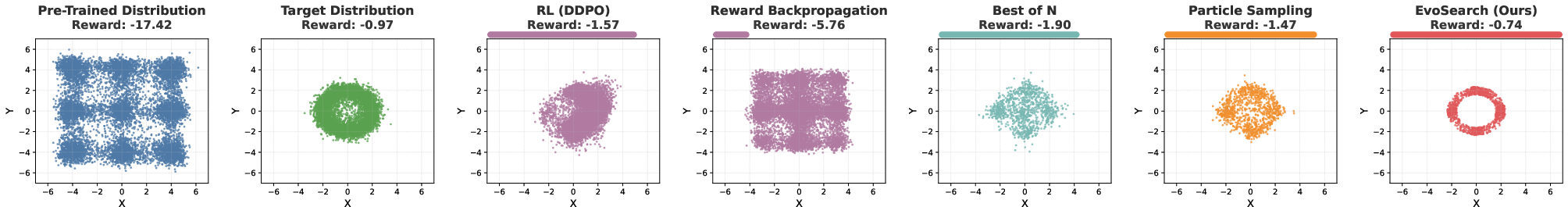
Abstract: As the marginal cost of scaling computation (data and parameters) during model pre-training continues to increase substantially, test-time scaling (TTS) has emerged as a promising direction for improving generative model performance by allocating additional computation at inference time. While TTS has demonstrated significant success across multiple language tasks, there remains a notable gap in understanding the test-time scaling behaviors of image and video generative models (diffusion-based or flow-based models). Although recent works have initiated exploration into inference-time strategies for vision tasks, these approaches face critical limitations: being constrained to task-specific domains, exhibiting poor scalability, or falling into reward over-optimization that sacrifices sample diversity. In this paper, we propose \textbf{Evo}lutionary \textbf{Search} (EvoSearch), a novel, generalist, and efficient TTS method that effectively enhances the scalability of both image and video generation across diffusion and flow models, without requiring additional training or model expansion. EvoSearch reformulates test-time scaling for diffusion and flow models as an evolutionary search problem, leveraging principles from biological evolution to efficiently explore and refine the denoising trajectory. By incorporating carefully designed selection and mutation mechanisms tailored to the stochastic differential equation denoising process, EvoSearch iteratively generates higher-quality offspring while preserving population diversity. Through extensive evaluation across both diffusion and flow architectures for image and video generation tasks, we demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches, achieves higher diversity, and shows strong generalizability to unseen evaluation metrics. Our project is available at the website https://tinnerhrhe.github.io/evosearch.
Sponsor
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.