- The paper presents a scalable divide-and-conquer approach that leverages multiple local SDFs to enhance 3D reconstruction quality.
- It employs volume rendering for adjacent node registration and a softmax-weighted blending mechanism to ensure smooth transitions.
- Experimental results on both synthetic and real datasets show significant improvements in capturing fine details and handling large-scale scenes.
Scalable and High-Quality Neural Implicit Representation for 3D Reconstruction
Introduction
The paper "Scalable and High-Quality Neural Implicit Representation for 3D Reconstruction" (2501.08577) addresses significant limitations in existing SDF-based neural implicit surface reconstruction methods by introducing a novel approach that integrates scalable, high-quality reconstruction capabilities. The authors focus on overcoming constraints related to the expressiveness and scalability of single-network models, proposing a divide-and-conquer strategy that enhances both the fidelity and practical applicability of 3D reconstructions across various complex scenes.
Methodology
The authors present a systematic approach to address the challenges inherent in traditional neural implicit methods by modeling objects or scenes as a composite of multiple local SDFs. This method includes three key components: constructing overlap relationships, adjacent nodes registration, and SDF blending.
Construction of Distribution and Overlap: The method begins by identifying overlapping regions within local radiance fields, leveraging object structures or data distributions to establish a meaningful partitioning strategy.
Adjacent Nodes Registration: By utilizing volume rendering for pose registration, the framework aligns adjacent nodes, ensuring a coherent global coordinate system. The registration process is optimized using an initial transformation followed by error rectification through rendering-based optimization.
SDF Blending: Local SDFs are seamlessly blended using a softmax-weighted mechanism to eliminate discontinuities, ensuring a smooth transition across overlapping areas (Figure 1).
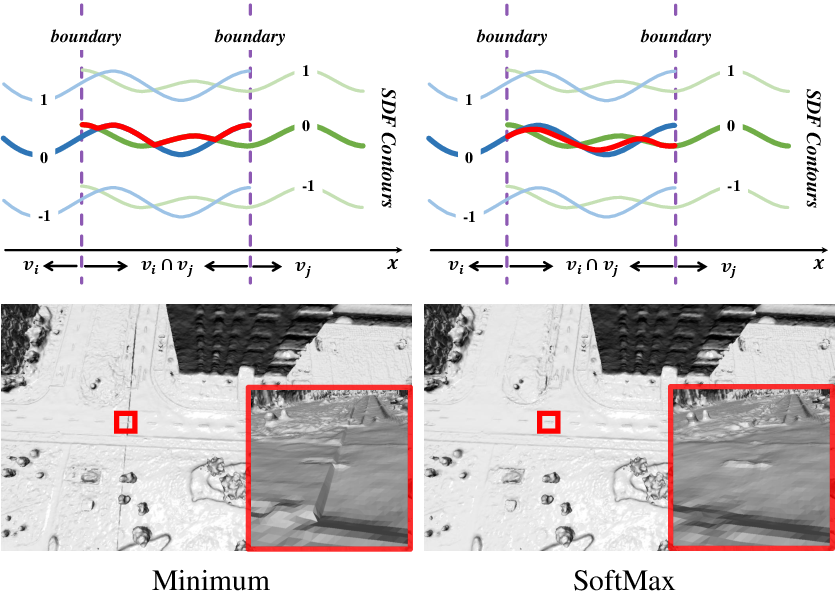
Figure 1: Demonstrates the effective smoothing achieved through Softmax weighting in SDF blending compared to direct minimum-value approaches.
Experimental Results
The proposed representation showcases marked improvements in high-fidelity detail capture, as evidenced by quantitative metrics and qualitative visualizations on diverse datasets including synthetic and real-world scenes.
High-Quality Reconstructions: Experimentation on datasets such as Lego and Jade demonstrated substantial enhancements in capturing intricate geometric details compared to baseline models using single MLPs. Partitioned nodes significantly contribute to improved reconstruction precision (Figures 4 and 5).
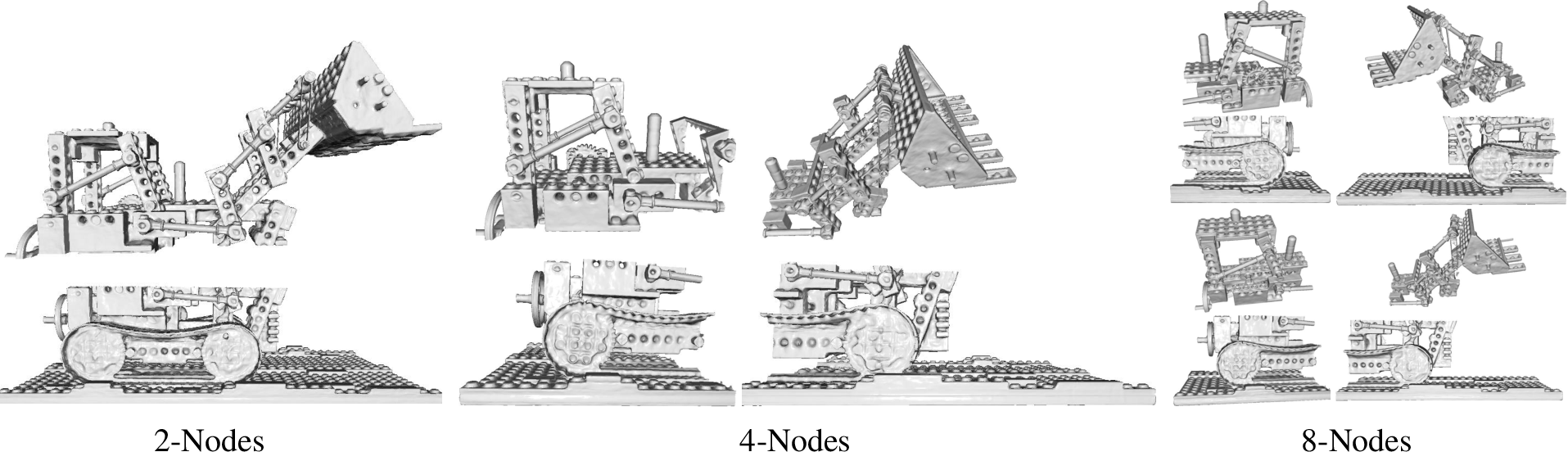
Figure 2: Node division strategies illustrate how spatial partitioning contributes to enhanced modeling fidelity.
