- The paper presents FlexiNS, a SmartNIC-centric network stack that decouples header and payload processing to overcome CPU and hardware limitations.
- It introduces innovative techniques such as a header-only offload TX path, in-cache RX processing, and DMA-only notification to optimize performance.
- Evaluation results show significant improvements in throughput, latency, and storage IOPS compared to traditional CPU-centric stacks.
FlexiNS: A SmartNIC-Centric, Line-Rate and Flexible Network Stack
FlexiNS presents an innovative approach to meeting the growing demands of network throughput and flexibility within modern cloud environments. It addresses the limitations of CPU-centric and hardware-offloaded network stacks by leveraging SmartNIC technologies, specifically using the Nvidia BlueField-3. This essay explores the architecture, design principles, and performance implications of FlexiNS, providing a comprehensive understanding for researchers in the field.
Introduction to FlexiNS
FlexiNS is designed to tackle the inefficiencies of traditional CPU-centric network stacks which suffer from high CPU and memory overheads. Similarly, hardware-offloaded stacks, while performant, lack the flexibility necessary for diverse application requirements. SmartNICs offer a compelling solution, combining programmability with performance, but face challenges such as bandwidth contention and memory constraints. FlexiNS overcomes these through innovative design choices that ensure high throughput and flexibility.
Network Stack Design
The network stack design of FlexiNS is centered on several core innovations to overcome inherent limitations in SmartNIC architectures.

Figure 1: Comparison of different network stack designs.
Architecture Overview
FlexiNS’s architecture incorporates several crucial components that allow it to balance programmability and performance:
The header-only offloading TX path is designed to alleviate bandwidth contention on the SmartNIC by separating packet header processing from payload transmission.

Figure 3: Comparison of TX path strategies.
This separation allows the NIC to handle payload data directly from host memory, reducing the load on the SmartNIC's Arm processor and achieving efficient data transmission. This approach also simplifies the programming model by offloading complex operations to hardware.
Unlimited-working-set In-Cache Processing RX Path
Addressing the memory bandwidth limitations in SmartNICs, the in-cache RX processing path facilitates packet processing directly within the cache, thus preventing cache evictions and unnecessary Arm memory access.

Figure 4: Architecture of unlimited-working-set in-cache processing execution pipe.
By leveraging the Last-Level Cache (LLC) for packet processing, FlexiNS ensures that the SmartNIC can accommodate bursty traffic patterns and large working sets, which might otherwise overwhelm the SmartNIC's memory capabilities.
DMA-only Notification Pipe and Latency Reduction
The DMA-only notification pipe is crucial for maintaining low-latency operations and high throughput, specifically improving over traditional PCIe-dependent mechanisms.


Figure 5: Performance of DMA-only notification pipe and low-latency QP.
This mechanism aligns with latency-sensitive applications by utilizing efficient DMA operations that bypass the latency bottlenecks introduced by standard WQE and CQE manipulation techniques.
Programmable Offloading Engine
FlexiNS empowers developers through a programmable offloading engine that facilitates custom data operations directly on the NIC, thus offering significant performance benefits for specialized tasks like batched RDMA operations.

