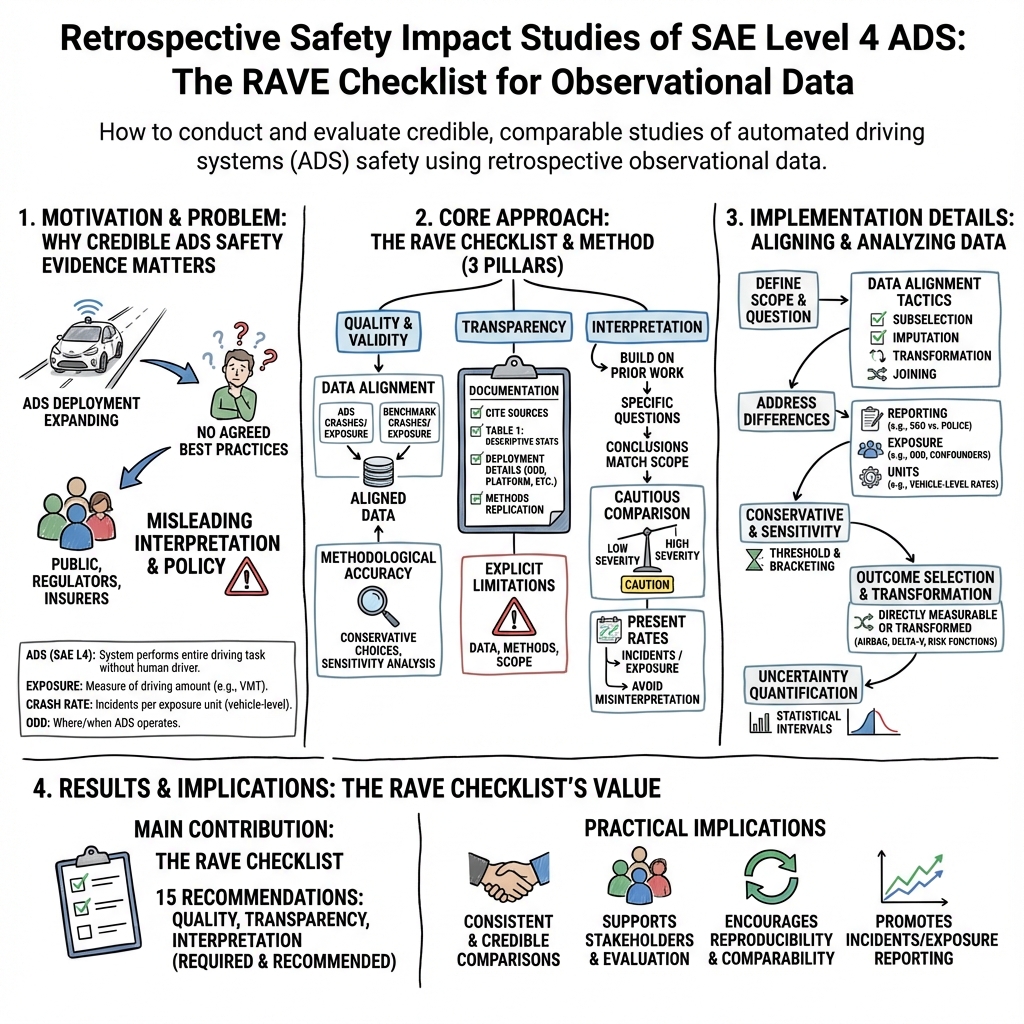
- The paper presents the RAVE checklist, offering 15 recommendations to improve the scientific rigor of retrospective ADS safety evaluations.
- It emphasizes quality, transparency, and interpretability by aligning data sources and mitigating challenges from heterogeneous operational environments.
- The checklist guides researchers in leveraging observational data to inform evidence-based policy and industry decision-making in automated driving systems.
Summary of "RAVE Checklist: Recommendations for Overcoming Challenges in Retrospective Safety Studies of Automated Driving Systems" (2408.07758)
This essay analyzes the comprehensive framework proposed by Scanlon et al. for conducting retrospective safety studies on automated driving systems (ADS). The paper presents the RAVE (Retrospective Automated Vehicle Evaluation) checklist, consisting of fifteen detailed recommendations aimed at enhancing the scientific rigor of ADS safety assessments. This work is intended to guide stakeholders, including researchers, policymakers, and industry professionals, in evaluating the real-world performance of ADS technologies, thus enabling informed decision-making.
Retrospective Safety Impact of ADS
The paper addresses a significant gap in traffic safety research concerning the evaluation of SAE Level 4 ADS, which are responsible for the entire driving task without human intervention. Given the increasing deployment of these systems, assessing their impact on safety is critical. The framework leverages traditional observational data methodologies, applying them to ADS to quantify safety benefits accurately.
The authors delineate two types of safety impact studies: prospective, which predict potential safety benefits of new technologies, and retrospective, which evaluate the observed safety performance post-deployment. As ADS deployment becomes more widespread, the retrospective approach gains importance, leveraging real-world data to assess efficacy.
RAVE Checklist Recommendations
The RAVE checklist is categorized into three focal areas: quality and validity, transparency, and interpretation. Each category addresses specific methodological concerns and ensures the robustness of evaluation studies.
Quality and Validity
Key recommendations emphasize the alignment of data from ADS and benchmark fleets, consideration of outcome measurability, methodological conservatism, and rigorous statistical analysis. Ensuring data compatibility and mitigating confounders is essential, given the heterogeneous nature of ADS deployments and their operating environments.
Transparency
Researchers are encouraged to cite all data sources and provide detailed descriptions of ADS and benchmark data compositions. Full disclosure of analysis methods is necessary to facilitate replication and critical evaluation. Additionally, limitations in data, methodology, and scope should be acknowledged to contextualize findings appropriately.
Interpretation
The paper advises researchers to build upon existing literature, ensuring research questions are clearly defined and conclusions are restrained to the scope of the study design. There is an emphasis on exercising caution when extrapolating findings across different severity levels of crashes, as underlying factors may vary significantly.
Practical and Theoretical Implications
The RAVE checklist holds significant implications for both practical applications and theoretical advancements in traffic safety. Practically, it aims to standardize the approach to ADS safety assessments, fostering consistency across studies, thereby enabling more reliable comparisons. Theoretically, the checklist encourages methodological innovation and refinement, essential for addressing unique challenges posed by ADS research, such as data heterogeneity and rapid technological evolution.
Future Directions
The paper anticipates that as ADS technologies evolve, the recommended practices will require continual adaptation. Future research may explore novel data sources and methodological frameworks aligned with emerging ADS characteristics. Additionally, there is potential for developing standardized guidelines to further support robust safety impact evaluations globally.
Conclusion
The "RAVE Checklist" establishes a foundational framework for retrospective ADS safety studies, aiming to enhance methodological rigor and support evidence-based policy decisions. By following the recommended practices, researchers can contribute to a comprehensive understanding of ADS safety performance, ultimately advancing the field of automated driving systems and their integration into modern traffic ecosystems.