InternLM-XComposer2.5-OmniLive: A Comprehensive Multimodal System for Long-term Streaming Video and Audio Interactions
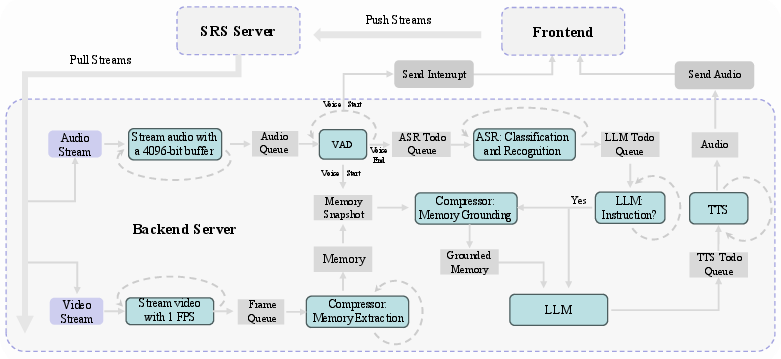
Abstract: Creating AI systems that can interact with environments over long periods, similar to human cognition, has been a longstanding research goal. Recent advancements in multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) have made significant strides in open-world understanding. However, the challenge of continuous and simultaneous streaming perception, memory, and reasoning remains largely unexplored. Current MLLMs are constrained by their sequence-to-sequence architecture, which limits their ability to process inputs and generate responses simultaneously, akin to being unable to think while perceiving. Furthermore, relying on long contexts to store historical data is impractical for long-term interactions, as retaining all information becomes costly and inefficient. Therefore, rather than relying on a single foundation model to perform all functions, this project draws inspiration from the concept of the Specialized Generalist AI and introduces disentangled streaming perception, reasoning, and memory mechanisms, enabling real-time interaction with streaming video and audio input. The proposed framework InternLM-XComposer2.5-OmniLive (IXC2.5-OL) consists of three key modules: (1) Streaming Perception Module: Processes multimodal information in real-time, storing key details in memory and triggering reasoning in response to user queries. (2) Multi-modal Long Memory Module: Integrates short-term and long-term memory, compressing short-term memories into long-term ones for efficient retrieval and improved accuracy. (3) Reasoning Module: Responds to queries and executes reasoning tasks, coordinating with the perception and memory modules. This project simulates human-like cognition, enabling multimodal LLMs to provide continuous and adaptive service over time.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.