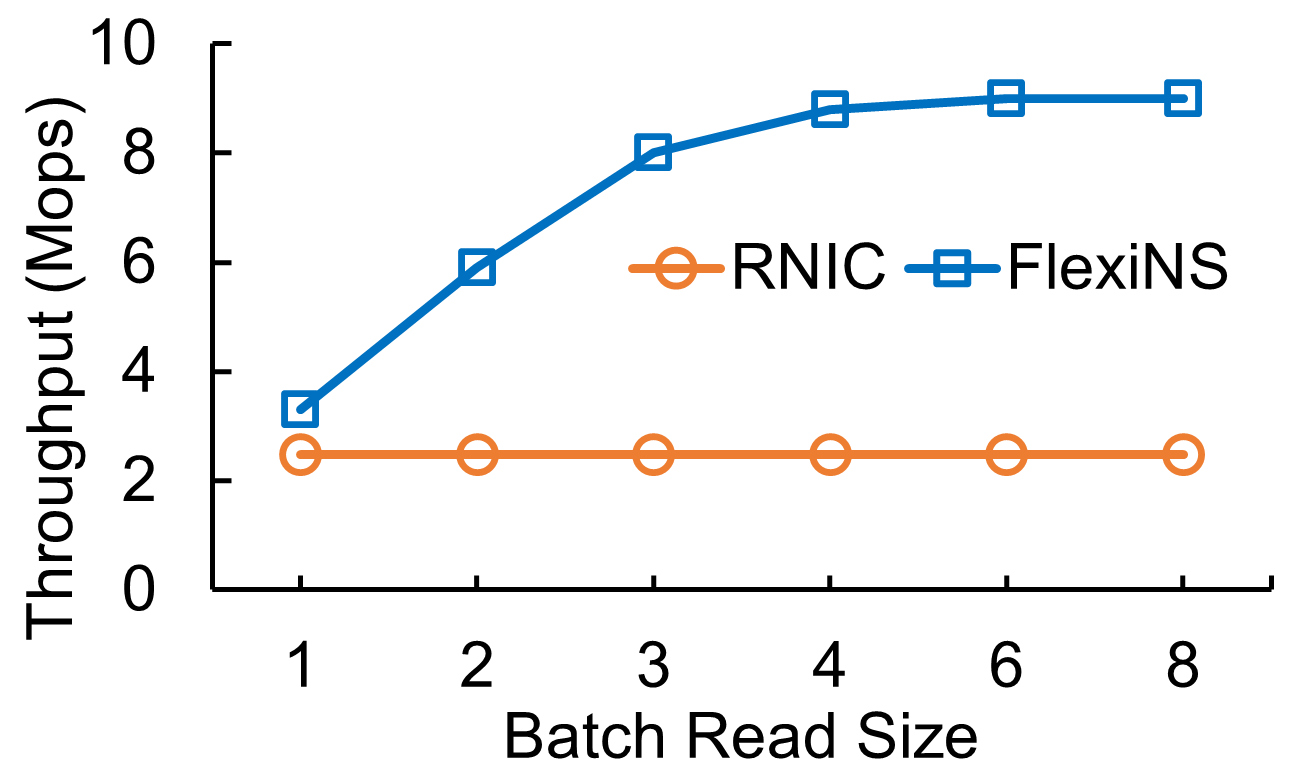
Figure 6: Programmable offloading functions performance.
This engine supports highly parallel operations through DMA, significantly reducing data transfer overheads for distributed applications, thereby