- The paper introduces SComGNN, a novel method that isolates low-frequency (relevance) and mid-frequency (dissimilarity) components for complementary item recommendation.
- It employs customized spectral filters and a two-stage attention mechanism to effectively transform spectral data into actionable spatial convolutions.
- Contrastive learning experiments on e-commerce datasets demonstrate significant improvements in Hit Rate and NDCG compared to traditional recommendation models.
Spectral-Based Graph Neural Networks for Complementary Item Recommendation
The paper "Spectral-Based Graph Neural Networks for Complementary Item Recommendation" introduces a novel approach for complementary item recommendation by leveraging spectral-based Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). This approach, termed Spectral-based Complementary Graph Neural Networks (SComGNN), aims to effectively capture and model the distinct attributes of complementarity between items: relevance and dissimilarity. The key innovation is the use of spectral properties to distinguish between low-frequency and mid-frequency components, associating these with relevance and dissimilarity, respectively.
Introduction to Complementary Item Recommendation
Complementary item recommendation is critical for e-commerce platforms, where the objective is to suggest items that enhance or are compatible with a previously purchased item. Conventional recommendations often focus on similarity, leading to substitutable item recommendations. However, complementary items share relevance while also exhibiting dissimilarity, such as an iPhone and AirPods Pro. Thus, capturing both attributes is pivotal to improving recommendation quality.

Figure 1: Item relationships in recommender systems.
Spectral Perspective on Complementary Relationships
The paper identifies that complementary item graphs predominantly consist of low-frequency and mid-frequency components in the spectral domain. Low-frequency components represent relevance, indicating node similarities within the graph. On the contrary, mid-frequency components depict dissimilarity, reflecting the inherent differences between complementary items. This dual spectral characteristic allows SComGNN to selectively process and enhance these attributes using specialized filtering techniques.


Figure 2: Spectrums of low-pass and mid-pass GCNs.
Methodology
Spectral-based GCN Filters
SComGNN employs customized spectral filters to isolate and extract low-frequency (relevance) and mid-frequency (dissimilarity) components via dedicated low-pass and mid-pass filters. These filters transform the graph's spectral information back into spatial executions, allowing for efficient node representation and convolution operations.
Attention Mechanism
The model integrates a two-stage attention mechanism. Initially, a pairwise attention mechanism adjusts the focus on relevance and dissimilarity for items in a pair, followed by a self-attention mechanism that refines these integrations independently.
Contrastive Learning
SComGNN leverages contrastive learning to optimize the model by distinguishing between correct (positive) and incorrect (negative) item pairs. This ensures that complementary items exhibit strong signal alignment, whereas non-complementary items are distanced in the representation space.
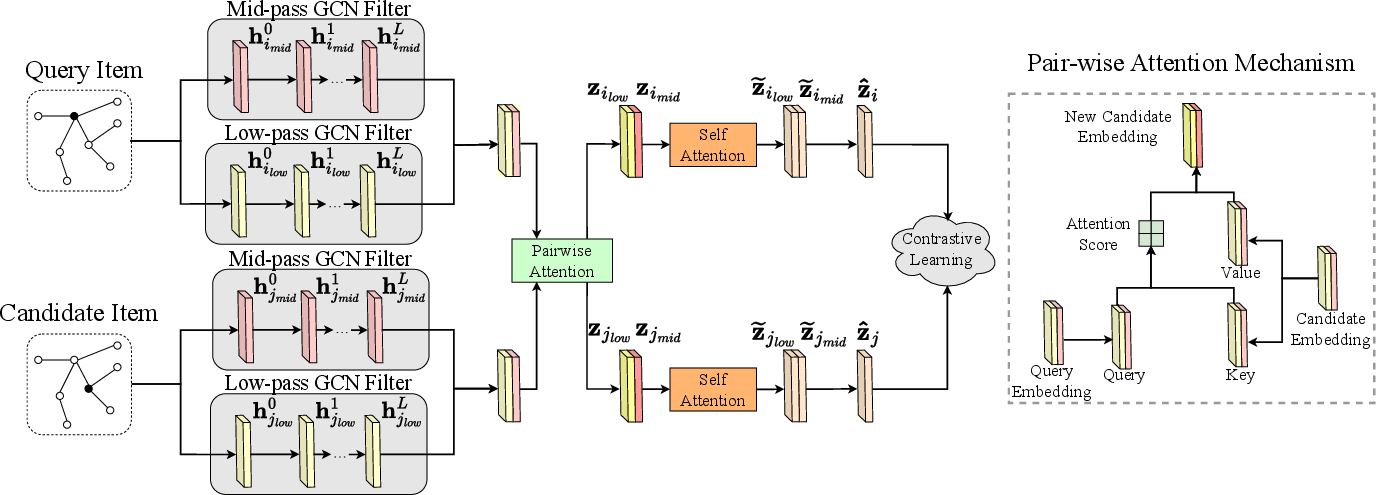
Figure 3: The overall framework of our proposed model SComGNN.
Experimental Evaluation
Empirical results on multiple e-commerce datasets demonstrate that SComGNN outperforms existing approaches significantly, especially in diverse marketplaces. Performance metrics such as Hit Rate (HR) and NDCG consistently show high scores across datasets, highlighting the advantage of spectral-based representation in capturing complementary relationships.
Implications and Future Directions
The application of spectral analysis within GNNs for item recommendation opens avenues for further refinement of GNN architectures to capture complex relationships. Future work could explore more sophisticated spectral filtering and attention mechanisms or extend this framework to support real-time recommendation systems with adaptive capabilities.
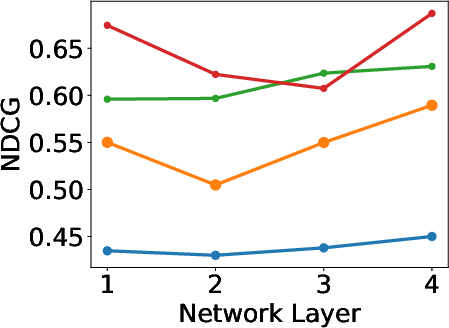

Figure 4: Hyperparameter sensitivity evaluation.
Conclusion
The paper presents a sound methodology for leveraging spectral properties of GNNs to enhance complementary item recommendations. By decoupling and balancing the dual attributes of relevance and dissimilarity, SComGNN achieves superior performance in identifying actionable and contextually complementary items, thereby enriching user interaction and satisfaction on e-commerce platforms.





