CloudLens: Modeling and Detecting Cloud Security Vulnerabilities
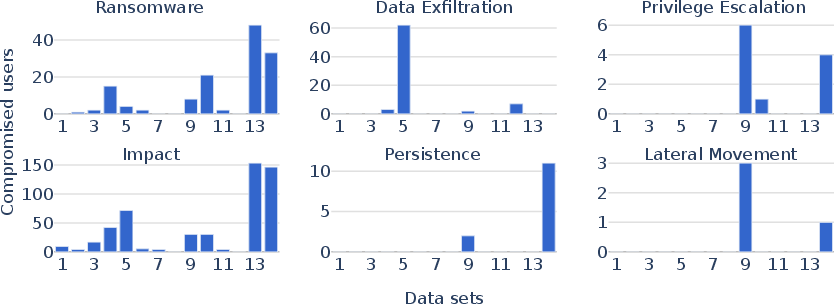
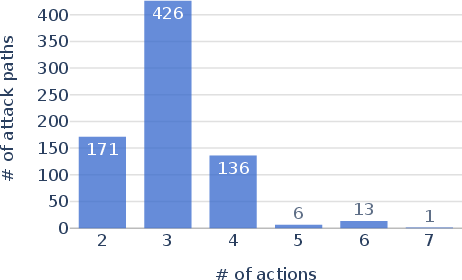
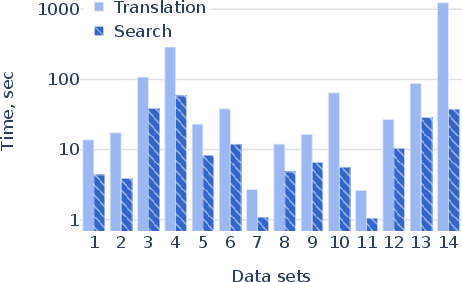
Abstract: Cloud computing services provide scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and collaboration. With their growing popularity, concerns about security vulnerabilities are increasing. To address this, first, we provide a formal model, called CloudLens, that expresses relations between different cloud objects such as users, datastores, security roles, representing access control policies in cloud systems. Second, as access control misconfigurations are often the primary driver for cloud attacks, we develop a planning model for detecting security vulnerabilities. Such vulnerabilities can lead to widespread attacks such as ransomware, sensitive data exfiltration among others. A planner generates attacks to identify such vulnerabilities in the cloud. Finally, we test our approach on 14 real Amazon AWS cloud configurations of different commercial organizations. Our system can identify a broad range of security vulnerabilities, which state-of-the-art industry tools cannot detect.
- Amazon AWS. 2023. AWS Documentation. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/.
- ATT&CK, M. 2021. ATT&CK Matrix for Enterprise. https://attack.mitre.org. Accessed: 2022-05-29.
- AWS. 2023. Shared Responsibility Model. https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/shared-responsibility-model/.
- Semantic-based Automated Reasoning for AWS Access Policies using SMT. In Formal Methods in Computer Aided Design (FMCAD), 1–9.
- Course of Action Generation for Cyber Security Using Classical Planning. In International Conference on International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, 12–21.
- CSA. 2023. Top Threats to Cloud Computing: Pandemic 11 Deep Dive. https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/artifacts/top-threats-to-cloud-computing-pandemic-eleven-deep-dive/.
- Fox, B. 2021. IAM Vulnerable. https://github.com/BishopFox/iam-vulnerable. Accessed: 2023-12-01.
- Fox, B. 2023. Bishop Fox. https://bishopfox.com. Accessed: 2023-12-01.
- Gietzen, S. 2021. AWS IAM Privilege Escalation – Methods and Mitigation. https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/aws-privilege-escalation-methods-mitigation/.
- Helmert, M. 2006. The Fast Downward Planning System. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 26(1): 191–246.
- Hoffmann, J. 2015. Simulated Penetration Testing: From “Dijkstra” to “Turing Test++”. In ICAPS, 364–372.
- Holmes, A. 2021. 533 million Facebook users’ phone numbers and personal data have been leaked online. https://www.businessinsider.com/stolen-data-of-533-million-facebook-users-leaked-online-2021-4. Accessed: 2022-05-29.
- Fixing Privilege Escalations in Cloud Access Control with MaxSAT and Graph Neural Networks. In IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE 2023). IEEE.
- Validating Datacenters at Scale. In Proceedings of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, 200–213.
- Using Constraint Programming and Graph Representation Learning for Generating Interpretable Cloud Security Policies. In International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,, 1850–1858.
- Kuenzli, S. 2020. Why are good AWS security policies so difficult? https://www.k9security.io/posts/2020/06/why-are-good-aws-security-policies-so-difficult. Accessed: 2023-12-01.
- Labs, R. S. 2019. S3 Ransomware Part 1: Attack Vector. https://rhinosecuritylabs.com/aws/s3-ransomware-part-1-attack-vector/#:~:text=Attacker%20creates%20a%20KMS%20key,not%20decrypt%20objects%20in%20S3. Accessed: 2023-12-01.
- An Annotated Review of Past Papers on Attack Graphs.
- Marks, G. 2021. A LinkedIn ‘Breach’ Exposes 92% Of Users. https://www.forbes.com/sites/quickerbettertech/2021/07/05/a-linkedin-breach-exposes-92-of-usersand-other-small-business-tech-news. Accessed: 2022-05-29.
- NCC Group. 2023. Principal Mapper. https://github.com/nccgroup/PMapper.
- Attack Planning in the Real World. In SecArt’10.
- One, C. 2022. Information on the Capital One Cyber Incident. https://www.capitalone.com/digital/facts2019/.
- Zanzibar: Google’s Consistent, Global Authorization System. In USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC).
- Pernet, C. 2021. Research reveals that IAM is too often permissive and misconfigured. https://www.techrepublic.com/article/research-iam-permissive-misconfigured/.
- Salesforce. 2023. Policy Sentry: IAM Least Privilege Policy Generator. https://policy-sentry.readthedocs.io/en/latest/.
- POMDPs Make Better Hackers: Accounting for Uncertainty in Penetration Testing. In AAAI.
- Scroxton, A. 2020. Leaky AWS S3 bucket once again at centre of data breach. https://www.computerweekly.com/news/252491842/Leaky-AWS-S3-bucket-once-again-at-centre-of-data-breach. Accessed: 2022-05-29.
- Unit42. 2022. IAM Your Defense Against Cloud Threats: The Latest Unit 42 Cloud Threat Research. https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/iam-cloud-threat-research/. Accessed: April 12, 2022.
Paper Prompts
Sign up for free to create and run prompts on this paper using GPT-5.
Top Community Prompts
Collections
Sign up for free to add this paper to one or more collections.