enhancing throughput and efficiency.
FlexiNS demonstrates substantial improvements in throughput and latency across a suite of performance benchmarks. It performs comparably with dedicated RNIC solutions while offering unprecedented flexibility.
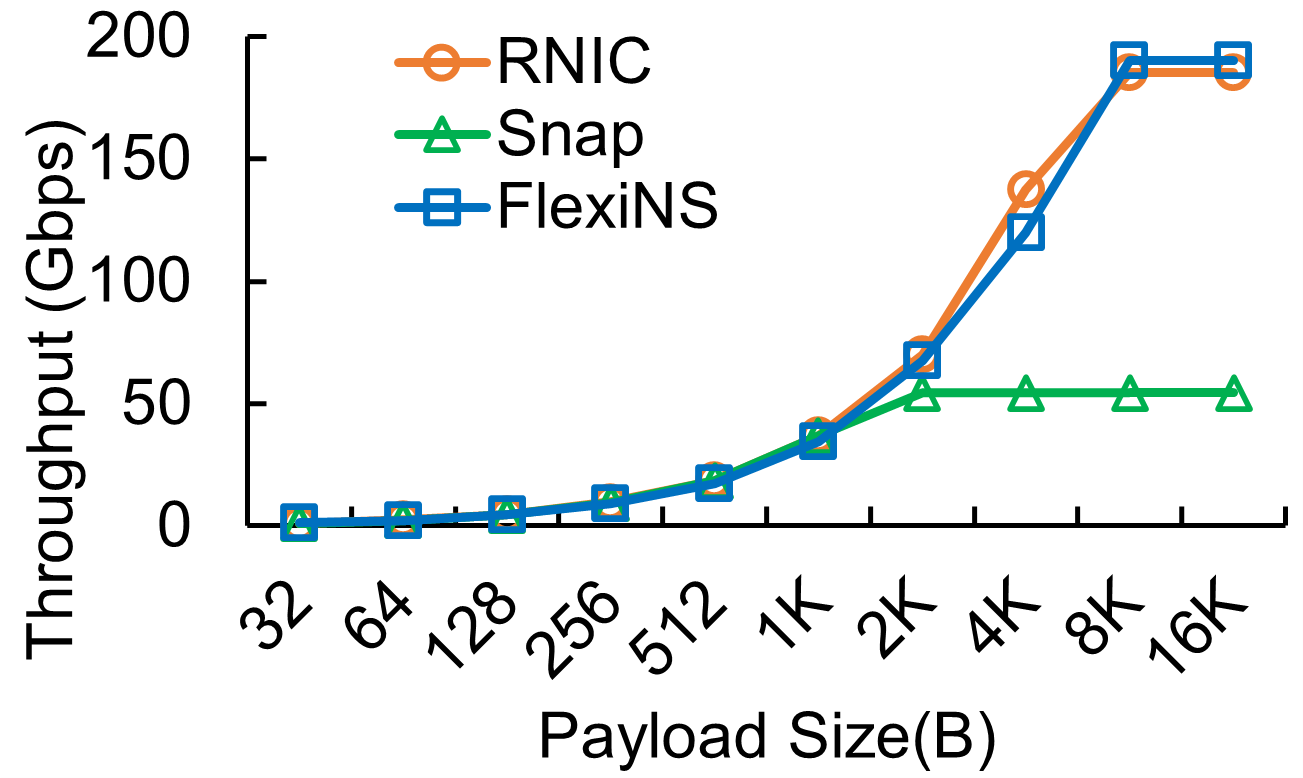
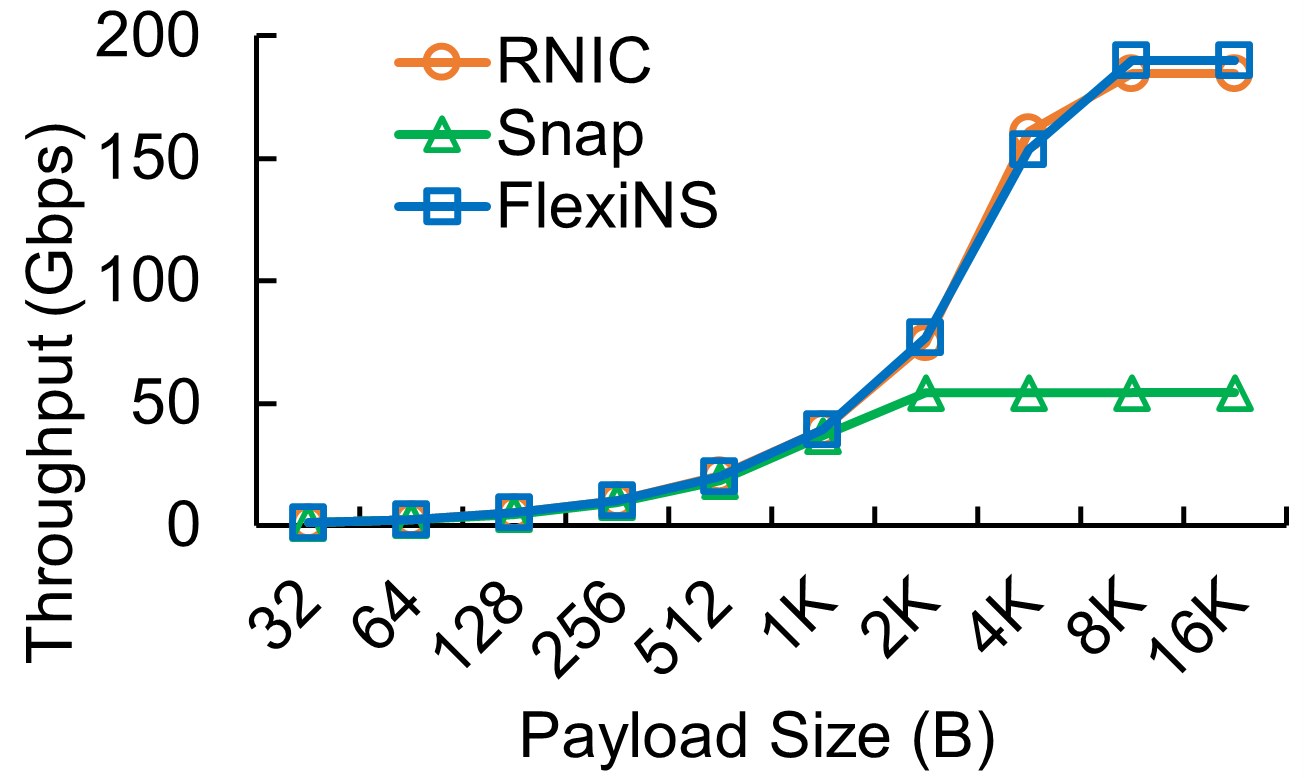

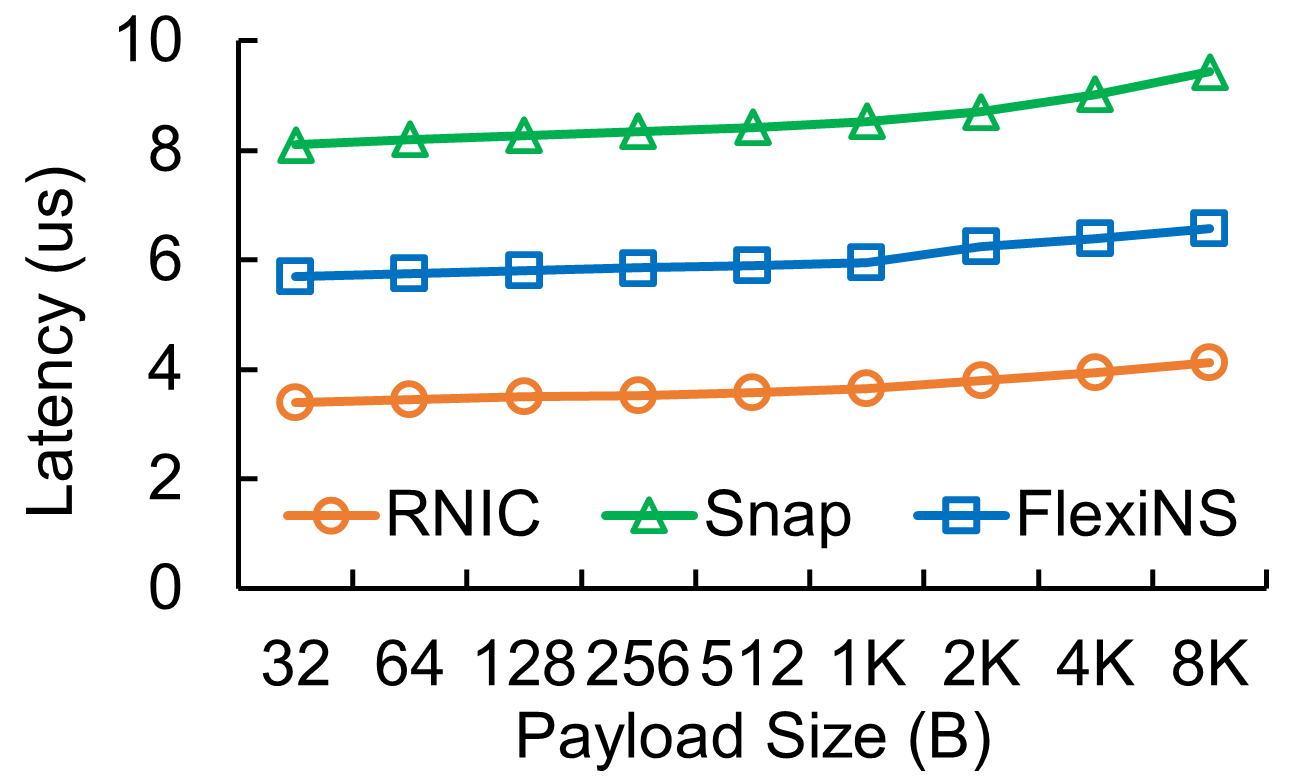
Figure 7: RDMA SEND/WRITE throughput and latency between a pair of connections on different hosts.