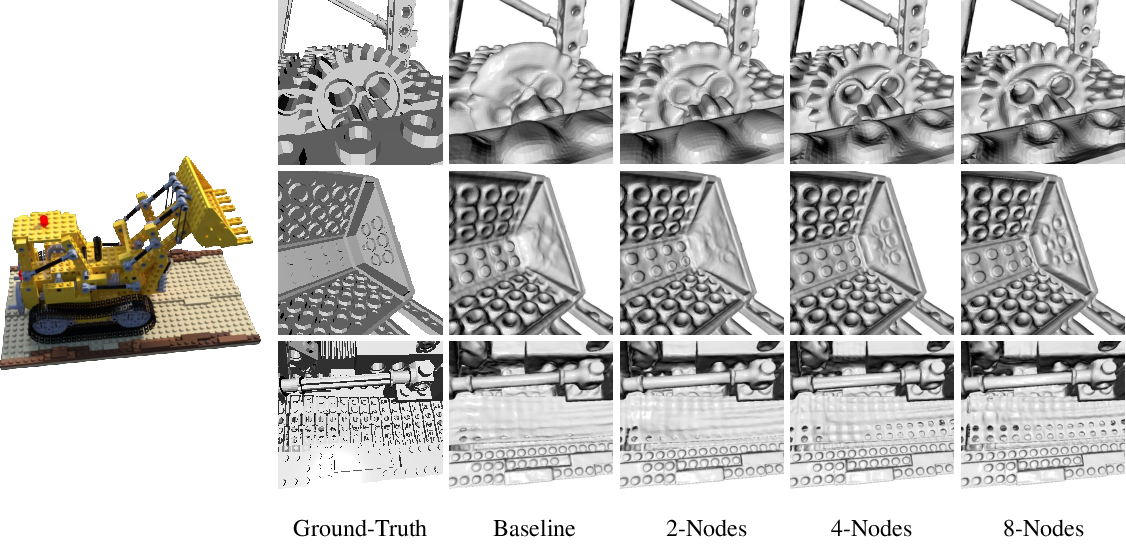
Figure 3: Highlights improvements in capturing finer details in 3D reconstructions through node-based representation refinement.
Scalability in Large-Scale Scenes: The ability to extend reconstruction to urban-scale environments is validated through the example of the Campus dataset, showcasing robust handling of extensive images and complex scene structures (Figures 10 and 11).
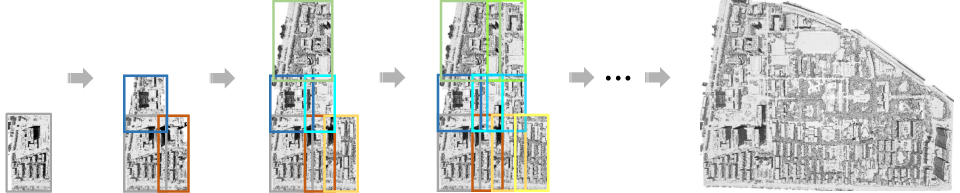
Figure 4: Depicts the process of scalable reconstruction across a large urban-scale scene.
Applications and Implications
The introduction of separate, independent local SDF nodes opens up various application possibilities, including:
Texture Generation: The framework facilitates high-quality texturing for large scenes, achieved through rasterization techniques that align with surface geometry.
Object-Level Editing: Leveraging independent node representation allows for flexible manipulation and spatial adjustments within reconstructed scenes, providing a significant advantage in applications requiring dynamic scene configurations.
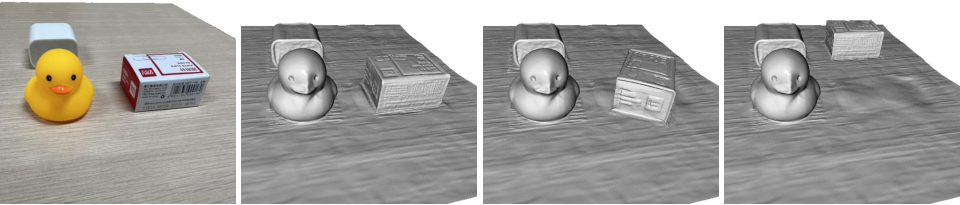
Figure 5: Demonstrates object-level editing capabilities enabled by isolated SDF node manipulation.
Conclusion
This paper successfully introduces a scalable and high-definition neural implicit representation for 3D reconstruction, addressing key limitations of previous methods through a robust divide-and-conquer strategy. The novel approach enhances the expressive power of neural networks across diverse and complex scenes, offering substantial improvements in reconstruction fidelity and scalability. Future work may explore optimizing the registration process and extending the method to other representations, including explicit 3D forms.




