- The paper introduces a dual-model system combining TurnGPT and VAP to improve natural turn-taking in HRI.
- It achieves faster responses (1.5s median) and significantly reduces interruption rates compared to traditional models.
- User studies confirm enhanced conversational fluency and human-likeness in interactions with the proposed system.
Applying General Turn-taking Models to Conversational Human-Robot Interaction
Introduction
The paper "Applying General Turn-taking Models to Conversational Human-Robot Interaction" explores advanced turn-taking models, specifically TurnGPT and Voice Activity Projection (VAP), to enhance conversational dynamics in Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). Traditional HRI systems rely on silence-based models which result in unnatural pauses and interruptions. The paper introduces a method to use these models in tandem to improve response generation and turn-taking accuracy, thereby significantly reducing response delays and interruptions. The proposed system is evaluated against a traditional baseline through empirical analysis using the Furhat robot and interactions with 39 adult participants.
System Architecture
The architectural design integrates TurnGPT and VAP models with autonomous response generation to improve turn-taking dynamics in robots.
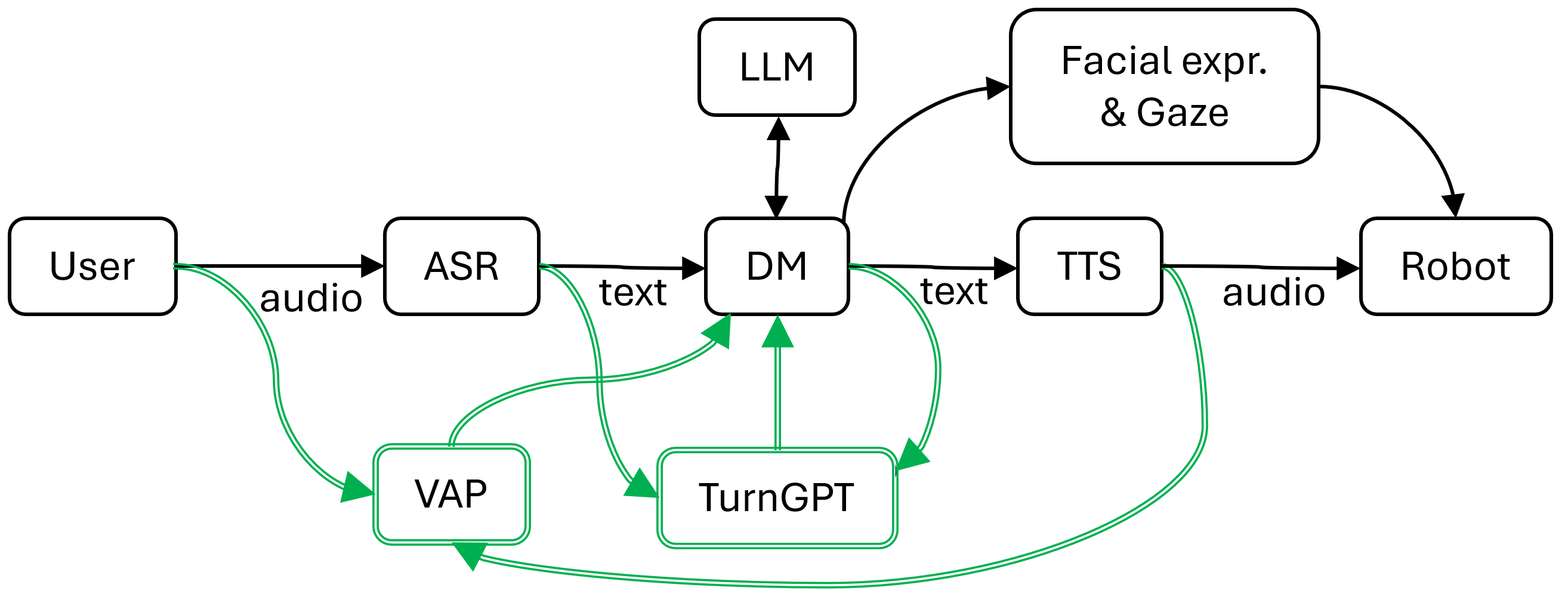
Figure 1: System architecture. New components in proposed system shown in green.
TurnGPT: Verbal Domain Predictions
TurnGPT is a LLM extension of GPT-2, incorporating syntactic and semantic cues to predict turn yields in dialogue. It analyzes text-based dialogue for pragmatic completeness, identifying transition-relevant places (TRPs) by assigning turn completion probabilities based on training on the SODA dataset. TurnGPT's rapid response capability allows near real-time predictions despite being limited to semantic aspects.
VAP: Acoustic Domain Predictions
VAP is a transformer-based acoustic model continuously predicting conversational dynamics based on raw audio input. VAP forecasts voice activity up to two seconds ahead, detecting turn-shifts and interruptions. Trained on large dialogue datasets such as Fisher and Switchboard corpora, VAP complements TurnGPT by incorporating prosodic and timing aspects, thus addressing the limitations of text-based predictions.
Evaluation Results
The proposed turn-taking system was evaluated with metrics including response time and interruption rates, showing significant improvements over traditional baseline systems.

Figure 2: Histogram of response times.
Response Time and Interruption Rate
The proposed system achieved faster response times with a median of 1.5 seconds compared to the baseline's 2.7 seconds and reduced interruption rates significantly (6.9% vs. 16.6%). The continuous predictions of TurnGPT and VAP enable more natural conversational flow and reduce user-perceived interruptions.
User Study
User preferences overwhelmingly favored the proposed system, highlighting its perceived fluency, human-likeness, and reduced effort required to maintain conversation dynamics.

Figure 3: Answers to the questionnaire. Significance levels indicate Bonferroni-corrected Wilcoxon signed-rank tests (∗p<0.05, ∗∗p<0.01, ∗∗∗p<0.001).
Discussion
The research demonstrates effective adaptation of human-human turn-taking models to HRI, with potential improvements through additional data specific to the interaction setting, such as gaze cues and multi-party interactions. Future studies could explore refined response preparation techniques and flexible turn-taking configurations to further reduce delays and enhance dialogue coherence.
Conclusion
The integration of TurnGPT and VAP models significantly enhances turn-taking dynamics in HRI systems, reducing both response delays and interruption rates. The study indicates a significant preference among participants for interactions with the proposed system, paving the way for more natural and efficient human-robot conversations in diverse settings. The paper establishes foundational research for deploying more human-like interaction models in autonomous systems without domain-specific fine-tuning requirements.