KVCache and Block Storage Performance
FlexiNS achieves significant improvements in KVCache transfer scenarios and distributed block storage IOPS, demonstrating its effectiveness in real-world applications. The introduction of optimized packet spraying mechanisms further enhances the achievable throughput beyond standard RDMA solutions.

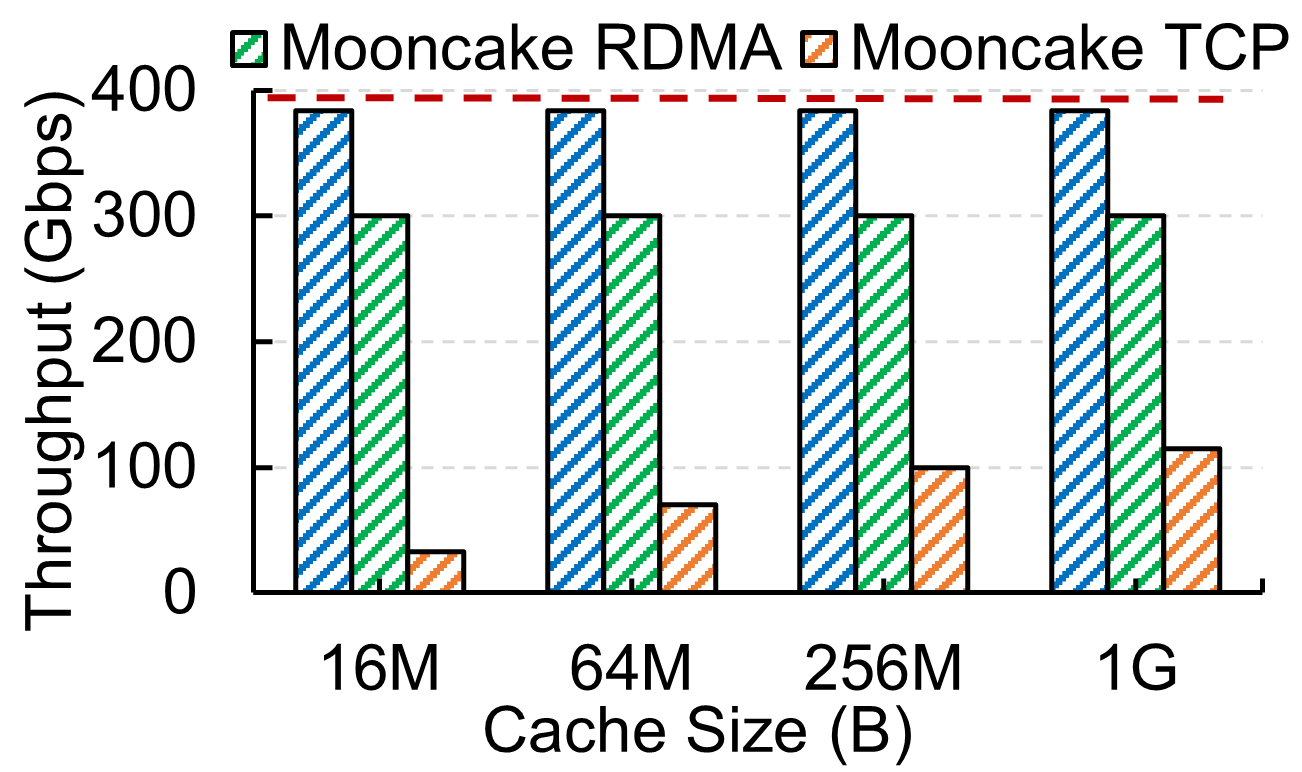
Figure 8: Throughput comparison of KVCache transfer.
Conclusion
FlexiNS effectively addresses the challenges posed by traditional network stack designs by leveraging SmartNIC capabilities to deliver flexible, line-rate network processing. Its design principles ensure that it meets the demands of modern cloud environments, balancing the trade-offs between hardware performance and software flexibility. The implications for future developments in AI-centric data processing and cloud networking are significant, with FlexiNS providing a scalable and adaptable framework for future innovations.













