- The paper reveals that distinct neurons in Vision-Language Models are specialized for processing visual, text, or both modalities.
- The methodology uses neuron activation observations and GPT-4 assisted explanations to accurately simulate and score activation patterns.
- Findings suggest earlier layers hold uni-modal neurons while higher layers predominantly contain multi-modal neurons, enhancing model interpretability.
Deciphering Functions of Neurons in Vision-LLMs
Introduction
The paper "Deciphering Functions of Neurons in Vision-LLMs" focuses on analyzing the internal mechanisms of Vision-LLMs (VLMs) to interpret the functions of individual neurons. Given the complexity and opacity of modern VLMs such as LLaVA, BLIP-2, and Qwen-VL, the need for transparency and interpretability is crucial for deploying AI systems in sensitive domains. This paper systematically investigates whether specialized neurons in VLMs are dedicated to processing visual-specific or text-specific information, using a framework involving neuron activation observations and explanations assisted by LLMs like GPT-4o.

Figure 1: To understand the function of a neuron, we observe the activations of this neuron on visual tokens and text tokens for each sample.
Methodology
The paper proposes a comprehensive methodology to understand neuron functions within VLMs. It involves the following steps:
- Neuron Activation Observation: Analyze the activations of neurons with respect to visual tokens and text tokens. Figure 1 illustrates how visual and text tokens are processed, where activation levels are visually represented by transparency and color intensity.
- Neuron Categorization: Identify different categories of neurons such as visual neurons, text neurons, multi-modal neurons, and unknown neurons based on their activation patterns.
- Automated Explanation Framework: Develop a framework using GPT-4o to automatically generate explanations for neuron functions and assess their reliability. The framework also includes a visual simulator to estimate activations for visual neurons.
- Simulation and Scoring: Simulate activation patterns for different neuron types and evaluate the explanations' accuracy using correlation metrics between simulated and true activations.
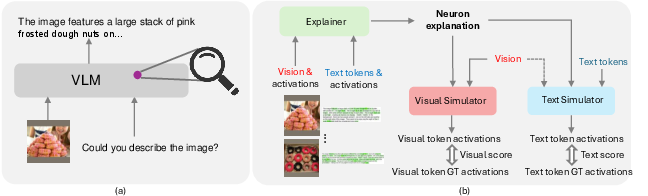
Figure 2: Illustration of our main workflow for investigating neuron functions in a VLM.
Findings on Neuron Types
Visual, Text, and Multi-Modal Neurons
The paper confirms the existence of distinct neuron types within VLMs. Visual neurons primarily respond to visual tokens while text neurons respond to text tokens. Multi-modal neurons react to both visual and text tokens, generally aligned with consistent concepts across modalities.

Figure 3: Visualization of neuron function categories, illustrating the activation distribution across visual and text tokens.
Neuron Distribution Analysis
By treating neuron categorization as a classification problem, the research analyzes neuron type distributions across VLM layers. Visual and text neurons predominantly occupy earlier layers, while multi-modal neurons are more frequent in higher layers, suggesting a division of labor in processing uni-modal versus multi-modal information.

Figure 4: Distribution of the four types of neurons (visual, text, multi-modal, unknown) over different layers.
Explanation and Simulation Insights
The framework's efficacy is demonstrated by generating accurate explanations, with high correlation scores between simulated and actual activations. The choice of samples (top-activated versus random) significantly impacts the quality of explanations, as shown by higher scores from top-activated sampling strategies.
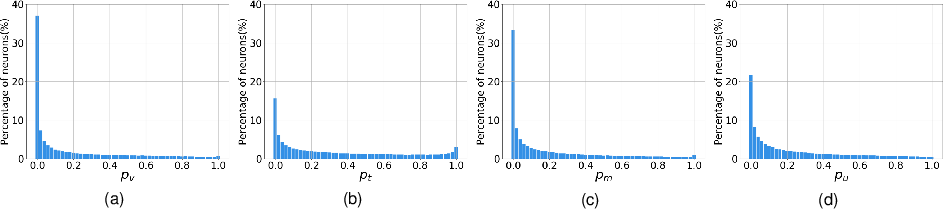
Figure 5: Visualization of simulation results for visual neurons, showcasing consistency between actual and simulated activations.
Implications and Future Work
The paper’s insights contribute significantly to understanding the internal workings of VLMs, paving the way for more interpretable and trustworthy AI systems. Understanding neuron functions could drive further advancements in VLM optimization and scalability. Future research could explore extending this methodology to attention layers or developing more sophisticated simulation models for multi-modal activations.
Conclusion
The paper systematically dissects the functions of neurons in VLMs, revealing distinct neuron categories and their distribution. By integrating advanced explanatory frameworks leveraging GPT-4o, the research offers a pathway to understanding and improving the transparency of complex AI models. This work is poised to inspire further research into developing responsible and interpretable AI systems in diverse applications.






